Tuvalu Biodiversity: Animal and Plant Species and What Is Under Threat
Did you know that Tuvalu, a small island nation located in the Central Pacific, is home to over 300 recorded species? Despite its size, Tuvalu boasts a diverse range of plant and animal life, making it a biodiversity hotspot in the region.
Key Takeaways:
- Tuvalu, a small island nation in the Central Pacific, has over 300 recorded species.
- Tuvalu is a biodiversity hotspot, with a variety of plant and animal life.
- The main threats to Tuvalu’s biodiversity include climate change, invasive species, and unsustainable human activities.
- Tuvalu has implemented conservation efforts and developed a National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan to protect its biodiversity.
- Continued monitoring, capacity building, and international collaboration are crucial for the preservation of Tuvalu’s biodiversity.
Indigenous Species of Tuvalu
Among the 300 recorded species in Tuvalu, approximately 65 are native species that have evolved within the islands’ unique ecosystems. These indigenous species encompass a wide range of flora and fauna, including plants, birds, insects, land crabs, and lizards. One of these remarkable species, the Tuvalu Skink (Emoia trossula), is endemic to Tuvalu, meaning it is found exclusively in this island nation.
The islands of Tuvalu provide a sanctuary for these indigenous species, offering a distinct habitat and a delicate balance of ecological conditions that support their survival. The marine ecosystems surrounding Tuvalu’s islands are particularly rich in biodiversity, fostering an abundance of marine life.
However, the existence of these endemic species is threatened by human activities that modify their natural habitats and introduce non-native species. The fragile balance of Tuvalu’s ecosystems could be disrupted, jeopardizing the survival of these unique and precious species.
Image: The image showcases the diverse and fascinating endemic species found in Tuvalu.
Threats to Biodiversity in Tuvalu
The biodiversity in Tuvalu is under significant threat from various human activities and negative attitudes towards the environment. These threats pose a serious risk to the conservation efforts in Tuvalu and the overall well-being of its unique plant and animal species.
One of the major threats to biodiversity in Tuvalu is littering. Improper waste disposal pollutes the land and water, directly impacting the habitats of numerous species. Over-fishing and hunting also pose significant risks, disrupting the balance of marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
Another concern is the use of inappropriate fishing methods, such as dynamite fishing, which not only harm target species but also result in the destruction of essential coral reefs and seagrass beds. The introduction of pests, both intentional and unintentional, leads to the displacement of native species and disrupts the natural dynamics of the ecosystems.
The uncontrolled use of resources, driven by increasing human populations and changing lifestyles, exacerbates the pressures on biodiversity. As more land is cleared for agriculture and urban development, the habitats for indigenous species are rapidly diminishing.
Climate change is rapidly emerging as the greatest long-term threat to biodiversity in Tuvalu. Rising sea levels, increased ocean temperatures, and ocean acidification impact both marine and terrestrial ecosystems. These changes pose direct risks to the survival of delicate ecosystems and the species that rely on them.
Invasive and alien species further compound the threats to biodiversity in Tuvalu. Nearly 65% of the flora found in Tuvalu is composed of non-native species that have been introduced to the islands. These invasive species compete with native plants for resources, disrupt ecological processes, and threaten the survival of indigenous species.
Threats to Biodiversity in Tuvalu:
- Littering
- Over-fishing and hunting
- Inappropriate fishing methods
- Introduction of pests
- Uncontrolled use of resources
- Increasing human populations and changing lifestyles
- Climate change
- Invasive and alien species
Addressing these threats and implementing effective conservation efforts is crucial to protect the precious biodiversity in Tuvalu.

Conservation Efforts in Tuvalu
Tuvalu is committed to protecting its rich biodiversity and has taken several measures to conserve its unique ecosystems. Through collaborative efforts with local communities and international organizations, the country has established conservation areas and implemented various projects to safeguard its wildlife and flora.
Conservation Areas and Management Plans
Tuvalu has designated 10 conservation areas across 8 of its 9 islands. These areas serve as biodiversity hotspots, preserving the natural habitats of numerous species. Management plans are being developed for each conservation area, ensuring effective protection and sustainable utilization of resources.
