Moldova Top Green Buildings
Moldova has been focusing on green growth and sustainable development as part of its efforts to promote a more eco-friendly and sustainable lifestyle. The country has implemented various initiatives and measures to encourage the construction of green buildings. These buildings are designed with innovative and eco-friendly features, making them energy efficient and environmentally sustainable. By adopting green building practices, Moldova aims to reduce its environmental footprint and contribute to a greener future.
Key Takeaways
- Moldova is committed to sustainable development and green growth.
- Green buildings in Moldova are designed with innovative and eco-friendly features.
- Moldova aims to reduce its environmental footprint through green building practices.
- Green buildings offer a range of benefits, from energy efficiency to improved indoor air quality.
- Moldova is making progress in advancing green building certification in the country.
The Importance of Green Transformation
Green transformation is a key priority for Moldova as it strives to achieve sustainable development and create a greener future. This transformation involves adopting a circular economy approach and decoupling economic growth from environmental degradation. It aims to reduce pollution, minimize the country’s environmental footprint, and promote green economic development.
Implementing green transformation measures is crucial for Moldova to align with international agreements and meet its policy priorities for sustainable development. By embracing green practices, the country can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, conserve natural resources, and improve the quality of life for its citizens.
Green economic development plays a significant role in Moldova’s green transformation journey. By promoting sustainable practices in sectors such as energy, transportation, and construction, the country can create jobs, stimulate innovation, and build a resilient economy that preserves and enhances the environment.
Green transformation is not just an environmental agenda; it is also an economic opportunity. By embracing sustainable practices, Moldova can unlock new markets, attract investment, and enhance its competitiveness on the global stage.
The Circular Economy Approach
The circular economy is a key component of Moldova’s green transformation strategy. It aims to minimize waste, promote resource efficiency, and foster sustainable consumption and production patterns. By shifting from a linear “take-make-dispose” model to a circular one, Moldova can reduce its reliance on finite resources, decrease pollution, and create a more sustainable and resilient economy.
In a circular economy, products and materials are designed to be reused, repaired, or recycled. Waste is seen as a valuable resource, and mechanisms are put in place to maximize resource recovery and minimize environmental impact. This approach not only reduces the strain on natural resources but also promotes innovation, job creation, and economic growth.
| Benefits of Green Transformation | Examples |
|---|---|
| Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions | Integration of renewable energy sources such as solar panels |
| Resource conservation | Use of sustainable materials and energy-efficient systems |
| Economic growth and job creation | Promotion of green economic sectors |
| Improved quality of life | Enhancing indoor air quality and creating healthier living spaces |
By prioritizing green transformation, Moldova can reap a multitude of benefits and create a sustainable future for generations to come.
Moldova’s Commitment to Green Growth
Moldova is firmly committed to achieving green growth and has set policy priorities to promote sustainable development. The country recognizes the importance of integrating environmental considerations into its development agenda to mitigate climate change and preserve natural resources. Moldova’s commitment to green growth is guided by its membership in international agreements, such as the Association Agreement with the European Union and the United Nations’ Agenda 2030 for Sustainable Development.
In accordance with the Association Agreement, Moldova has made significant progress in aligning its policies and practices with the environmental objectives of the European Union. The agreement aims to promote sustainable development and enhance cooperation in areas such as climate change mitigation, biodiversity conservation, and the transition to a circular economy.
Under the Agenda 2030, Moldova has identified specific policy priorities that focus on sustainable development and environmental protection. These priorities include promoting clean and renewable energy, implementing sustainable agriculture practices, improving waste management systems, and ensuring access to clean water and sanitation. By prioritizing these areas, Moldova aims to create a more sustainable and resilient future for its citizens.
Policy Priorities for Green Growth
In its pursuit of green growth, Moldova has identified several key policy priorities:
- Transitioning to a low-carbon economy by promoting renewable energy sources and energy efficiency measures.
- Protecting and restoring natural ecosystems to enhance biodiversity and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
- Developing sustainable transportation systems to reduce emissions and improve air quality.
- Promoting sustainable agriculture practices to ensure food security and protect the environment.
- Strengthening waste management systems to reduce pollution and promote recycling and reuse.
