Afghanistan Biodiversity: Animal and Plant Species and What Is Under Threat
Afghanistan is home to a remarkable array of animal and plant species, making it a biodiversity hotspot. However, this rich natural heritage is currently under threat due to various factors.
Over the last three decades, Afghanistan’s biodiversity has faced significant challenges, including the devastating impact of war and human activities such as overgrazing, fuel collection, and the exploitation of large herbivorous animals. These factors have led to a decline in the country’s biodiversity and pose serious risks to its fragile ecosystems.
Despite these challenges, Afghanistan boasts an impressive diversity of species. The country is home to approximately 118-147 species of mammals, 472-510 species of birds, 92-112 species of reptiles, 6-8 species of amphibians, 101-139 species of fish, 245 species of butterflies, and 3500-4000 vascular plant species. However, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has identified 39 species and 8 subspecies as being globally threatened with extinction.
Protecting and conserving Afghanistan’s biodiversity is of utmost importance to ensure the long-term survival of these unique species and their habitats. It is crucial to address the threats facing Afghanistan’s biodiversity and take proactive measures to safeguard its rich natural heritage for future generations.

Key Takeaways:
- Afghanistan’s biodiversity faces threats due to war, overgrazing, fuel collection, and the exploitation of large herbivorous animals.
- The country is home to a diverse range of animal and plant species, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, butterflies, and vascular plants.
- 39 species and 8 subspecies in Afghanistan are currently listed as globally threatened with extinction.
- Conserving Afghanistan’s biodiversity is crucial to protecting its unique species and their habitats.
- Urgent action is needed to address the threats and preserve Afghanistan’s rich natural heritage for future generations.
Afghanistan’s Unique Bio-geographical Provinces
Afghanistan, with its diverse landscapes and ecosystems, is home to eight distinct bio-geographical provinces. These provinces play a crucial role in supporting the country’s rich biodiversity and are essential for its ecological balance and conservation efforts.
Seven of these bio-geographical provinces belong to the Palaearctic Realm, which encompasses Europe, Asia north of the Himalayas, and North Africa. The Palaearctic Realm is known for its diverse flora and fauna, including iconic species like the Siberian tiger, the Caspian seal, and the snow leopard. Afghanistan’s Palaearctic provinces showcase the region’s unique characteristics and host a plethora of plant and animal species.
The eighth province, located in the lower Kabul River Valley, has origins in the Indo-Malayan region. This area displays distinct characteristics influenced by the Indo-Malayan biodiversity hotspot, which is globally recognized for its exceptional species richness and endemism. The Indo-Malayan origin of this province adds to the overall biodiversity significance of Afghanistan.
This province, with its Indo-Malayan origin, showcases unique ecological characteristics and adds to the overall diversity of Afghanistan’s bio-geographical regions. It is home to a variety of plant and animal species that thrive in the distinct environmental conditions of the lower Kabul River Valley. This region is of immense importance for biodiversity conservation efforts in Afghanistan.
Understanding Afghanistan’s bio-geographical provinces is essential for the conservation and management of its rich biodiversity. These provinces provide unique habitats for countless species and contribute to the overall ecological resilience of the country. By acknowledging and protecting the diverse ecosystems within these provinces, we can ensure the long-term survival of Afghanistan’s precious flora and fauna.
Some Afghan Mammals
Afghanistan’s diverse geography, which includes mountains, deserts, and forests, supports a variety of mammal species. Some of the common mammals found in Afghanistan include:
- Snow Leopard (Panthera uncia): These elusive big cats are primarily found in the mountainous regions, particularly in the Hindu Kush and Pamir ranges.
- Asiatic Black Bear (Ursus thibetanus): Also known as the Himalayan black bear, it inhabits the forests and mountainous areas.
- Markhor (Capra falconeri): This wild goat species is known for its impressive spiral horns and is typically found in the rugged mountains.
- Gray Wolf (Canis lupus): Wolves are widespread and can be found in various habitats, including mountains and deserts.
- Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx): This medium-sized wildcat prefers forested areas and mountainous regions.
- Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes): A highly adaptable species, the red fox can be found in a variety of habitats across Afghanistan.
- Caracal (Caracal caracal): This medium-sized wildcat with distinctive tufted ears is found in the arid and semi-arid regions.
- Pallas’s Cat (Otocolobus manul): Also known as the manul, this small wildcat inhabits the steppes and mountainous regions.
- Striped Hyena (Hyaena hyaena): Found in arid and semi-arid regions, the striped hyena is a scavenger that plays a crucial role in the ecosystem.
- Rhesus Macaque (Macaca mulatta): This primate is commonly found in forested regions and near human settlements.
- Wild Boar (Sus scrofa): These omnivorous mammals inhabit forests and areas near water sources.
- Indian Crested Porcupine (Hystrix indica): This large rodent is found in various habitats, including mountains, forests, and agricultural areas.
- Golden Jackal (Canis aureus): These adaptable canines are found in various habitats, including grasslands and human-altered landscapes.
These species represent a fraction of the mammalian diversity in Afghanistan, which is shaped by the country’s varied climates and topographies. Conservation efforts are critical for many of these species, particularly those threatened by habitat loss and poaching.
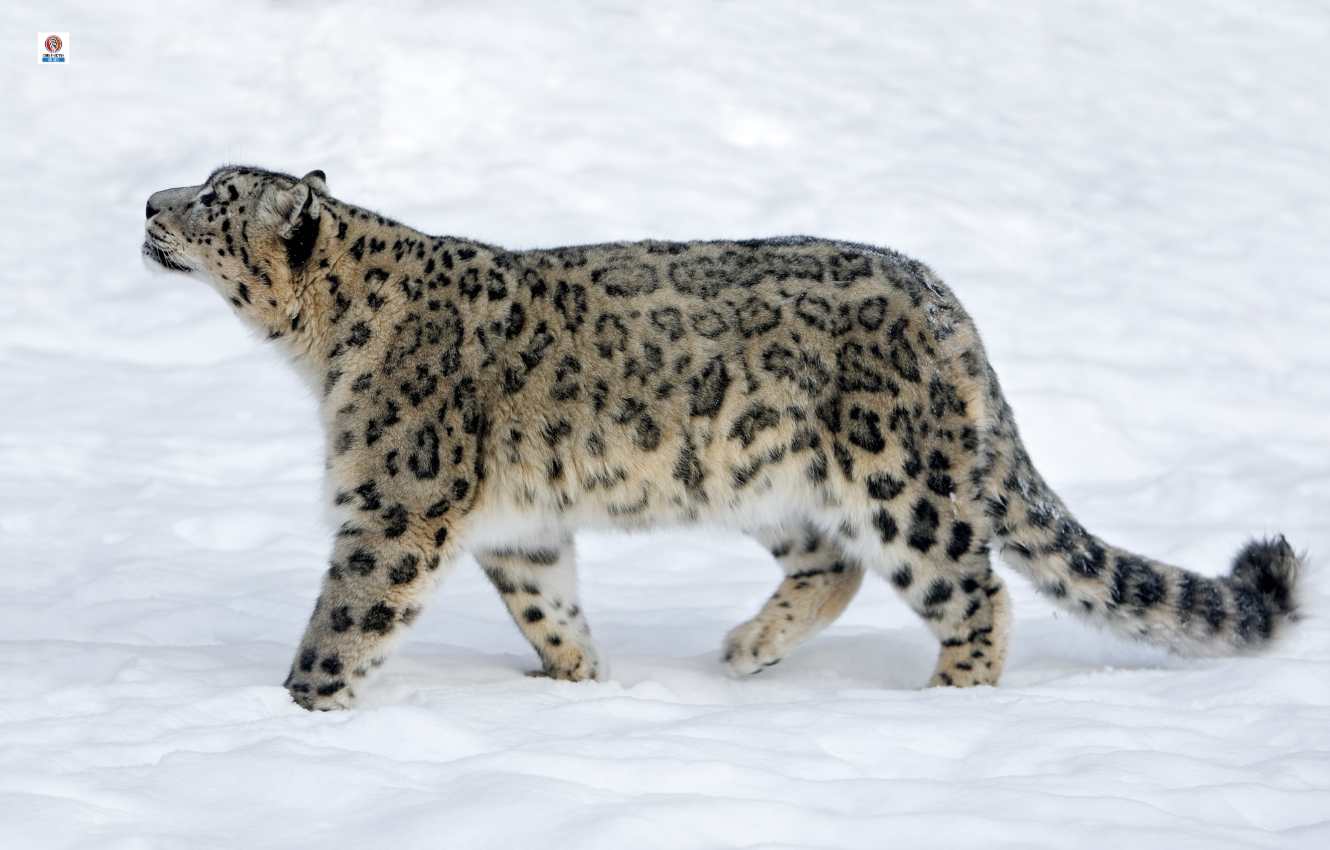

Endangered Species in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, with its rich biodiversity, is home to several endangered species. As per the latest data from the IUCN Red List, 39 species and 8 subspecies in Afghanistan are classified as endangered and face the threat of extinction. These include a diverse range of large mammals, whose populations have declined significantly over the years due to hunting and habitat destruction.
