Kazakhstan Biodiversity: Animal and Plant Species and What Is Under Threat
Wildlife plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy ecosystems and supporting life on our planet. However, human activity, unsustainable agriculture, poaching, industrial development, and logging have put thousands of species at risk of extinction. According to a World Wildlife Fund report, about 69 percent of wildlife disappeared between 1970 and 2022. Climate change, including frequent droughts, floods, and deforestation, poses a significant threat to the diversity of wildlife and our planet’s survival.
Explore the incredible biodiversity of Kazakhstan, home to a wide range of animal and plant species. Discover the efforts being made to protect these precious resources and learn about the challenges they face.
Key Takeaways:
- Kazakhstan’s wildlife is diverse, with 835 species of vertebrates and 387 plant species.
- Conservation efforts in Kazakhstan include habitat protection, fighting poaching, and developing ecological tourism.
- Initiatives focused on snow leopard and Bukhara deer conservation have shown positive results.
- Kazakhstan has established a network of protected areas to safeguard biodiversity.
- Financial support from organizations like USAID and the Global Environment Facility plays a crucial role in biodiversity conservation.
Stay tuned to learn more about the fascinating wildlife of Kazakhstan and the efforts being made to protect it.
Wildlife of Kazakhstan
The nature of Kazakhstan is incredibly diverse, consisting of deserts, semi-deserts, steppes, forests, and mountain ranges. Within this varied landscape, there are 835 species of vertebrates in Kazakhstan, including 178 mammal species, 489 bird species, 49 reptile species, and 104 fish species. Additionally, 387 plant species and 131 vertebrate species are on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List, indicating their threatened status.
Kazakhstan’s unique geography and climate create a habitat for an array of animal and plant species. The country is a biodiversity hotspot, home to numerous endemic species found nowhere else in the world. Its vast territory encompasses diverse ecosystems, from the arid deserts of the south to the lush forests in the north. This rich biodiversity plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of nature and provides invaluable ecological services.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the notable animal and plant species found in Kazakhstan:
- Kazakhstan Biodiversity: With over 178 mammal species, Kazakhstan boasts a diverse mammal population. This includes iconic species such as the snow leopard, Saiga antelope, Eurasian lynx, and the endangered Bukhara deer.
- Avian Diversity: Kazakhstan is a paradise for birdwatchers, with 489 bird species recorded. The steppe eagle, Dalmatian pelican, black stork, and saker falcon are just a few of the many bird species found here.
- Reptiles and Fish: The country’s varied landscapes provide habitats for 49 reptile species, including the Caspian turtle and Central Asian cobra. In Kazakhstan’s rivers and lakes, 104 fish species can be found, such as the sturgeon and the Balkhash perch.
- Flora and Vegetation: The plant life in Kazakhstan is equally diverse, with 387 plant species on the IUCN Red List. The country is home to unique flora like the Tulpar tulip, Glaucium grantii, and the Kazakhstan thistle.
The conservation of these precious species and their habitats is essential for maintaining the delicate balance of Kazakhstan’s ecosystems. Efforts to preserve biodiversity and protect endangered species are underway through the establishment of national parks, nature reserves, and conservation initiatives.
Kazakhstan’s Endangered Species
The diverse wildlife of Kazakhstan faces numerous threats, including habitat loss, poaching, climate change, and pollution. As a result, many animal and plant species are listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List. Here are some examples:
| Endangered Animal Species | Status |
|---|---|
| Snow Leopard | Endangered |
| Saiga Antelope | Critically Endangered |
| Eurasian Lynx | Least Concern |
| Bukhara Deer | Endangered |
| Saker Falcon | Vulnerable |
The conservation of these species and their habitats is of utmost importance to ensure their survival and maintain the ecological balance in Kazakhstan. Ongoing conservation efforts, including habitat restoration, anti-poaching measures, and public awareness campaigns, are crucial in protecting these endangered species.