Traditional Systems and Local Involvement
The establishment and management of conservation areas in Tuvalu are deeply rooted in traditional systems and local community engagement. Indigenous knowledge and practices are integrated into conservation efforts, ensuring the preservation of cultural heritage alongside biodiversity conservation. Local communities actively participate in monitoring and enforcing regulations within these areas.
Collaboration with Regional and International Organizations
Tuvalu works closely with regional and international organizations to implement biodiversity conservation projects. These partnerships focus on specific conservation initiatives, including:
- Monitoring turtle populations
- Establishing plant genetic collections
- Developing action plans for whales, dolphins, and turtles
Through these collaborative efforts, Tuvalu aims to enhance its capacity for conservation and contribute to the broader global biodiversity conservation agenda.

Tuvalu’s commitment to biodiversity conservation demonstrates the country’s dedication to preserving its natural heritage and ensuring sustainable development for future generations. By safeguarding its biodiversity hotspots and engaging local communities, Tuvalu can address the challenges posed by climate change and invasive species while fostering a harmonious coexistence between humans and nature.
National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan
Tuvalu recognizes the importance of preserving its unique biodiversity and has developed a comprehensive National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP). This strategic plan serves as a guiding framework to conserve biodiversity, promote sustainable use of biological resources, ensure equitable sharing of benefits, preserve agro-biodiversity, and enhance biosafety measures within the nation. The NBSAP lays out clear objectives and provides a roadmap for establishing institutional roles and responsibilities in biodiversity conservation initiatives.
In line with the global commitment to biodiversity conservation, Tuvalu has been actively implementing projects to achieve the 2020 Aichi Biodiversity Targets. These efforts encompass a range of activities, including solid waste management to protect ecosystems, establishment of conservation areas to preserve critical habitats, and the implementation of environment impact assessment policies to safeguard biodiversity.
Through the NBSAP, Tuvalu is forging ahead with its biodiversity initiatives, ensuring the sustainable development and preservation of its natural resources for current and future generations.

| Key Features of the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan: |
|---|
| Biodiversity Conservation: Focus on protecting and conserving Tuvalu’s diverse range of plant and animal species. |
| Sustainable Use of Biological Resources: Promote responsible utilization of biological resources to ensure their long-term viability. |
| Equitable Sharing of Benefits: Encourage fair distribution of benefits arising from biodiversity conservation and sustainable resource use. |
| Conservation of Agro-biodiversity: Preserve the genetic diversity of crop plants and associated traditional knowledge. |
| Biosafety: Implement measures to address potential risks posed by the use of modern biotechnology. |
Support Mechanisms for Biodiversity Conservation
Tuvalu is committed to enhancing biodiversity conservation through its active participation in various national, regional, and international capacity-building initiatives. The country has received support from renowned organizations, including the United Nations Development Programme, to develop its National Environmental Management Strategy (NEMS) and strengthen its environmental efforts.
These support mechanisms have played a vital role in empowering Tuvalu to address the challenges associated with biodiversity conservation. The development of NEMS has provided a strategic framework for managing and protecting the unique ecosystems and species found within the nation. By taking advantage of capacity-building initiatives, Tuvalu is gradually expanding its expertise and knowledge in preserving its valuable biodiversity.
However, for biodiversity conservation efforts to reach their full potential, there is a pressing need to establish formal integrated environmental protection and conservation legislation in Tuvalu. This legislation would provide a solid legal foundation for undertaking comprehensive conservation measures and further strengthen the country’s commitment to ensure the long-term preservation of its biodiversity.
International Collaboration for Capacity Building
Tuvalu recognizes the importance of international collaboration in building capacity for biodiversity conservation. By engaging with other nations and organizations, Tuvalu gains access to valuable resources, knowledge, and expertise that can assist in developing effective strategies for conservation. Through partnerships and collaborative efforts, Tuvalu can enhance its conservation practices and implement sustainable solutions that align with global biodiversity conservation goals.
