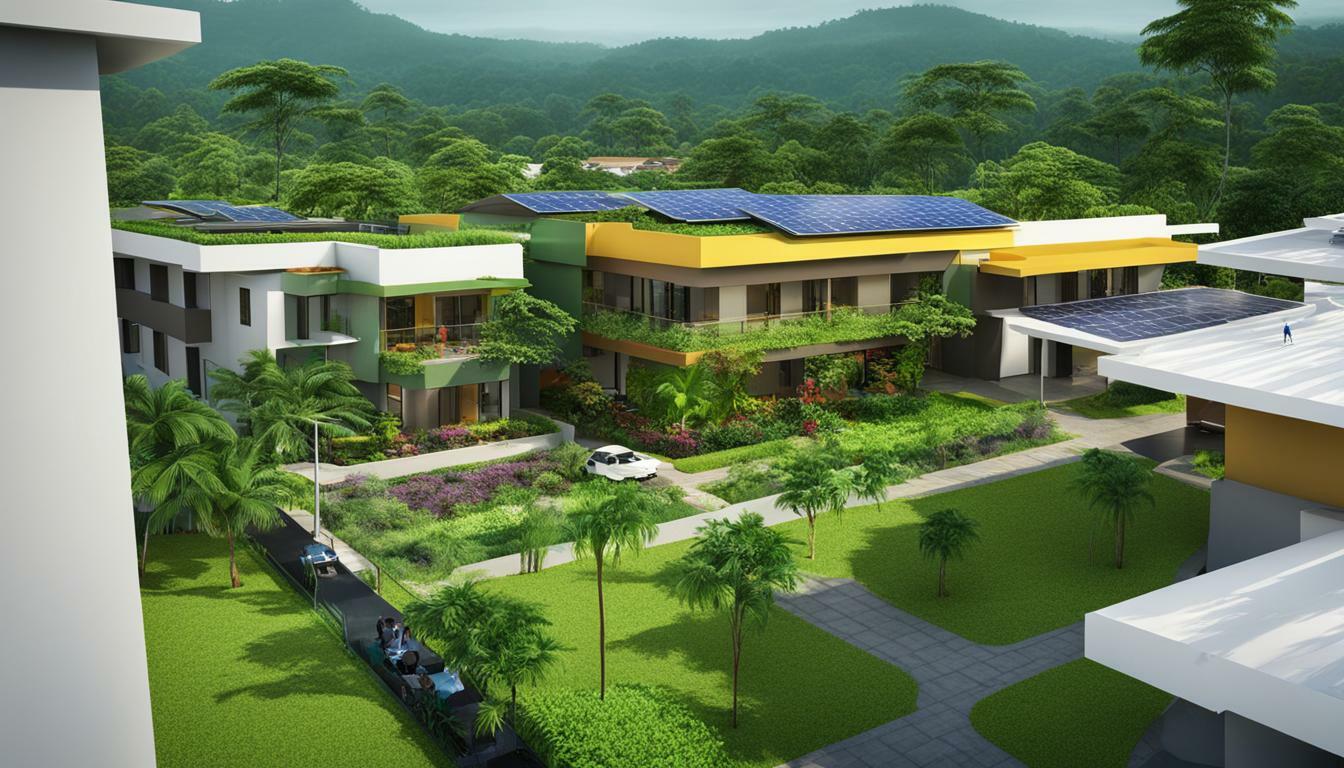
Malawi Top Green Buildings
Malawi is making waves in sustainable architecture with its top green buildings. These eco-friendly constructions are paving the way for a greener future while maintaining functionality and aesthetic appeal. By prioritising eco-friendly construction practices, these projects are not only minimising their environmental impact but also contributing to the preservation of Malawi’s natural resources and reducing carbon emissions.
Key Takeaways
- Sustainable architecture in Malawi is setting new standards for environmentally conscious construction.
- Eco-friendly buildings are designed to reduce environmental impact and preserve natural resources.