Wildlife Conservation in Kazakhstan
In recent years, Kazakhstan has made significant progress in wildlife protection. Collaborating with the Government of Kazakhstan, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) has implemented various initiatives to conserve valuable animal species. These efforts encompass a range of conservation activities, including environmental protection, fighting against poaching, the creation of ecological corridors, reforestation, wildlife monitoring, improving environmental education, and developing ecological tourism.
Kazakhstan currently boasts a remarkable network of protected natural areas, providing a home to a diverse array of animals and birds. With 14 national parks, 10 nature reserves, and 7 reserves, the country offers vital habitats for wildlife to flourish and thrive. These protected areas play a pivotal role in safeguarding the rich biodiversity found in Kazakhstan.
“Conservation is not just an isolated effort; it involves a holistic approach that considers the entire ecosystem. By protecting wildlife and preserving their habitats, we are ensuring the long-term survival of these species and contributing to a healthier and more sustainable planet.”
Environmental education also plays a crucial role in wildlife conservation. Through educational initiatives, local communities gain an understanding of the importance of biodiversity and the need to preserve it. Enhanced public awareness helps foster a sense of responsibility and ownership towards Kazakhstan’s wildlife heritage.
Moreover, the development of ecological tourism provides economic opportunities and incentives for local communities to engage in responsible wildlife conservation. Tourism activities that focus on sustainable practices and respect for the environment allow visitors to appreciate the beauty and diversity of Kazakhstan’s wildlife while simultaneously benefiting local economies.
Overall, the collective efforts of the UNDP, the Government of Kazakhstan, and local communities have brought about positive change in wildlife conservation. By valuing and protecting Kazakhstan’s biodiversity, we are paving the way for a future where wildlife can thrive and contribute to the ecological balance of our planet.
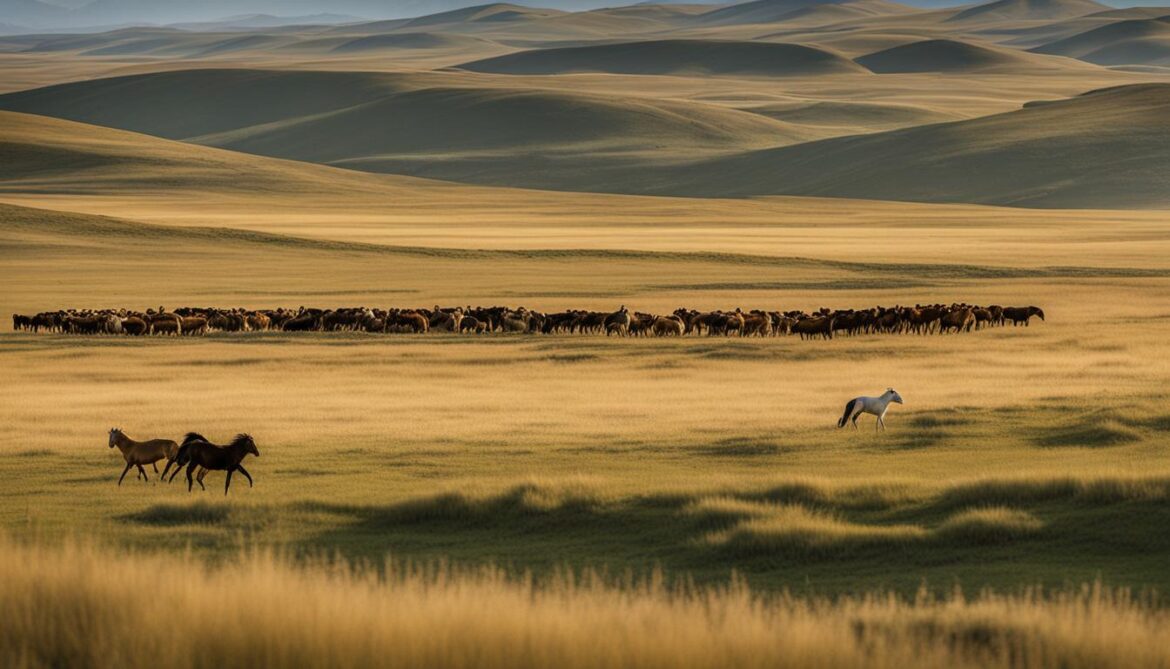

Kazakhstan’s Wildlife Conservation Achievements
| Initiatives | Achievements |
|---|---|
| Environmental Protection Measures | Preservation of natural habitats and prevention of habitat destruction |
| Poaching Prevention | Reduction in illegal hunting activities and protection of endangered species |
| Ecological Corridor Creation | Facilitation of wildlife movement and migration, ensuring genetic diversity |
| Reforestation Efforts | Restoration of degraded ecosystems and enhancement of carbon sequestration |
| Wildlife Monitoring | Effective tracking of animal populations, enabling evidence-based conservation strategies |
| Environmental Education | Increased awareness and knowledge among local communities, fostering conservation mindset |
| Ecological Tourism Development | Creation of sustainable tourism opportunities, promoting wildlife conservation and benefiting local economies |