These endangered species play a vital role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem and are an integral part of Afghanistan’s natural heritage. Without immediate conservation efforts, these vulnerable species may disappear forever, causing irreparable loss to the country’s biodiversity.
“The conservation of endangered species is a matter of utmost urgency,” says Dr. Susan Thompson, a leading expert in wildlife conservation. “We must take action to protect their habitats, enforce anti-poaching measures, and raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity.”
“Preserving biodiversity is not only crucial for the survival of these endangered species, but it also has broader implications for ecological balance and human well-being,” adds Dr. Thompson.
Protecting Endangered Species
Efforts to protect endangered species in Afghanistan are of significant importance. Conservation organisations, local communities, and the government need to collaborate to implement effective measures that ensure the survival of these species.
The first step is to identify and protect critical habitats where these endangered species thrive. Conservation areas, national parks, and wildlife reserves can serve as safe havens for these animals, allowing their populations to recover. Additionally, strict anti-poaching measures and the enforcement of wildlife protection laws are essential to prevent further harm to these species.
Educating the public about the value of biodiversity and the negative consequences of species extinction is crucial. Awareness campaigns, educational programs, and community engagement can inspire action and foster a sense of responsibility towards protecting endangered species.
Endangered Species in Afghanistan
| Category | Species |
|---|
| Mammals | Lion (Panthera leo) |
| Mammals | Giant Panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) |
| Birds | Indian Peafowl (Pavo cristatus) |
| Birds | Great Indian Bustard (Ardeotis nigriceps) |
| Reptiles | Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) |
| Reptiles | Aldabra Tortoise (Aldabrachelys gigantea) |
| Amphibians | Goliath Frog (Conraua goliath) |
| Fish | Vaquita (Phocoena sinus) |
These are just a few examples of the endangered species in Afghanistan. Urgent conservation actions are needed to protect and preserve their habitats, ensuring their survival for future generations.

Protected Areas in Afghanistan
Afghanistan is home to several protected areas that play a vital role in biodiversity conservation. These areas, although not officially recognized by the current government, contribute to the preservation of unique ecosystems and wildlife habitats.
“Protected areas are crucial for safeguarding biodiversity and ensuring the long-term survival of vulnerable species.”
Currently, Afghanistan has 15 protected areas, including one Category II national park and six Category IV wildlife or waterfowl reserves. These protected areas serve as sanctuaries for a variety of plant and animal species.
Category II National Park:
The only Category II national park in Afghanistan is Band-e-Amir National Park. Situated in the Bamyan Province, it is known for its stunning lakes and majestic landscapes. The park is home to several endangered species, including the elusive snow leopard and the Afghan urial.
Category IV Wildlife or Waterfowl Reserves:
Afghanistan has six Category IV reserves that are designated for wildlife or waterfowl conservation. These reserves provide essential habitats for a wide range of species and contribute to the overall biodiversity of the country. Some of the noteworthy reserves include:
- Khoshkak Wildlife Reserve
- Sheway Farming Complex
- Qargha-Karkar Riverine Wetland
In addition to these reserves, other protected areas in Afghanistan include biodiverse regions such as the Wakhan Corridor and the Ghorband Valley. These areas are recognized for their ecological significance and contribute to the overall conservation efforts in the country.