- Green building practices in Malawi contribute to the reduction of carbon emissions.
- Top green buildings in Malawi showcase the potential for sustainable infrastructure in the country.
- These eco-friendly constructions promote a greener, more sustainable future for Malawi.
DURABRIC: Transforming Sustainable Construction in Malawi
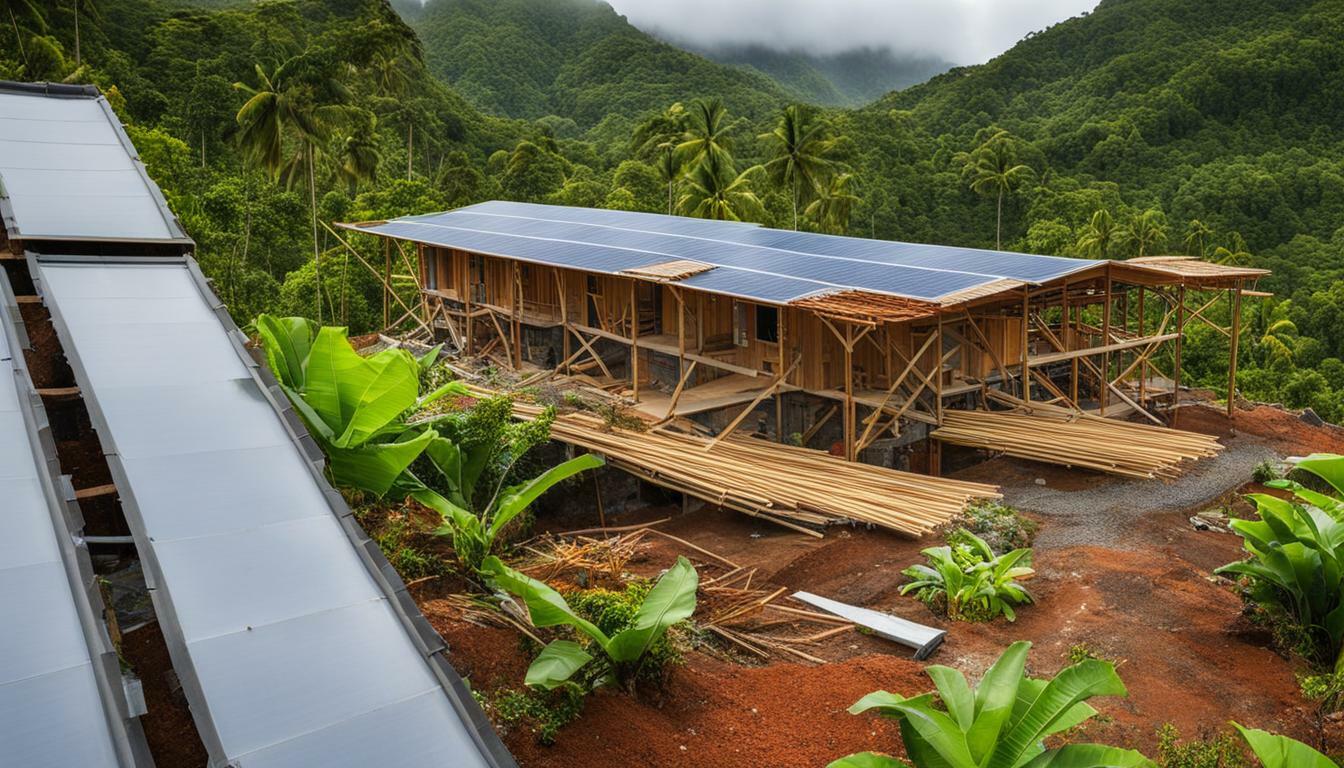
In the quest for environmentally friendly architecture in Malawi, the introduction of DURABRIC technology has been a game-changer. This innovative approach to sustainable construction is revolutionizing the way buildings are constructed, significantly reducing their environmental impact. DURABRIC blocks are made of local earth, sand, cement, and water, eliminating the need for firing and therefore reducing carbon emissions associated with traditional clay bricks. By utilizing this eco-friendly building material, green building projects in Malawi are promoting sustainable design practices and contributing to the preservation of natural resources.