Snow Leopard Conservation in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, with its unique geographical location as a cross-border region for snow leopard migration, has become a focal point for the international scientific community interested in snow leopard conservation. The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), in collaboration with the Institute of Zoology of the Republic of Kazakhstan, has been at the forefront of efforts to study and protect snow leopard populations in various regions of the country.
The primary objective of this UNDP-GEF initiative is to identify crucial habitat areas, understand migration routes, and minimize potential threats to snow leopards. By implementing modern technologies such as camera traps, thermal imagers, and drones, researchers can effectively monitor snow leopard populations, record their numbers, and track their migratory patterns.
The research conducted by the UNDP and the Institute of Zoology has yielded valuable insights into the behavior and habitat preferences of snow leopards in Kazakhstan. These findings are used to develop proposals for conservation measures and management strategies to ensure the long-term survival of this magnificent species.
The UNDP-GEF initiative aims to protect snow leopards by implementing sustainable conservation practices, raising awareness about their importance, and promoting collaboration among stakeholders. Snow leopards play a crucial role in maintaining the biodiversity of the region and preserving the delicate ecological balance.
Kazakhstan’s commitment to snow leopard conservation is evident in the efforts made by organizations, researchers, and local communities. By working together, they strive to safeguard this iconic species and secure a future where snow leopards continue to roam freely in their natural habitats.
Bukhara Deer Conservation in Kazakhstan
The Bukhara deer, once extinct in Kazakhstan, has been successfully reintroduced in the Ile-Balkhash Nature Reserve. The World Wildlife Fund (WWF), UNDP, and the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources have collaborated on a project to restore the Bukhara deer population in Kazakhstan. Since 2018, almost 140 individuals have been brought to the reserve, where they have adapted and are now breeding.
The reintroduction project aimed to revive the population of Bukhara deer, a critically endangered species, and create a sustainable environment for their survival. The Ile-Balkhash Nature Reserve, located in southeastern Kazakhstan, was chosen as a suitable habitat for their reintroduction due to its diverse ecosystems and protected status.
The project involved careful planning and implementation to ensure the successful adaptation of Bukhara deer in their new environment. The reintroduced individuals were closely monitored to track their behavior, reproductive patterns, and interactions with other wildlife in the reserve. This valuable data helped inform ongoing conservation efforts and ensure the long-term success of the project.
The collaboration between the WWF, UNDP, and the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources demonstrates the commitment of Kazakhstan to wildlife conservation and biodiversity preservation. Through their joint efforts, the Bukhara deer population in Kazakhstan is gradually recovering, providing hope for the future of this iconic species.