However, the lack of official recognition, clearly defined boundaries, and proper management pose challenges to the effectiveness of these protected areas in preserving biodiversity. It is crucial for the current government to invest in strengthening the governance and management of these areas to ensure their long-term conservation.
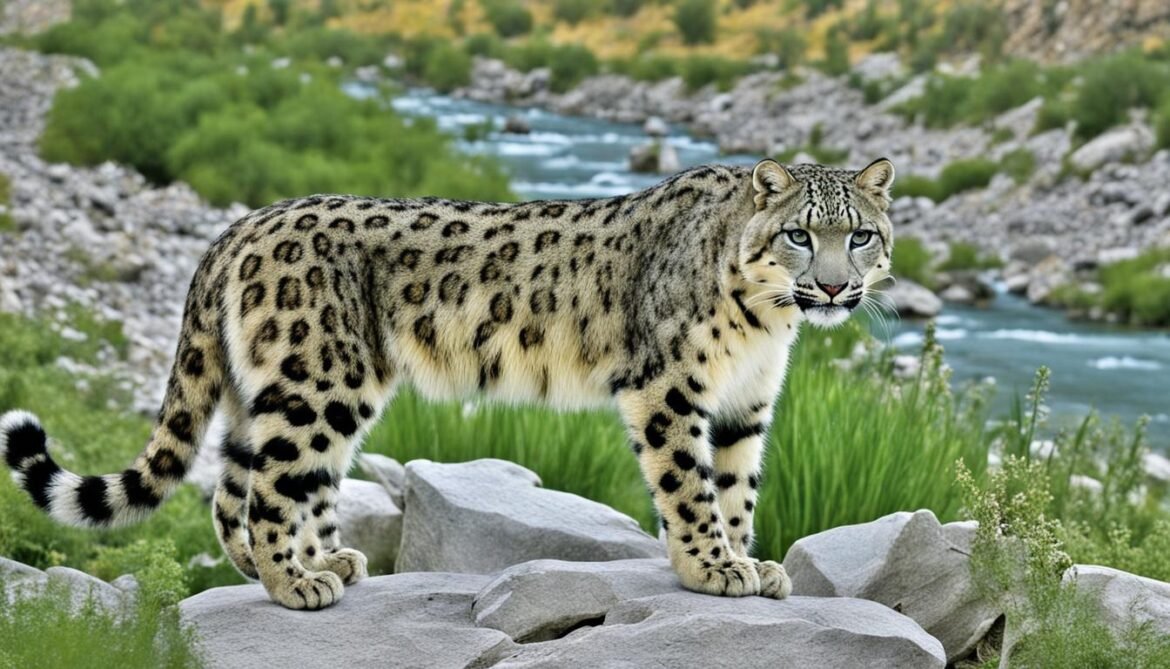

| Protected Area | Category | Location |
|---|
| Band-e-Amir National Park | Category II | Bamyan Province |
| Khoshkak Wildlife Reserve | Category IV | Hirat Province |
| Sheway Farming Complex | Category IV | Faryab Province |
| Qargha-Karkar Riverine Wetland | Category IV | Kabul Province |
Forest Cover in Afghanistan
In Afghanistan, the forest cover is primarily found in the monsoon-influenced eastern part of the country. These forests, consisting of both deciduous and evergreen true forests, once extended across approximately 5% of the total surface area of Afghanistan.
However, recent analyses indicate that only a mere 5% of the original forests may still exist today. This significant decline in forest cover is alarming and necessitates urgent attention and conservation efforts.
The open woodlands, which were once dominant across 38% of Afghanistan’s land, were predominantly characterized by pistachio and juniper trees. However, satellite image analysis conducted in 2002 revealed that the tree density had become too low to be detected, suggesting that this unique ecosystem is now on the brink of extinction.