The use of DURABRIC in green building projects is not only beneficial for the environment but also for the local communities. The production of DURABRIC blocks provides job opportunities and helps stimulate economic growth, particularly in rural areas where the resources for traditional brick production may be limited. Additionally, the affordability and accessibility of DURABRIC make it a practical choice for sustainable construction, ensuring that eco-friendly architecture is within reach for all communities in Malawi.
The Benefits of DURABRIC for Sustainable Design
DURABRIC offers several advantages for sustainable design in Malawi:
- Reduced carbon emissions: By eliminating the firing process, DURABRIC significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to traditional clay bricks.
- Preservation of natural resources: The use of DURABRIC helps save trees by minimizing the demand for wood fuel traditionally used for firing bricks.
- Job creation and economic growth: The production of DURABRIC blocks stimulates local economies and creates employment opportunities, particularly in rural areas.
- Affordability and accessibility: DURABRIC is an affordable and accessible building material, making sustainable construction options available to a wider range of communities in Malawi.
DURABRIC is a prime example of how innovative technologies and materials are transforming sustainable construction practices in Malawi. By harnessing the power of local resources and minimizing environmental impact, DURABRIC is paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future in the country.
| Advantages of DURABRIC for Sustainable Design | Traditional Clay Bricks | DURABRIC Blocks |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Emissions | High carbon emissions due to firing process | Significantly reduced carbon emissions as no firing is required |
| Natural Resource Preservation | Contributes to deforestation through wood fuel consumption | Helps save trees by eliminating the need for wood fuel |
| Job Creation | Limited employment opportunities in brick production | Stimulates local economies and creates job opportunities |
| Affordability | Expensive due to the cost of firing and transportation | Cost-effective and accessible for all communities |
Leading the Way in Green Building Certification: Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence
The Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence at KUHeS Lilongwe Campus have set a new benchmark in green building practices in Malawi. These innovative structures have become the first buildings in the country to receive EDGE certification, a green building certification offered by the International Finance Corporation (IFC). The certification recognizes their adherence to internationally recognized benchmarks for energy, material, and water savings.
Constructed by the Old Mutual Investment Group (OMIG), the Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence showcase the commitment to sustainable infrastructure and eco-construction in Malawi. By incorporating green building practices, these halls of residence are not only minimizing their environmental impact but also creating healthier and more comfortable living spaces for their residents.
The EDGE certification is a testament to the efforts made to integrate sustainability into the design and construction of these buildings. Through the use of energy-efficient lighting, insulation, and water-efficient fixtures, the halls of residence significantly reduce their energy and water consumption. The materials used in their construction are locally sourced, promoting the use of sustainable building materials and supporting the local economy.
Innovative Features of the Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence:
- Energy-efficient lighting systems
- High-performance insulation
- Water-efficient fixtures
- Locally sourced construction materials
These buildings serve as inspiring examples of how sustainable infrastructure can be integrated into Malawi’s built environment. The EDGE certification not only highlights the achievements of the Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence but also sets a precedent for future green building projects in the country, encouraging the adoption of eco-construction practices and the development of sustainable infrastructure.
Table: Comparison of Energy and Water Savings
| Building | Energy Savings (%) | Water Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Mbiri Hall of Residence | 35 | 45 |
| Tsogolo Hall of Residence | 40 | 50 |
| Average Building in Malawi | – | 25 |
The comparison table above demonstrates the significant energy and water savings achieved by the Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence compared to the average building in Malawi. The implementation of energy-efficient lighting systems and water-efficient fixtures has resulted in a 35-40% reduction in energy consumption and a 45-50% reduction in water consumption. These savings contribute to the overall sustainability of the buildings and reduce their environmental impact.