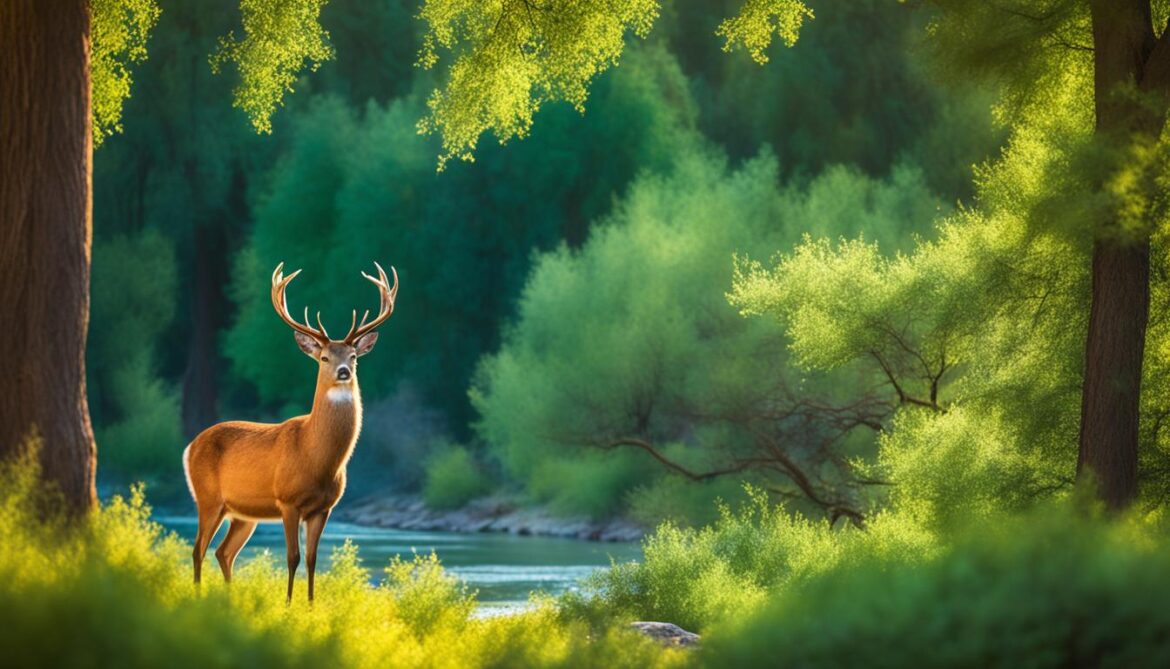

The reintroduction project not only benefits the Bukhara deer but also contributes to the overall ecological balance of the Ile-Balkhash Nature Reserve. By reintroducing this keystone species, the project aims to restore natural processes and promote biodiversity conservation in the region.
Bukhara Deer Conservation Project Highlights
- Collaboration between the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), UNDP, and the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources
- Reintroduction of almost 140 Bukhara deer individuals since 2018
- Successful adaptation and breeding of Bukhara deer in the Ile-Balkhash Nature Reserve
- Monitoring and research to track behavior, reproductive patterns, and interactions
- Contribution to biodiversity conservation and ecological balance in the reserve
Bukhara Deer Conservation Status and Future
“The reintroduction of Bukhara deer in Kazakhstan showcases the positive outcomes of dedicated conservation efforts. Through ongoing monitoring and protection measures, we can ensure the long-term survival and thriving of this remarkable species.”
| Current Population | Habitat | Conservation Status |
|---|---|---|
| Approximately 140 individuals | Ile-Balkhash Nature Reserve, Kazakhstan | Critically Endangered |
Kulan Rehabilitation in Kazakhstan
The kulan, another species once extinct in Kazakhstan, has been successfully reintroduced to its former habitat. The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is implementing an initiative to reintroduce kulans to the Ile-Balkhash Nature Reserve. This reintroduction project aims to restore the population of kulans in their native range and ensure the long-term survival of this endangered species.
As part of the project, around 60 kulans have been transported to the Ile-Balkhash Nature Reserve, where suitable habitat conditions have been created to support their reintroduction. The reserve, located in southeastern Kazakhstan, provides a diverse and expansive landscape that is ideal for the kulan’s grazing needs. With its grassy steppes and freshwater sources, the reserve offers an environment that closely resembles the kulan’s natural habitat.