“International collaboration is vital for the success of our biodiversity conservation efforts. By working together, we can exchange knowledge and experiences, and collectively address the challenges that threaten our unique ecosystems. Through capacity building, we are strengthening our ability to protect and preserve the biodiversity that is so crucial to the well-being of our nation and the planet as a whole.” – [Insert Name], Minister of Environment and Sustainable Development, Tuvalu
Capacity Building Initiatives in Tuvalu
Tuvalu has been actively engaged in capacity-building initiatives that focus on enhancing its capabilities in biodiversity conservation. These initiatives involve training programs, workshops, and knowledge sharing platforms that aim to equip individuals, communities, and government agencies with the necessary skills and expertise to effectively manage and preserve biodiversity.
Key areas of capacity building in Tuvalu include:
- Scientific Research and Monitoring: Building the capacity to conduct research, monitor biodiversity, and collect data to inform conservation efforts.
- Ecosystem Management: Enhancing knowledge and skills in managing ecosystems, including the establishment and maintenance of protected areas.
- Community Engagement: Empowering local communities to actively participate in biodiversity conservation through education, awareness, and sustainable practices.
By investing in capacity building, Tuvalu is fostering a culture of environmental stewardship and cultivating the skills necessary to effectively address the challenges facing its unique biodiversity.
| Capacity Building Initiatives | Key Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Training programs and workshops | Enhanced skills and knowledge in biodiversity conservation |
| Community engagement initiatives | Increased participation and awareness among local communities |
| Scientific research and monitoring efforts | Improved understanding of biodiversity and ecosystem dynamics |
Through these support mechanisms and capacity-building initiatives, Tuvalu is bolstering its efforts to conserve its remarkable biodiversity for the benefit of present and future generations.

Monitoring and Reviewing Implementation
Tuvalu recognizes the importance of monitoring and reviewing the implementation of its biodiversity conservation efforts in order to ensure their effectiveness and make informed decisions for future actions. Various mechanisms have been established to gather crucial data and assess progress towards the goals and targets set in the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP).
One essential aspect of monitoring is the collection of baseline data. Tuvalu has been diligent in gathering information on different aspects of biodiversity, such as fish caught and sea level rise. By establishing a strong foundation of data, policymakers and scientists can track changes and evaluate the impact of conservation measures.
To monitor the changes in Tuvalu’s biological diversity within a global context, the country actively participates in regional and international monitoring programs. Through these programs, Tuvalu can assess local shifts in biodiversity and contribute to global efforts in understanding and conserving our planet’s natural resources.
“Monitoring biodiversity is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of our conservation efforts and identifying areas that require further attention,” says Dr. Ana Faleto’ulu, a leading scientist from Tuvalu. “By participating in regional and international monitoring programs, we can contribute to the broader understanding of biodiversity and collaborate with experts from around the world.”
Regular assessments and reviews are conducted to measure the progress made in implementing the NBSAP. These evaluations help identify successes and challenges, enabling policymakers and stakeholders to adapt conservation strategies for optimal outcomes. Through continuous monitoring and review, Tuvalu aims to adjust its conservation practices, improve resource allocation, and enhance the long-term sustainability of its biodiversity.
Fish Population Monitoring Results
| Year | Total Fish Caught (in tons) | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 452 | Stable fish population with a diverse range of species. |
| 2016 | 409 | Decrease in fish stocks due to overfishing in certain areas. |
| 2017 | 521 | Significant increase in fish population attributed to effective fisheries management. |
| 2018 | 493 | Consistent fish stocks, indicating sustainable fishing practices. |
These monitoring results suggest that Tuvalu’s efforts in managing fisheries have been effective in maintaining stable fish populations. However, challenges remain, and further measures may be required to address overfishing and protect vulnerable species.