The EDGE certification of the Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence is a testament to the success of green building practices in Malawi. These buildings are leading the way in sustainable infrastructure and setting a new standard for eco-construction in the country. With their innovative features and commitment to energy and water savings, they serve as inspiring examples for future green building projects in Malawi.

LC3 Technology: A Game-Changer for Green Construction in Malawi
The launch of LC3 technology in Malawi is a significant milestone for the green construction movement in the country. LC3, which stands for Limestone Calcined Clay Cement, is a sustainable building material that offers numerous advantages over traditional cement. It is made by blending limestone and calcined clay, which not only reduces the carbon footprint of the cement production process but also utilizes locally available resources.
LC3 technology aims to make Malawi a leader in environmentally friendly cement production by reducing the environmental impact of the building material sector. This innovative approach addresses multiple sustainability challenges by minimizing carbon emissions, saving natural resources, and promoting local economic development. By leveraging the support and funding from the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ), the adoption and implementation of LC3 technology is set to transform the way buildings are constructed in Malawi.
The use of LC3 technology in green construction projects in Malawi will result in energy-efficient buildings that contribute to sustainable infrastructure development. LC3 cement has the potential to significantly decrease the embodied energy of building materials, making it a more environmentally friendly choice. Additionally, LC3-based concrete offers enhanced durability and thermal performance, leading to reduced energy consumption and operational costs over the lifespan of a building. By incorporating LC3 technology into their designs, architects and builders in Malawi can create sustainable, energy-efficient structures that contribute to a greener future.
The Benefits of LC3 Technology in Green Construction
By embracing LC3 technology in the construction industry, Malawi can reap numerous benefits in terms of sustainable building materials, energy-efficient buildings, and overall sustainable infrastructure development. Some key advantages of LC3 technology include:
- Reduced carbon emissions: The production of LC3 cement emits up to 40% less carbon dioxide compared to traditional cement production, supporting the country’s efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Local resource utilization: LC3 cement utilizes limestone and clay, which are readily available in Malawi, reducing the reliance on imported materials and supporting local economies.
- Enhanced durability: LC3-based concrete offers improved durability and resistance to chemical and physical degradation, resulting in longer-lasting buildings that require fewer repairs and maintenance.
- Improved thermal performance: LC3-based concrete has better thermal properties, reducing heat transfer through walls and floors and contributing to energy-efficient building designs.
- Cost-effective: LC3 technology offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional cement, making sustainable construction more accessible and affordable for developers and homeowners alike.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced carbon emissions | The production of LC3 cement emits up to 40% less carbon dioxide compared to traditional cement production, supporting the country’s efforts to mitigate climate change. |
| Local resource utilization | LC3 cement utilizes limestone and clay, which are readily available in Malawi, reducing the reliance on imported materials and supporting local economies. |
| Enhanced durability | LC3-based concrete offers improved durability and resistance to chemical and physical degradation, resulting in longer-lasting buildings that require fewer repairs and maintenance. |
| Improved thermal performance | LC3-based concrete has better thermal properties, reducing heat transfer through walls and floors and contributing to energy-efficient building designs. |
| Cost-effective | LC3 technology offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional cement, making sustainable construction more accessible and affordable for developers and homeowners alike. |

Environmental and Social Benefits of Green Buildings in Malawi
Green buildings in Malawi offer a range of environmental and social benefits. By reducing carbon emissions and conserving resources, these buildings have a positive impact on the environment, helping to mitigate climate change and preserve natural habitats. Additionally, green buildings create job opportunities and stimulate economic growth, particularly in rural communities. The use of sustainable construction materials and energy-efficient designs improves the quality and standard of living for residents, making these buildings safer and more comfortable.