To monitor the behavior and migration routes of the reintroduced kulans, modern technologies are being utilized. By using satellite tracking collars, researchers can collect valuable data on the movements and habitat preferences of the species. This information is essential for understanding kulan behavior and ensuring their successful integration into the reserve.
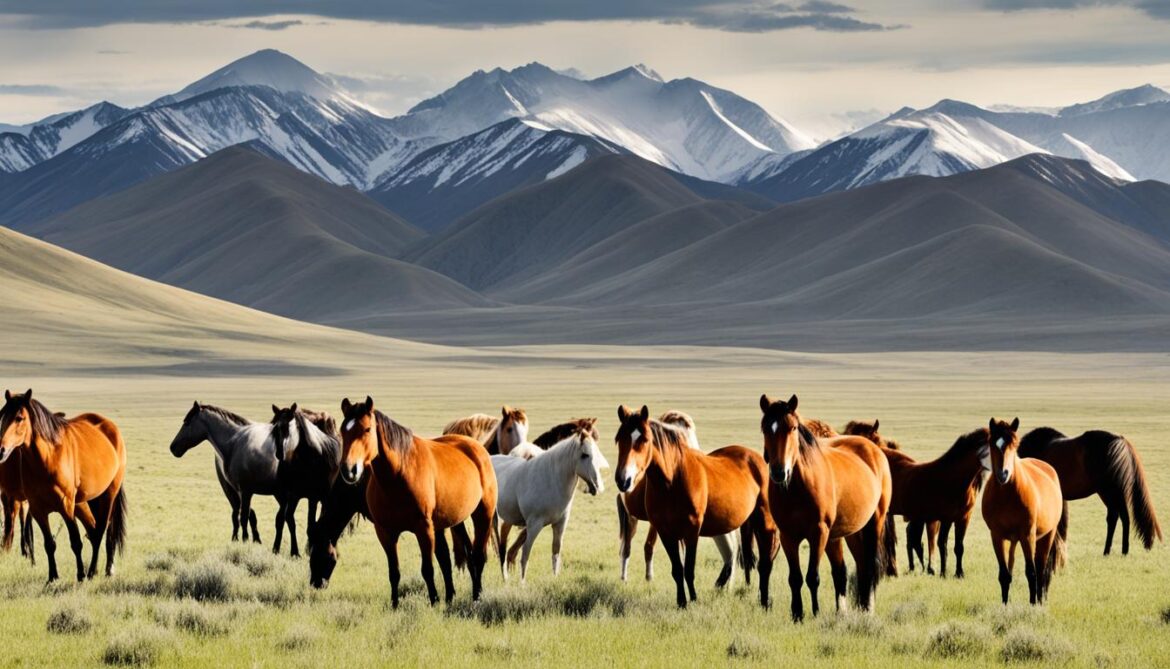

“The reintroduction of kulans to the Ile-Balkhash Nature Reserve is a critical step in preserving this iconic species and restoring the natural balance of the ecosystem. By rehabilitating the kulan population, we are not only protecting the species but also contributing to the overall biodiversity conservation efforts in Kazakhstan.”
The kulan rehabilitation project in Kazakhstan exemplifies the ongoing commitment to wildlife conservation and biodiversity preservation in the country. Through collaborative efforts between the UNDP, local communities, and conservation organizations, Kazakhstan is taking significant strides towards safeguarding its natural heritage and ensuring a sustainable future for its wildlife.
Protected Areas and Biodiversity Conservation
Kazakhstan is committed to the conservation of biodiversity through the establishment and development of protected natural areas. Currently, the country boasts 14 national parks, 10 nature reserves, and 7 reserves, all of which serve as crucial habitats for a diverse range of animals and birds. These protected areas play a vital role in safeguarding Kazakhstan’s rich biodiversity and ensuring the long-term survival of endangered species.