Preserving and restoring forest cover in Afghanistan is vital not only for the country’s biodiversity but also for the numerous ecological benefits these forests provide. Forests play a critical role in maintaining soil stability, regulating water cycles, and preventing erosion.
To illustrate the extent of the decline in forest cover and the urgent need for conservation measures, here is a comparison between the original forest cover and the current state:
| Forest Type | Original Forest Cover | Current Forest Cover |
|---|
| Deciduous Forests | Approximately 5% of the surface area | Estimated to be significantly lower than the original extent |
| Evergreen Forests | Approximately 5% of the surface area | Estimated to be significantly lower than the original extent |
| Woodlands | Once dominated 38% of Afghanistan’s land | Considered close to extinction due to low tree density |
It is crucial for Afghanistan to prioritise the protection and restoration of forest ecosystems. Efforts should focus on reforestation initiatives, sustainable forest management practices, and raising awareness about the importance of forests in preserving biodiversity and promoting environmental stability.
The Importance of Forest Cover Conservation
Conserving forest cover in Afghanistan carries immense significance for several reasons:
- 1. Biodiversity Preservation: Forests are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic to specific forest types. By preserving forest cover, Afghanistan can safeguard the unique biodiversity that these ecosystems support.
- 2. Climate Regulation: Forests play a crucial role in regulating the climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen through photosynthesis. Protecting forest cover contributes to mitigating climate change and maintaining a stable and healthy environment.
- 3. Water Resources: Forests help regulate water cycles by reducing runoff, increasing water infiltration, and maintaining moisture levels in the soil. The preservation of forest cover is essential for ensuring a sustainable and reliable water supply.
- 4. Soil Conservation: Forests act as natural buffers against soil erosion, protecting agricultural land and preventing sediment from entering rivers and water bodies, which can cause pollution and further degrade ecosystems.
By prioritising forest cover conservation, Afghanistan can work towards a more sustainable future, fostering a healthier environment and preserving its rich biodiversity for generations to come.

Wetlands and Water Resources in Afghanistan
Wetlands are of immense significance to biodiversity in Afghanistan, particularly given the arid nature of the country. These wetlands provide crucial habitats for diverse plant and animal species, contributing to the overall biodiversity significance of Afghanistan. They serve as vital breeding grounds, feeding areas, and shelters for a variety of species.

However, the water resources in these wetlands are under threat. Many wetlands in Afghanistan are drying up due to a combination of factors such as climate change, unsustainable water use, and upstream dam construction. The consequences are far-reaching, causing the loss of vegetation, soil erosion, and the spread of sand into fields, cities, and roads.
One of the significant impacts of wetland drying is the loss of biodiversity. As wetlands shrink, the unique habitats that support various plant and animal species disappear, leading to the decline or loss of species that depend on wetland ecosystems for their survival. This loss of biodiversity has far-reaching ecological implications, affecting the overall balance of ecosystems.
Furthermore, the drying of wetlands also contributes to water scarcity. Wetlands are natural water storage systems that help regulate water flow, recharge groundwater, and filter pollutants. The loss of these wetlands results in reduced water availability, making communities more vulnerable to droughts and affecting agricultural productivity.
To mitigate the negative impacts on wetlands and water resources, measures must be taken to conserve and restore these precious ecosystems. This includes implementing sustainable water management practices, promoting awareness about the importance of wetlands, and establishing protected areas to ensure the long-term preservation of these critical habitats.
Impact of Human Activity on Biodiversity
The decline in biodiversity in Afghanistan is primarily a result of human activity. Habitat destruction, overgrazing, pollution, and the introduction of foreign species have all contributed to the degradation and loss of biodiversity in the country. These human-induced factors have had severe consequences on the delicate ecosystems and native species of Afghanistan.
“Habitat destruction is one of the leading causes of biodiversity loss in Afghanistan. The conversion of natural habitats into agricultural land, urbanization, and infrastructure development have fragmented ecosystems and displaced numerous plant and animal species,” says Dr. Zia, a renowned environmental biologist at Kabul University.