By addressing these policy priorities, Moldova aims to achieve a greener and more sustainable future in line with its commitments under the Association Agreement and Agenda 2030.
| Policy Priority | Description |
|---|---|
| Transition to a low-carbon economy | Promoting renewable energy sources and energy efficiency measures to reduce carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. |
| Protection and restoration of natural ecosystems | Preserving biodiversity, improving soil quality, and restoring degraded ecosystems to enhance resilience to climate change. |
| Sustainable transportation systems | Investing in public transportation, promoting cycling and walking infrastructure, and encouraging the use of electric vehicles to reduce emissions and improve air quality. |
| Sustainable agriculture | Supporting farmers in implementing sustainable practices, such as organic farming and agroforestry, to improve food security and protect natural resources. |
| Waste management | Developing efficient waste management systems, including recycling and composting, to reduce pollution and promote a circular economy. |
Moldova’s commitment to green growth and sustainable development is an important step towards creating a more environmentally friendly and resilient future. By aligning its policies and practices with international agreements and prioritizing key areas for action, Moldova is laying the foundation for a greener and more sustainable economy.
Moldova’s Economic Landscape
Moldova, a lower-middle-income country in Eastern Europe, has a diverse economic landscape that has experienced consistent growth since the late 1990s. However, it has faced contractions during the global financial crisis and the recent COVID-19 pandemic. Moldova’s economy is primarily service-oriented, with a significant agricultural sector contributing to its GDP. Personal remittances from Moldovans working abroad have also played a vital role in supporting many households in the country. Furthermore, Moldova has established strong trade partnerships with Romania, other European Union member states, and Russia.
| Economic Sector | Contribution to Moldova’s GDP |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | 28% |
| Industry | 14% |
| Services | 58% |
As shown in the table above, agriculture plays a significant role in Moldova’s economy, contributing 28% to its GDP. The industry sector contributes 14%, while services make up the largest portion at 58%. This economic structure reflects Moldova’s focus on developing a diversified and service-oriented economy.
Moldova’s reliance on remittances from its citizens working abroad is another essential aspect of its economic landscape. Personal remittances have provided a stable source of income for many households, contributing to poverty reduction and overall economic stability in the country.
“Moldova has made significant progress in developing a diverse economic landscape, with a strong focus on its service sector and agricultural activities. Remittances from Moldovans working abroad have been crucial in supporting the economy and improving the living standards of many families.” – Economic Analyst
In terms of international trade, Moldova has established strong partnerships with neighboring countries and other European Union member states. Romania is one of Moldova’s key trade partners, with which it shares close economic and cultural ties. Additionally, trade with Russia provides important export opportunities for Moldovan goods. These trade partnerships play a vital role in driving economic growth and generating income for the country.

Moldova’s Low-Emission National Development Program
Moldova has implemented a comprehensive low-emission national development program to address the pressing issue of greenhouse gas emissions. This program aims to reduce emissions by 70% to 88% compared to 1990 levels by 2030. Moldova recognizes the need for significant action in key sectors such as energy and transport to achieve this ambitious target.
The energy sector is one of the major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions in Moldova. The national development program focuses on implementing energy-efficient measures and promoting the use of renewable energy sources. By transitioning to cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions, Moldova can significantly reduce its carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
The transport sector is another crucial focus area for Moldova’s low-emission development program. It aims to improve the efficiency of transportation systems, encourage the use of sustainable modes of transport, and reduce emissions from vehicles. By implementing measures such as promoting public transport, investing in infrastructure for cycling and walking, and encouraging the adoption of electric vehicles, Moldova can make significant progress in reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the transport sector.

Moldova’s low-emission national development program plays a crucial role in the country’s efforts to achieve a more sustainable future. By addressing emissions from the energy and transport sectors, Moldova is taking significant steps towards mitigating climate change and creating a greener environment for its citizens.