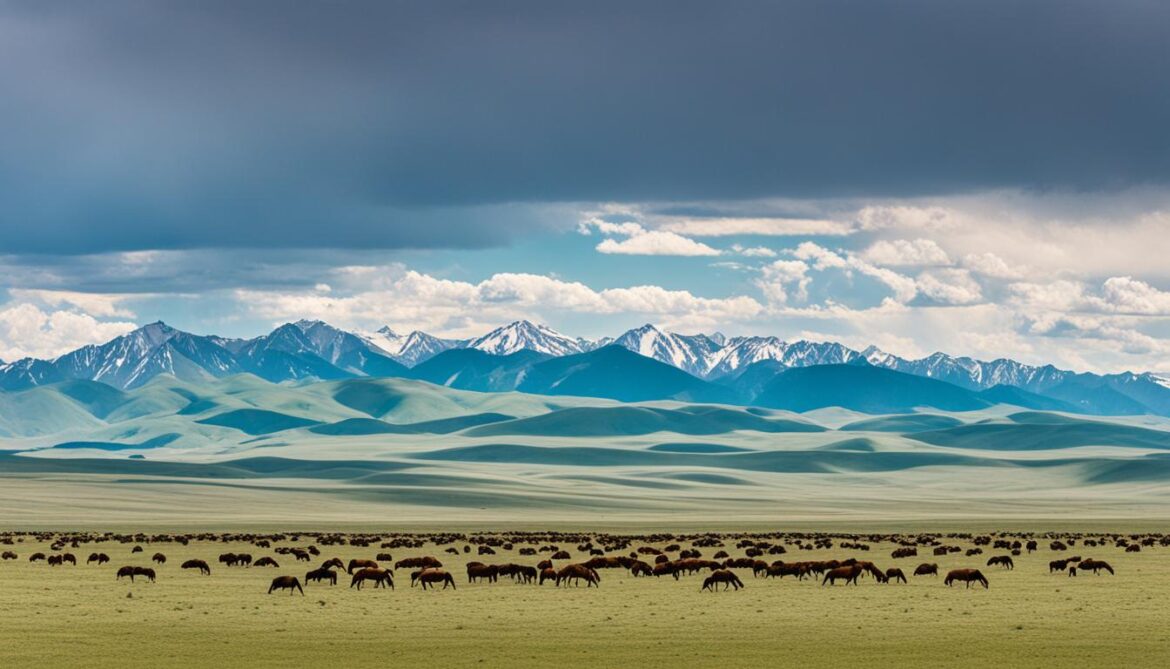

Protected areas are essential for preserving the unique ecosystems and the numerous species that call Kazakhstan home. These areas serve as havens for wildlife, providing them with the necessary resources and habitats to thrive. By creating a network of protected areas, Kazakhstan actively contributes to the conservation and preservation of its natural heritage.
Biodiversity conservation in Kazakhstan is not limited to a few isolated areas but extends throughout the country. These protected areas encompass a variety of ecosystems, ranging from vast steppes and forests to majestic mountain ranges. Each of these ecosystems supports a wide array of plant and animal species, fostering a delicate balance and ensuring the sustainability of Kazakhstan’s natural environment.
The Importance of Protected Areas
“Protected areas are the cornerstone of biodiversity conservation efforts in Kazakhstan. They provide safe habitats for endangered species, enable ecological restoration, and promote sustainable land and resource management. Moreover, these areas serve as living laboratories for scientific research and environmental education, raising awareness about the value of biodiversity and the need for its protection.” – Dr. Nurzhan Bakirov, Environmental Scientist
In addition to safeguarding biodiversity, protected areas offer various benefits to local communities and the wider society. They support ecotourism, providing opportunities for visitors to appreciate the beauty of Kazakhstan’s natural landscapes, observe diverse wildlife, and experience unique cultural heritage. Furthermore, protected areas contribute to the regulation of local climates, water resources, and carbon sequestration, playing a crucial role in mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Efforts to create and maintain protected areas in Kazakhstan require collaboration between the government, local communities, and international organizations. Together, they develop and implement policies, conservation strategies, and management plans to ensure the effective preservation of these areas for future generations.