The environmental impact of buildings in Malawi is a significant concern. Traditional construction methods often rely on materials that have a negative impact on the environment, such as clay bricks that require firing and contribute to deforestation. Green buildings, on the other hand, prioritize the use of locally sourced and eco-friendly materials. For example, the implementation of DURABRIC technology eliminates the need for firing bricks, reducing carbon emissions and preserving trees. By minimizing waste and optimizing resource management, green buildings in Malawi help to protect the natural environment and promote sustainable development.
Furthermore, green buildings have important social benefits for communities in Malawi. The construction of green buildings creates job opportunities, particularly in the manufacturing and installation of sustainable construction materials. By prioritizing the use of locally sourced materials, green buildings support local economies, contributing to economic growth and poverty reduction. Additionally, the energy-efficient designs of green buildings reduce energy costs for residents, making them more affordable and accessible. These buildings also prioritize safety and comfort, providing healthier and more livable spaces for people to work and live in. Overall, green buildings in Malawi promote social equity and improve the quality of life for individuals and communities.
“Green buildings in Malawi offer a sustainable solution to environmental and social challenges, creating a better future for all.”

| Benefits of Green Buildings in Malawi | Environmental | Social |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced carbon emissions | ✔ | |
| Conservation of resources | ✔ | |
| Job creation | ✔ | |
| Economic growth | ✔ | |
| Improved energy efficiency | ✔ | |
| Enhanced safety and comfort | ✔ |
Affordability and Accessibility of Green Buildings in Malawi
One of the key aims of green building projects in Malawi is to make sustainable infrastructure affordable and accessible to all communities. These buildings are designed to incorporate cost-effective sustainable design features and materials, ensuring that environmental solutions do not come at a high price. By utilizing locally sourced materials and innovative technologies, green buildings are able to minimize construction costs while still prioritizing sustainability.
Table:
| Key Factors | Affordability and Accessibility Solutions |
|---|---|
| Cost-Effective Design | Green buildings in Malawi prioritize cost-effective design strategies that optimize resource efficiency and minimize waste. This includes efficient floor plans, passive heating and cooling systems, and the use of renewable energy sources. |
| Locally Sourced Materials | By utilizing locally sourced materials, green buildings in Malawi reduce transportation costs, support local economies, and minimize the environmental impact associated with long-distance shipping. This also enhances the accessibility of sustainable construction solutions for communities. |
| Innovative Technologies | The integration of innovative technologies, such as DURABRIC blocks and LC3 cement, not only reduces construction costs but also ensures long-term affordability and accessibility of green buildings in Malawi. These technologies provide sustainable alternatives to traditional building materials, making them more widely available. |
Moreover, the affordability and accessibility of green buildings in Malawi are also supported by the commitment of stakeholders, including the government and private sector partners. Through the implementation of policies and regulations that promote sustainable construction practices, the government plays a crucial role in creating an enabling environment for affordable green buildings. Public-private partnerships, such as the collaboration between Old Mutual Investment Group (OMIG) and the International Finance Corporation (IFC), provide expertise, resources, and funding to drive the development of green buildings across the country.
Benefits of Affordable and Accessible Green Buildings
- Improved Quality of Life: Affordable and accessible green buildings enhance the living conditions of residents by providing energy-efficient, comfortable, and healthy spaces. This contributes to better overall well-being and a higher quality of life.
- Social Equity: By ensuring that sustainable infrastructure is within reach for all communities, affordable and accessible green buildings promote social equity and inclusivity. They help bridge the gap between urban and rural areas, providing equal opportunities for sustainable development.
- Long-Term Savings: Green buildings not only have lower upfront costs but also offer long-term savings through reduced energy and water consumption. The use of energy-efficient technologies and sustainable design features result in lower utility bills, making these buildings financially sustainable for occupants in the long run.
Overall, the affordability and accessibility of green buildings in Malawi are key factors in driving the widespread adoption of sustainable construction practices. By making sustainable infrastructure more attainable for all communities, these buildings contribute to a greener, more inclusive, and economically sustainable future for the country.