Overgrazing by livestock, primarily due to the high demand for meat and dairy products, has had a significant impact on vegetation and soil erosion. The excessive grazing pressure has led to the deterioration of rangelands, affecting the survival of native plant species and disrupting the balance of the ecosystem.
Pollution from various sources, including industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and inadequate waste management, has contaminated freshwater bodies and soil, posing a significant threat to aquatic species and terrestrial organisms alike. The accumulation of pollutants has disrupted the natural habitats and caused the decline of sensitive species.
The introduction of foreign species has also wreaked havoc on Afghanistan’s biodiversity. Invasive plants and animals, such as the giant hogweed and red-eared slider turtle, compete with native species for resources and often outcompete them, leading to the displacement or extinction of local flora and fauna.
Urgent action is needed to address these threats and ensure the sustainable management and use of biological resources. Strategies must be implemented to mitigate habitat destruction, promote sustainable grazing practices, reduce pollution, and control the introduction of invasive species. By adopting these measures, Afghanistan can preserve its unique biodiversity and safeguard the future of its ecosystems.
| Human Activity | Impact on Biodiversity |
|---|
| Habitat destruction | Loss of natural habitats, displacement of species |
| Overgrazing | Deterioration of rangelands, disruption of ecosystem balance |
| Pollution | Contamination of freshwater bodies and soil, negative effects on aquatic and terrestrial species |
| Introduction of foreign species | Competition with native species, displacement or extinction of local flora and fauna |
Water Resources and Biodiversity Conservation
In Afghanistan, the conservation of biodiversity and the management of water resources are closely intertwined. The agricultural sector, which heavily relies on water, contributes to over half of the country’s GDP and provides livelihoods for a significant portion of the population. However, Afghanistan faces challenges such as water shortages, poor water management practices, and the loss of glaciers, which directly impact the conservation of biodiversity and the sustainable utilization of water resources.
To address these challenges and ensure the long-term preservation of biodiversity, efforts must be made to protect and preserve wetlands. Wetlands play a vital role in maintaining ecosystem health, providing essential habitats for a wide range of plant and animal species. They also act as natural water filters, helping to improve water quality. Preserving wetlands promotes the conservation of biodiversity and helps safeguard water resources.
Another important aspect of water resources management is the protection of watersheds. Watersheds, the areas that drain into a particular river or lake, are critical for maintaining the quantity and quality of water resources. Protecting watersheds involves measures such as reforestation, soil conservation, and sustainable land use practices. These actions not only help conserve biodiversity but also contribute to ensuring the availability of clean water for both humans and wildlife.
Improving water management practices is essential for maintaining the delicate balance between water resources and biodiversity conservation in Afghanistan. This includes implementing effective water storage and irrigation systems, promoting water-efficient technologies and practices, and raising awareness about the importance of sustainable water use. By integrating these measures, Afghanistan can minimize water shortages, enhance biodiversity protection, and promote the sustainable development of its water resources.

National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan
Afghanistan recognises the importance of protecting its unique biodiversity and is working towards the development of a comprehensive National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP). This plan aims to address the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity in the country, serving as a roadmap for biodiversity conservation efforts.
The NBSAP will play a crucial role in guiding future actions to protect and manage Afghanistan’s diverse ecosystems and species. It will outline strategies and measures to conserve biodiversity, mitigating the threats it faces and promoting sustainable practices for its preservation.
The development of the NBSAP reflects Afghanistan’s commitment to biodiversity conservation and aligns with the global goals of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). By implementing this plan, Afghanistan aims to contribute to the conservation of biodiversity on a national and international scale.
“The National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan will provide a comprehensive framework to safeguard Afghanistan’s unique biodiversity and ensure its sustainable use for the benefit of present and future generations.”