The Role of International Collaboration
“International collaboration is essential in biodiversity conservation, as it allows for the sharing of knowledge, expertise, and resources. Through partnerships with organizations like the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), Kazakhstan benefits from global best practices, funding support, and technical assistance, enhancing its conservation efforts and promoting sustainable development.” – Dr. Anna Petrova, Biodiversity Conservation Specialist
The international community recognizes the importance of biodiversity conservation in Kazakhstan and actively supports the country’s efforts. Through collaborative initiatives, joint research projects, and capacity-building programs, international organizations contribute to the conservation of Kazakhstan’s unique ecosystems and species.
| Protected Areas in Kazakhstan | Establishment Year | Size (sq km) |
|---|---|---|
| Naurzum State Nature Reserve | 1931 | 2,062 |
| Altyn-Emel National Park | 1996 | 4,451 |
| Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve | 1968 | 12,172 |
| Ile-Balkhash State Nature Reserve | 1971 | 8,095 |
| Katon-Karagay National Park | 1996 | 643 |
These protected areas, along with others, contribute significantly to the preservation of Kazakhstan’s biodiversity and serve as examples of successful conservation practices.
Kazakhstan’s Biodiversity Strategy and Policy Framework
Kazakhstan recognizes the critical importance of biodiversity conservation and has implemented a comprehensive strategy and policy framework to protect its rich natural heritage. The country has established a robust legislative framework, including laws and regulations, that aim to safeguard biodiversity and preserve the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Institutions such as the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources play a crucial role in implementing initiatives and projects that support biodiversity conservation. Through their active involvement, Kazakhstan is able to collaborate with international partners, harnessing expertise and resources to further its conservation goals.
Kazakhstan’s National Environment Action Plan (NEAP) reflects the country’s commitment to biodiversity conservation and the sustainable use of biological diversity. The NEAP outlines key strategies and actions to address the challenges faced by biodiversity and promote sustainable development.
The NEAP focuses on various aspects of biodiversity conservation, including the protection and restoration of ecosystems, sustainable management of natural resources, and the integration of biodiversity considerations into sectoral planning and decision-making processes. By incorporating biodiversity concerns into national policies and programs, Kazakhstan aims to ensure the long-term preservation of its unique wildlife and habitats.
Kazakhstan’s biodiversity strategy and policy framework are vital tools for guiding conservation efforts and promoting sustainable development. Through effective implementation and collaboration with stakeholders, the country aims to protect its natural heritage for future generations.
To illustrate the scale and impact of Kazakhstan’s biodiversity strategy, consider the following table:
| Key achievements of Kazakhstan’s biodiversity strategy and policy framework |
|---|
| Establishment of a legislative framework to protect biodiversity |
| Active involvement of institutions such as UNDP and Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources in conservation initiatives |
| Inclusion of biodiversity considerations in Kazakhstan’s National Environment Action Plan |
| Integration of biodiversity concerns into national policies and programs |
| Collaboration with international partners to leverage expertise and resources |

USAID’s Role in Biodiversity Conservation in Kazakhstan
USAID has played a significant role in supporting biodiversity conservation in Kazakhstan. Through its programs, USAID has contributed to the protection of biodiversity and the conservation of globally significant ecosystems. The agency has collaborated with local organizations and the government to implement initiatives focused on environmental protection, wildlife conservation, and ecological tourism. USAID’s efforts align with Kazakhstan’s biodiversity strategy and policy framework.
One of the key programs USAID has supported in Kazakhstan is the Sustainable Development of Nature Management (SDNM) project. This project aims to promote sustainable land and resource management practices that protect and enhance biodiversity. It focuses on improving environmental governance, sustainable forest management, and strengthening the capacity of local communities and institutions to manage natural resources.
“USAID’s partnership with Kazakhstan has been instrumental in advancing biodiversity conservation in the country. By working closely with local organizations, we have been able to develop and implement effective strategies for protecting endangered species and their habitats.”