The Role of Government and Partnerships in Green Building Initiatives
Government support for green buildings in Malawi has played a crucial role in driving the adoption of sustainable construction practices. Through policies and regulations, the government has created an enabling environment that promotes the use of sustainable building materials and energy-efficient designs. This support not only helps to reduce the environmental impact of construction projects but also creates opportunities for economic growth and job creation.
One example of government support is the collaboration between the Old Mutual Investment Group (OMIG) and the International Finance Corporation (IFC) in the construction of the Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence. These buildings, which have received EDGE certification, are leading the way in green building practices in Malawi. This partnership showcases how public-private collaborations can drive sustainable infrastructure development and set new standards for eco-construction in the country.
“The government of Malawi plays a crucial role in supporting green building initiatives. Through policies and regulations that promote the use of sustainable building materials and energy-efficient designs, the government is creating an enabling environment for green construction.”
In addition to government support, public-private partnerships in green building initiatives have also been instrumental in advancing sustainable construction practices in Malawi. These partnerships bring together expertise, resources, and funding from both the public and private sectors to accelerate the adoption of green building practices. By leveraging the strengths of each stakeholder, these partnerships drive innovation, knowledge sharing, and long-term sustainability in the construction industry.
Overall, the role of government and partnerships in green building initiatives in Malawi is vital for creating a sustainable future. With continued support and investment, the impact of green buildings in the country will continue to grow, contributing to the preservation of natural resources, reduction of carbon emissions, and improvement of the quality of life for all Malawians.

Education and Training for Green Building Professionals in Malawi
Educating and training individuals in sustainable architecture and green building practices is essential for driving the development of green buildings in Malawi. By equipping professionals with the knowledge and skills needed to implement sustainable construction practices, we can ensure the continued growth and success of the green building movement in the country.
Training programs and on-site workshops are being conducted to educate local manufacturers and builders on sustainable design principles and construction techniques. These programs focus on topics such as energy-efficient building practices, the use of environmentally friendly materials, and the integration of renewable energy systems. By providing hands-on training and practical guidance, these initiatives empower professionals to make informed decisions and implement sustainable solutions in their projects.
In addition to on-site training, educational institutions are incorporating sustainable architecture and design principles into their curricula. By integrating these principles into the education system, future architects, engineers, and construction professionals will be equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to contribute to the development of sustainable infrastructure in Malawi. This will ensure a sustainable and environmentally conscious approach to construction in the years to come.
“Education and training are essential for building a workforce of green building professionals in Malawi.”
| Key Benefits of Education and Training for Green Building Professionals in Malawi |
|---|
| 1. Enhanced Knowledge and Skillset |
| 2. Improved Implementation of Sustainable Construction Practices |
| 3. Promotion of Innovation and Technological Advancements |
| 4. Increased Awareness and Adoption of Green Building Strategies |
| 5. Development of a Sustainable Workforce for Future Projects |
By investing in education and training for green building professionals, Malawi can create a skilled workforce that is capable of driving the sustainable development of its built environment. This will not only benefit the environment but also contribute to economic growth and social well-being, making Malawi a leader in sustainable architecture and construction.

The Future of Sustainable Architecture in Malawi: Green Building Trends
The future of sustainable architecture in Malawi is marked by ongoing innovation and a commitment to environmentally friendly practices. As the country continues to prioritize sustainable development, green building trends are emerging that will shape the landscape of construction in Malawi. These trends encompass various aspects, from design and materials to technology and community engagement. By embracing these trends, Malawi can further enhance the sustainability and resilience of its built environment.
A Shift Towards Net-Zero Energy Buildings
One of the key trends in green building in Malawi is the increasing focus on net-zero energy buildings. These are structures that generate as much renewable energy as they consume, resulting in a net annual energy consumption of zero. With advancements in solar power technology and energy-efficient building design, net-zero energy buildings are becoming more achievable and cost-effective. This trend not only reduces reliance on non-renewable energy sources but also contributes to long-term energy cost savings for building owners and occupants.