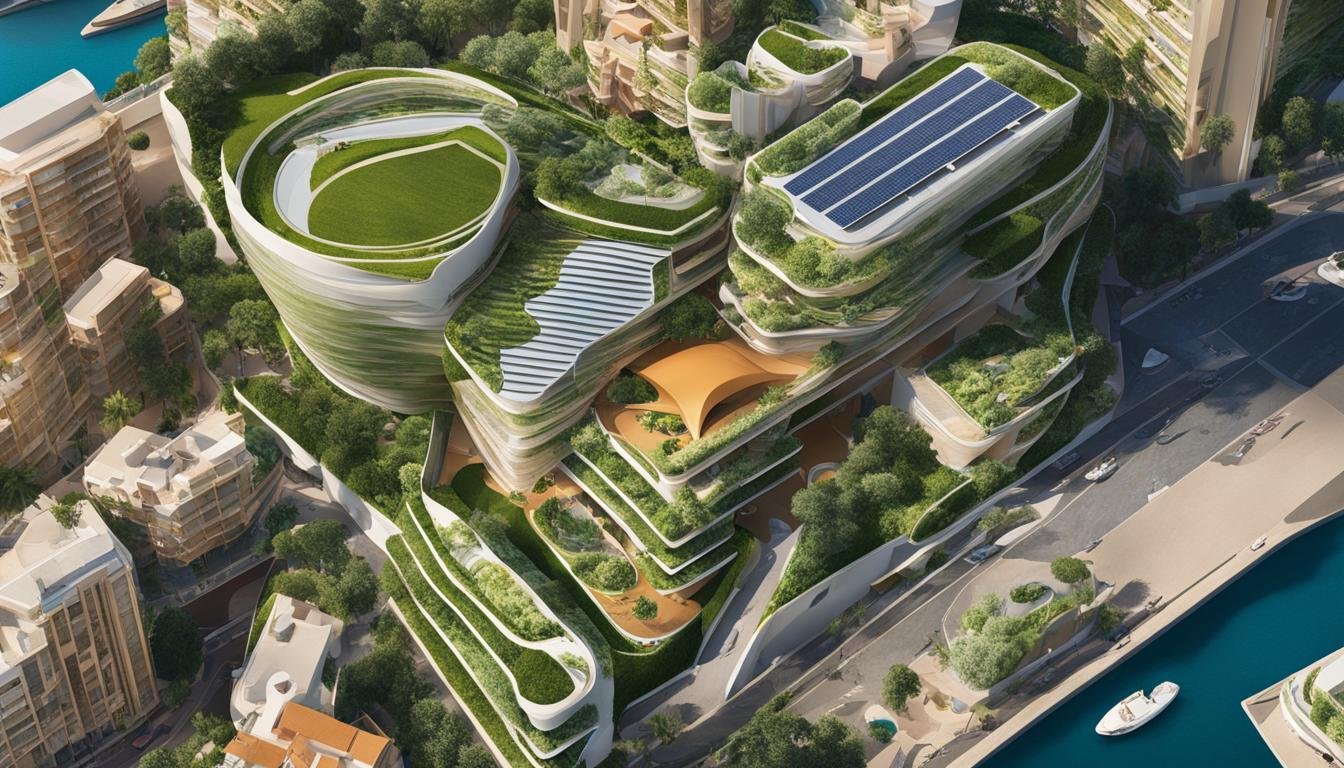
The Benefits of Green Buildings
Green buildings bring a host of advantages to both the environment and the people who occupy them. These buildings are designed with a focus on eco-friendly design, sustainable materials, and energy conservation techniques. By incorporating these elements into the construction process, green buildings contribute to a more sustainable future and create healthier living and working spaces.
One of the key advantages of green buildings is their emphasis on eco-friendly design. This includes features such as natural lighting, efficient insulation, and renewable energy sources. By maximizing natural light, green buildings reduce the need for artificial lighting, leading to energy savings and a more pleasant indoor environment. Efficient insulation helps regulate temperature, reducing the demand for heating and cooling systems and minimizing energy consumption. The integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, further reduces the carbon footprint of green buildings.
Sustainable materials play a vital role in the construction of green buildings. These materials are sourced and manufactured in an environmentally responsible manner, minimizing the depletion of natural resources and reducing waste. Additionally, sustainable materials often have improved durability and require less maintenance, resulting in long-term cost savings. By using sustainable materials, green buildings contribute to the preservation of the environment and promote a more responsible approach to construction.
Energy conservation techniques are another important aspect of green buildings. These techniques focus on minimizing energy consumption throughout the building’s lifecycle. Examples include the use of energy-efficient appliances, smart lighting systems, and water-saving fixtures. By implementing these techniques, green buildings help reduce the strain on natural resources and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, energy conservation measures can result in significant cost savings for building owners and occupants.
In recognition of their sustainable design and environmental benefits, green buildings can also obtain green building certification. Certification programs, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), evaluate and verify the sustainability of a building. By achieving green building certification, buildings demonstrate their commitment to environmentally responsible practices and provide assurance to occupants and stakeholders.