– Ministry of Environment, Afghanistan
Key Objectives of the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan
- Identify and protect critical habitats and ecosystems
- Promote sustainable land and water management practices
- Enhance conservation efforts for endangered species
- Strengthen capacity building and collaboration among stakeholders
- Integrate biodiversity conservation into development planning
Expected Outcomes of the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan
- Improved conservation and management of biodiversity
- Increased awareness and understanding of the value of biodiversity
- Enhanced ecosystem resilience and services
- Greater participation and engagement of local communities
- Contribution to the achievement of global biodiversity targets
The National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan will provide the necessary framework and guidelines to address the specific challenges faced by Afghanistan’s biodiversity. By implementing effective conservation measures and promoting sustainable practices, Afghanistan can ensure the long-term preservation of its rich natural heritage.
| Key Components of the NBSAP | Actions and Implementation |
|---|
| 1. Biodiversity Assessment and Monitoring | Establish a comprehensive biodiversity monitoring system and conduct regular assessments to track biodiversity trends. |
| 2. Protected Areas Management | Strengthen the management and governance of protected areas to ensure effective conservation and protection of biodiversity. |
| 3. Sustainable Use of Biological Resources | Promote sustainable practices for the utilization of biological resources, ensuring their conservation and sustainable management. |
| 4. Capacity Building and Awareness | Enhance the capacity of relevant stakeholders and raise awareness about the value and importance of biodiversity conservation. |
Conclusion
Afghanistan’s biodiversity is incredibly diverse and valuable, but it faces numerous threats that require immediate action for conservation and protection. Habitat destruction, overgrazing, pollution, and climate change are significant challenges that must be addressed to safeguard the country’s unique animal and plant species and their habitats.
Efforts should focus on developing a comprehensive National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan to guide conservation efforts effectively. Establishing and managing protected areas is crucial in preserving biodiversity and providing safe havens for vulnerable species. Additionally, promoting sustainable water resource management practices is vital for the long-term survival of Afghanistan’s biodiversity.
By implementing these protection measures, Afghanistan can play a significant role in global conservation efforts and ensure the preservation of its rich biodiversity for future generations to admire and enjoy.
FAQ
What is the status of biodiversity in Afghanistan?
Afghanistan’s biodiversity has suffered greatly in the last three decades due to factors like habitat destruction, overgrazing, and exploitation of large herbivorous animals. The country is home to a diverse range of animal and plant species, but 39 species and 8 subspecies are currently listed as globally threatened with extinction.
How many protected areas are there in Afghanistan?
Afghanistan has 15 protected areas, including one national park and six wildlife or waterfowl reserves. However, these areas are not officially recognized by the government, which limits their effectiveness in preserving biodiversity.
What is the current state of forest cover in Afghanistan?
Forest cover in Afghanistan is limited to the monsoon-influenced eastern part of the country. Recent analyses suggest that only 5% of the original forests may still exist. Open woodlands dominated by pistachio and juniper trees are close to extinction.
Why are wetlands important for biodiversity in Afghanistan?
Wetlands in Afghanistan provide crucial habitats for various plant and animal species. They play a vital role in supporting the overall biodiversity of the country. However, many wetlands are drying up, leading to the loss of vegetation, soil erosion, and other negative impacts.
What are the major threats to biodiversity in Afghanistan?
The decline in biodiversity in Afghanistan is primarily due to human activity. Habitat destruction, overgrazing, pollution, and the introduction of foreign species are some of the major threats to the country’s biodiversity.
How are water resources linked to biodiversity conservation in Afghanistan?
Water resources in Afghanistan are closely linked to biodiversity conservation. The country relies heavily on water for agriculture, which accounts for over half of its GDP. However, water shortages, poor management, and the loss of glaciers pose significant challenges to biodiversity conservation.
Does Afghanistan have a National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan?
Afghanistan has not yet prepared its National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP). However, efforts are underway to develop a comprehensive plan that will address the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity in the country.
What measures can be taken to protect biodiversity in Afghanistan?
Urgent action is needed to conserve and protect Afghanistan’s unique animal and plant species and their habitats. Efforts should focus on developing a comprehensive National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan, establishing and effectively managing protected areas, and promoting sustainable water resource management practices.
How can Afghanistan contribute to global conservation efforts?
By taking measures to protect and manage its biodiversity, Afghanistan can ensure the long-term survival of its unique animal and plant species. This will also contribute to global conservation efforts and the preservation of Earth’s biodiversity.
Source Links



























Post comments (2)