Integration of Smart Building Technologies
Another significant trend in sustainable architecture is the integration of smart building technologies. These technologies utilize sensors, automation, and data analytics to optimize building performance and enhance occupant comfort. In Malawi, the adoption of smart building technologies can lead to improved energy efficiency, water management, and indoor air quality. By leveraging real-time data and advanced control systems, smart buildings can respond dynamically to changing environmental conditions, reducing resource consumption and improving overall building operations.
Promotion of Circular Economy Principles
Malawi is also witnessing a growing shift towards the promotion of circular economy principles in green building practices. The circular economy aims to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency by reusing, recycling, and repurposing materials. In the context of construction, this involves incorporating sustainable and locally sourced materials, designing for disassembly and adaptability, and implementing waste management strategies. By embracing circular economy principles, the construction industry in Malawi can reduce its environmental footprint, conserve resources, and contribute to a more sustainable future.

Case Studies of Successful Green Building Projects in Malawi
Several successful green building projects in Malawi serve as inspiring examples of sustainable construction practices. These projects showcase the effective integration of sustainability principles in design, construction, and operation, setting a benchmark for future green building initiatives in the country.
Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence
The Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence at KUHeS Lilongwe Campus are leading the way in green building certification in Malawi. These buildings have received EDGE certification, a prestigious green building certification offered by the International Finance Corporation (IFC). Constructed by the Old Mutual Investment Group (OMIG), they adhere to internationally recognized benchmarks for energy, material, and water savings. The Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence represent a significant achievement in green building practices and contribute to the development of sustainable infrastructure in Malawi.
DURABRIC Technology
The implementation of DURABRIC technology has transformed sustainable construction in Malawi. Unlike traditional clay bricks that contribute to deforestation and require firing, DURABRIC blocks are made of local earth, sand, cement, and water without the need for firing. This innovative approach significantly reduces carbon emissions and saves trees. The use of DURABRIC in green building projects promotes environmentally friendly architecture and sustainable design practices, making it a game-changer in the construction industry.
LC3 Technology
The launch of LC3 technology in Malawi has brought significant advancements to the green construction movement. Supported by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ), LC3 technology aims to make Malawi a leader in environmentally friendly cement production. By boosting local and greener cement production, LC3 technology contributes to the development of sustainable building materials and energy-efficient buildings, furthering the overall sustainability of the country’s infrastructure.
These case studies of successful green building projects in Malawi demonstrate the tangible benefits of sustainable construction practices. With the Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence showcasing green building certification and the implementation of DURABRIC and LC3 technologies revolutionizing construction methods, Malawi is making significant strides in the development of sustainable architecture and building practices. These projects serve as models for future green building initiatives and highlight the country’s commitment to creating a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future.
| Case Study | Description |
|---|---|
| Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence | Leading the way in green building certification, these halls of residence have received EDGE certification and adhere to internationally recognized benchmarks for energy, material, and water savings. |
| DURABRIC Technology | This innovative technology eliminates the need for firing traditional clay bricks, significantly reducing carbon emissions and saving trees in the construction process. |
| LC3 Technology | LC3 technology aims to make Malawi a leader in environmentally friendly cement production, contributing to the development of sustainable building materials and energy-efficient buildings. |
Conclusion
The development of top green buildings in Malawi represents a significant step towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future. These buildings not only minimize their environmental impact but also contribute to social and economic development in the country.
Through innovative technologies, partnerships, and the commitment of stakeholders, Malawi is on the path to becoming a leader in sustainable architecture and green building practices. With continued support and investment, the impact of green buildings in Malawi will continue to grow, making a positive difference for current and future generations.
Malawi’s top green buildings showcase the successful integration of sustainable design, construction, and operation. They set a benchmark for future green building projects in the country, promoting eco-friendly construction practices and sustainable architecture. With a growing awareness of the environmental and social benefits of sustainable construction, Malawi is embracing green building practices and becoming a role model for other nations.