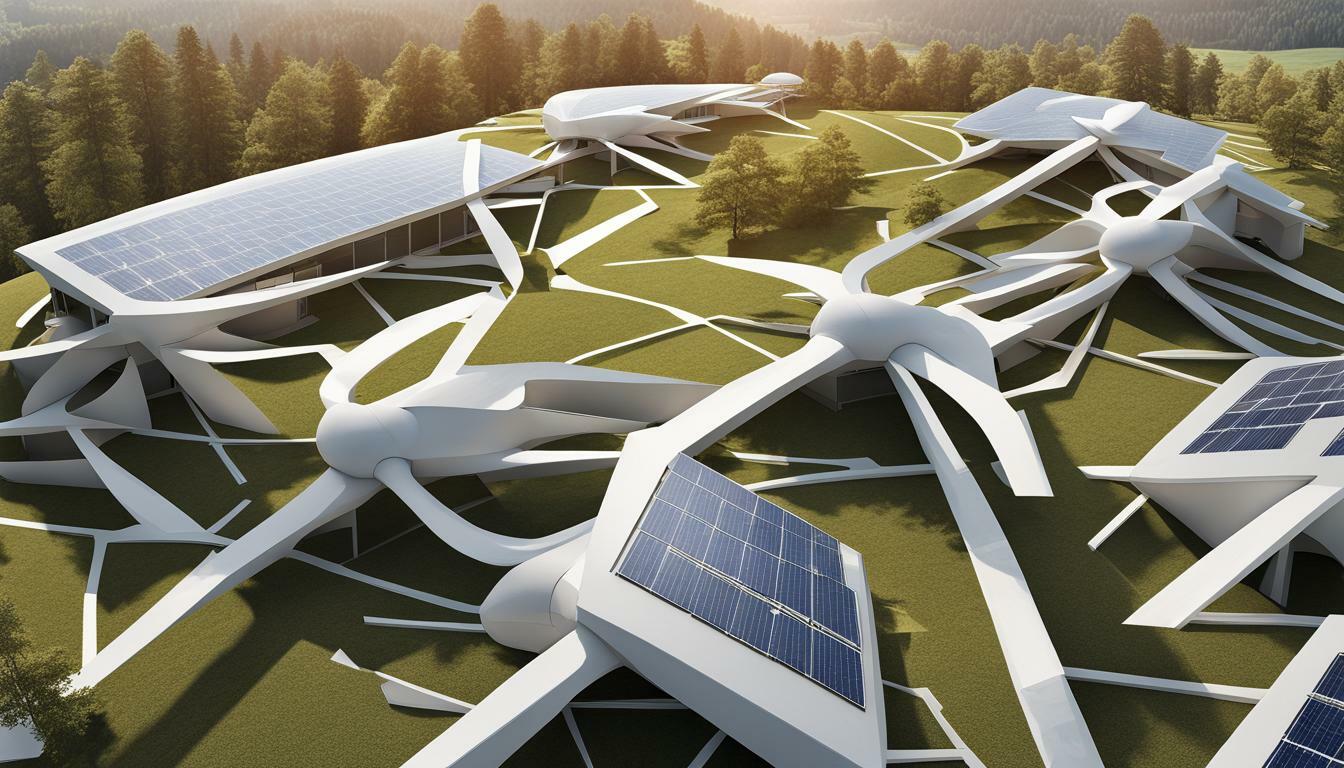
Green Building Trends in Moldova
In recent years, Moldova has witnessed a significant shift towards green building practices and innovation. The country’s commitment to sustainable development has led to the emergence of eco-friendly buildings that incorporate the latest trends in green design and construction. These trends reflect Moldova’s determination to create a more sustainable and environmentally conscious built environment.
One of the key trends in green building in Moldova is the integration of renewable energy sources. Solar panels and geothermal systems are being increasingly incorporated into building designs, allowing for the generation of clean and sustainable energy. This integration not only reduces reliance on traditional energy sources but also contributes to a significant reduction in carbon emissions.
Another emerging trend in Moldova is biophilic design. This design approach incorporates natural elements, such as plants, water features, and natural lighting, into the built environment. By bringing nature indoors, biophilic design creates a healthier and more visually appealing space for occupants. Studies have shown that biophilic design improves productivity, enhances well-being, and reduces stress levels.
“Green building trends in Moldova are aligned with global sustainability goals and reflect the country’s commitment to creating a greener and more livable future,” says Dr. Elena Gheorghiu, an expert in sustainable architecture.
Overall, the green building trends in Moldova are paving the way for a more sustainable and environmentally conscious construction industry. The integration of renewable energy sources and the adoption of biophilic design principles not only contribute to reduced environmental impact but also create healthier and more comfortable spaces for individuals and communities.

Advancing Green Building Certification in Moldova
Moldova is making significant progress in advancing green building certification in the country. Leading certification programs such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), and the WELL Building Standard are being implemented in Moldova. These certification programs assess the environmental performance and sustainability of buildings, considering factors such as energy efficiency, water conservation, indoor air quality, and occupant health and well-being.