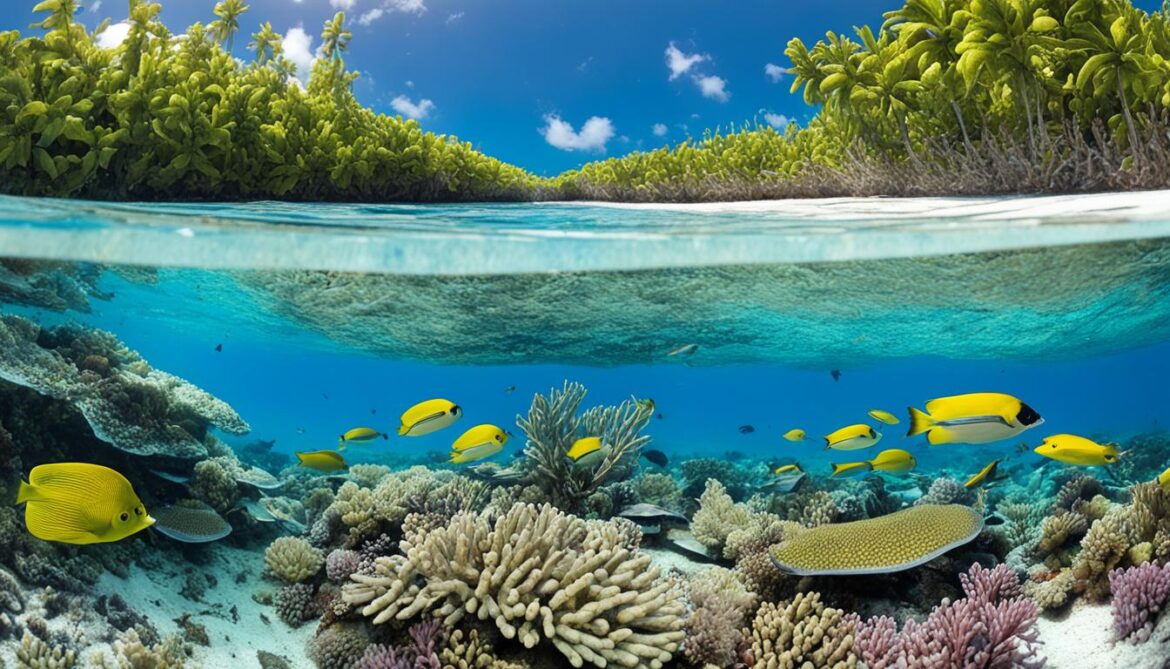

Image: Drone view of the vibrant coral reefs surrounding Tuvalu, showcasing the rich marine biodiversity.
Invasive Species in Tuvalu
Tuvalu, like many other regions, faces significant challenges from invasive species. In fact, nearly 65% of the flora found in the country is classified as alien species. These invasives pose a direct threat to the native plants and animals of Tuvalu.
One of the key issues associated with invasive species is their ability to compete for resources with native species. This competition can lead to the displacement or even extinction of native species, disrupting the delicate balance of the island’s ecosystems. The introduction and spread of invasive species are primarily driven by human activities, such as the deliberate or accidental introduction of new plants and animals for agricultural and landscaping purposes. These unintended consequences have the potential to cause irreversible damage to Tuvalu’s unique biodiversity.
Efforts are being made to prevent and manage invasive species through ongoing projects and initiatives. These measures include the development of strict biosecurity protocols to minimize the introduction of invasive species, as well as the implementation of control and eradication programs to mitigate their impact. Additionally, public awareness campaigns and educational programs aim to educate the local community on the importance of preserving native species and the potential risks of introducing invasive species.
“Invasive species pose a real threat to Tuvalu’s fragile ecosystems. It is crucial that we take immediate action to protect and preserve our native plants and animals.”
The fight against invasive species in Tuvalu requires a collaborative and multidisciplinary approach involving government agencies, local communities, and international organizations. By working together, we can safeguard the unique biodiversity of Tuvalu for future generations.

Conclusion
Tuvalu, with its unique biodiversity, faces numerous challenges from the impacts of climate change, invasive species, and unsustainable human activities. However, the country has taken significant steps to address these threats through conservation efforts and the development of a National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan.
While these measures are commendable, continued monitoring, capacity building, and international collaboration are crucial to ensure the long-term preservation of Tuvalu’s diverse ecosystems, particularly its marine biodiversity. Protecting and conserving the rich biodiversity of Tuvalu is not only essential for the sustainable development of the nation but also for the well-being of its people.
By safeguarding Tuvalu’s biodiversity, including its marine ecosystems, the country can promote ecological resilience, sustainable resource management, and the protection of valuable habitats. This will contribute to the overall resilience of Tuvalu’s ecosystems and help preserve the delicate balance necessary for the survival of countless species and the maintenance of ecosystem services.