As the journey towards sustainability continues, Malawi will continue to explore innovative technologies, implement green building practices, and prioritize the preservation of natural resources. The commitment of the government, public-private partnerships, and the education and training of green building professionals will further enhance Malawi’s position as a leader in sustainable architecture and eco-friendly construction.
FAQ
What are the Malawi Top Green Buildings?
The Malawi Top Green Buildings are sustainable constructions designed to minimize their environmental impact while providing functional and aesthetically pleasing spaces. They incorporate green building practices to reduce carbon emissions and preserve natural resources.
What is DURABRIC and how is it transforming sustainable construction in Malawi?
DURABRIC is a revolutionary technology that is transforming sustainable construction in Malawi. It is a building block made of local earth, sand, cement, and water, which eliminates the need for firing clay bricks and reduces carbon emissions. DURABRIC promotes environmentally friendly architecture and sustainable design practices in green building projects.
Which buildings have received EDGE certification in Malawi?
The Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence at KUHeS Lilongwe Campus are the first buildings in Malawi to receive EDGE certification. These halls of residence adhere to internationally recognized benchmarks for energy, material, and water savings, showcasing the commitment to green building practices and eco-construction in Malawi.
How does LC3 technology contribute to green construction in Malawi?
LC3 technology aims to boost local and greener production of cement in Malawi. It reduces the environmental impact of the building material sector and helps develop sustainable building materials and energy-efficient buildings. With the support of the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ), LC3 technology aims to make Malawi a leader in environmentally friendly cement production.
What are the environmental and social benefits of green buildings in Malawi?
Green buildings in Malawi help mitigate climate change by reducing carbon emissions and conserve natural resources. They create job opportunities and stimulate economic growth, particularly in rural communities. The use of sustainable construction materials and energy-efficient designs improves the quality of living for residents, making buildings safer and more comfortable.
Are green buildings in Malawi affordable and accessible?
Yes, green buildings in Malawi are designed to be affordable and accessible for all. They incorporate cost-effective sustainable design features and materials, making them environmentally friendly solutions without compromising affordability. The use of locally sourced materials and innovative technologies contributes to their affordability and accessibility.
What role does the government play in supporting green building initiatives in Malawi?
The government of Malawi plays a crucial role in supporting green building initiatives. Through policies and regulations that promote the use of sustainable building materials and energy-efficient designs, the government creates an enabling environment for green construction. Public-private partnerships drive the development of green buildings by bringing together expertise, resources, and funding.
How does education and training contribute to sustainable construction in Malawi?
Education and training are essential for building a workforce of green building professionals in Malawi. Green building projects provide on-site training and skill development programs for local manufacturers and builders to implement sustainable construction practices. Educational institutions incorporate sustainable architecture and design principles into their curricula, preparing the next generation of professionals.
What does the future hold for green buildings in Malawi?
The future of green buildings in Malawi looks promising, with a growing awareness of their environmental and social benefits. Innovative technologies like DURABRIC and LC3 will drive the development of sustainable architecture. Ongoing research and development will further enhance the sustainability of buildings, making Malawi a leader in the field.
Can you provide examples of successful green building projects in Malawi?
The Mbiri and Tsogolo Halls of Residence and the implementation of DURABRIC technology are successful examples of green building projects in Malawi. These projects showcase the integration of sustainability principles in design, construction, and operation, setting a benchmark for future green building initiatives in the country.
Source Links
- https://devalt.org/newsletter/apr22/lead.htm
- https://www.climateimpact.com/global-projects/14trees-sustainable-building-malawi/
- https://www.oldmutual.co.mw/about-us/news/old-mutual-investment-group-pioneers-green-building-approach-as-its-student-hostel-becomes-the-first-building-in-malawi-to-receive-ifcs-edge-certification/