LEED is one of the most widely recognized green building certification programs globally. It provides a framework for building owners and operators to design, construct, operate, and maintain their buildings in an environmentally responsible and resource-efficient manner. BREEAM, on the other hand, focuses on sustainable building design, construction, and operation. It evaluates various aspects of a building, including energy and water use, materials selection, and site sustainability. The WELL Building Standard emphasizes the health and well-being of building occupants by focusing on aspects such as air quality, water quality, lighting, and comfort.
| Certification Program | Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) | Energy efficiency, water conservation, indoor air quality, sustainable materials |
| BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) | Sustainable building design, construction, and operation |
| WELL Building Standard | Occupant health and well-being, air and water quality, lighting, comfort |
By adopting these green building certification programs, Moldova is ensuring that its buildings meet stringent sustainability standards. This not only helps reduce the environmental impact of buildings but also creates healthier and more comfortable spaces for occupants. Green building certification also provides a competitive advantage, as certified buildings are increasingly preferred by tenants and investors who prioritize sustainability.

Moldova’s focus on advancing green building certification highlights its commitment to sustainable development and the transition towards a more environmentally friendly built environment. By encouraging the adoption of green building practices and certification, Moldova is contributing to global efforts to mitigate climate change and create a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Moldova has emerged as a leader in green building practices in Eastern Europe, focusing on sustainable architecture, eco-friendly construction, and green building practices. The country’s commitment to green growth and sustainable development has resulted in innovative and eco-friendly buildings that contribute to a more sustainable future.
Green buildings in Moldova prioritize energy efficiency and occupant well-being, offering numerous benefits such as improved energy conservation and enhanced comfort. By continuing to prioritize green building practices and certification, Moldova is paving the way for a greener and more sustainable built environment.
With an emphasis on sustainable architecture, eco-friendly construction, and green building practices, Moldova has set an example for other countries in the region. By adopting these practices and promoting sustainable development, Moldova is creating a greener future for its citizens and contributing to global efforts in fighting climate change.
FAQ
What are green buildings?
Green buildings are constructed with innovative and eco-friendly features that make them energy efficient and environmentally sustainable. They are designed with elements such as energy-efficient systems, sustainable materials, and energy-conservation techniques. Green building certification programs ensure that buildings meet specific sustainability standards.
What are the benefits of green buildings?
Green buildings offer numerous benefits. They help reduce energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions, leading to a smaller environmental footprint. Additionally, green buildings improve indoor air quality, create healthier and more comfortable living and working spaces, and contribute to overall occupant well-being.
How does Moldova promote green building practices?
Moldova has implemented various initiatives and measures to encourage the construction of green buildings. The country focuses on sustainable architecture and eco-friendly construction practices, adopting energy-efficient design and green building certification programs such as LEED, BREEAM, and the WELL Building Standard.
What is green transformation?
Green transformation refers to the implementation of green and circular economy principles to reduce pollution and decouple economic growth from environmental degradation. It involves promoting green economic development and adopting measures to minimize the environmental impact of economic activities.
How does Moldova prioritize green growth?
Moldova has set policy priorities to promote green growth and achieve sustainable development. The country’s green growth indicators help track progress towards the goals outlined in the Association Agreement and Agenda 2030. Moldova compares its green transformation progress with other countries and develops supplementary national indicators to monitor its performance in green economic development.
What is Moldova’s economic landscape?
Moldova is a lower-middle-income country with a diverse economic landscape. It has a service-oriented economy, with a significant agricultural sector. Personal remittances from Moldovans working abroad are an important source of income. The country’s main trade partners include Romania, other European Union member states, and Russia.
What is Moldova’s low-emission national development program?
Moldova has developed a low-emission national development program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The program aims to achieve a reduction of 70% to 88% compared to 1990 levels by 2030. It focuses on key sectors such as energy, transport, buildings, industry, agriculture, waste, and forestry, proposing specific measures to reduce emissions in each sector.
What are the green building trends in Moldova?
Moldova is witnessing a growing trend towards green building practices and innovation. The integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and geothermal systems, is becoming more common. Biophilic design, which incorporates natural elements into the built environment, is also gaining popularity in sustainable construction practices.
How is green building certification advancing in Moldova?
Moldova is making significant progress in advancing green building certification. Certification programs such as LEED, BREEAM, and the WELL Building Standard are being implemented. These programs assess the environmental performance and sustainability of buildings, considering factors such as energy efficiency, water conservation, indoor air quality, and occupant health and well-being.
Source Links
- https://www.greenpolicyplatform.org/case-studies/towards-green-transformation-moldova
- https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/sites/986fb125-en/index.html?itemId=/content/component/986fb125-en
- https://eu4climate.eu/2021/06/17/moldova-sets-sectoral-targets-for-reducing-greenhouse-gas-emissions-with-the-support-of-the-european-union/