USAID has also invested in the development of ecotourism as a means to promote biodiversity conservation and support local communities. The agency has supported the creation of nature-based tourism opportunities in protected areas, providing sustainable economic benefits while raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity.
USAID Biodiversity Conservation Initiatives in Kazakhstan
Some of the key biodiversity conservation initiatives implemented by USAID in Kazakhstan include:
- Conservation of Snow Leopards: USAID has supported projects aimed at protecting and monitoring snow leopards in Kazakhstan. These initiatives involve the use of innovative technologies such as camera traps and satellite collars to track snow leopard populations and gather valuable data for conservation efforts.
- Rangeland Management: USAID works with local communities and government entities to promote sustainable rangeland management practices. By improving livestock grazing practices and strengthening pasture management systems, USAID aims to preserve critical habitat for endangered species.
- Community-based Conservation: USAID has facilitated the establishment of community-based conservation initiatives in Kazakhstan. These initiatives empower local communities to actively participate in the management and protection of natural resources, helping to safeguard biodiversity for future generations.
Through these and other initiatives, USAID continues to play a crucial role in supporting biodiversity conservation in Kazakhstan. By collaborating with local stakeholders and aligning efforts with national strategies, USAID is contributing to the long-term preservation of Kazakhstan’s rich natural heritage.

Financing Biodiversity Conservation in Kazakhstan
The financing of biodiversity conservation in Kazakhstan is a critical aspect of sustaining conservation efforts. Without adequate funding, it becomes challenging to implement crucial initiatives and projects that protect and preserve the country’s diverse wildlife and ecosystems.
Financing biodiversity conservation in Kazakhstan requires strong commitment from both national and international organizations. Initiatives such as the Biodiversity and Sustainable Forestry Initiative (BIOFOR) have been instrumental in diverting more finance towards biodiversity conservation. BIOFOR focuses on promoting sustainable forestry practices while also supporting the preservation of biodiversity. It recognizes the inherent value of conserving natural resources and the importance of sustainable economic development.
Kazakhstan has also received financial support from international organizations like the Global Environment Facility (GEF) for its biodiversity conservation projects. GEF plays a crucial role in mobilizing significant funds to address pressing environmental challenges worldwide. Through its programs, GEF works closely with governments, non-governmental organizations, and local communities to provide financial assistance for conservation initiatives in Kazakhstan.
Financial Support for Biodiversity Conservation in Kazakhstan
| Organization | Type of Support |
|---|---|
| Biodiversity and Sustainable Forestry Initiative (BIOFOR) | Direct funding for sustainable forestry practices and biodiversity conservation |
| Global Environment Facility (GEF) | Financial assistance for biodiversity conservation projects |
These financial investments are crucial for the successful implementation of biodiversity conservation projects in Kazakhstan. They enable the government and local organizations to carry out initiatives such as habitat restoration, protected area management, species reintroduction programs, and community-based conservation efforts.
Continued financial investments in biodiversity conservation are necessary to ensure the long-term success of conservation efforts in Kazakhstan. Adequate funding will enable the country to strengthen its protected area network, implement robust monitoring and enforcement measures, and promote sustainable practices that safeguard both wildlife and local communities.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Kazakhstan has made remarkable strides in biodiversity conservation, demonstrating its commitment to protecting valuable animal species and preserving natural areas. Through close collaboration between the government, international organizations like the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), and local communities, significant progress has been achieved.
However, the work is far from over. Ongoing threats, including climate change and human activities, necessitate continued vigilance and investment in biodiversity conservation. By safeguarding wildlife and preserving ecosystems, Kazakhstan is not only securing a sustainable future for its people but also contributing to the global effort towards environmental sustainability.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for Kazakhstan to maintain its momentum in biodiversity conservation. By implementing effective policies, strengthening collaboration, and engaging communities, the country can build upon its successes and further protect its diverse range of species and habitats. Through sustained efforts, Kazakhstan can continue to be a leader in biodiversity conservation and inspire others around the world to follow suit.