Namibia Biodiversity and the Built Environment
Did you know that Namibia is home to one of the highest proportions of protected land in the world? With over 40% of its territory designated as protected areas, Namibia is a global leader in conservation efforts. This remarkable commitment to preserving its biodiversity showcases the country’s dedication to sustainable development and environmental impact reduction. Let’s delve into the intricate relationship between Namibia’s biodiversity and the built environment, exploring the challenges, strategies, and future prospects of this unique ecosystem.
Key Takeaways:
- Namibia boasts one of the highest proportions of protected land in the world, with over 40% of its territory designated as protected areas.
- The preservation of Namibia’s biodiversity is crucial for achieving sustainable development and reducing environmental impact.
- Challenges such as habitat loss, poaching, overgrazing, and climate change threaten the biodiversity of Namibia.
- Conservation strategies, community involvement, and sustainable building practices are essential to safeguard Namibia’s unique animal and plant species.
- Namibia’s commitment to conservation is evident in the establishment of protected areas, community-based initiatives, and the development of a National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan.
Namibia’s Unique Animal Species
Namibia is home to a diverse array of unique animal species that contribute to the extraordinary biodiversity of the region. From the world’s largest cheetah population to the largest free-roaming population of black rhinos in Africa, Namibia’s wildlife is both fascinating and vital to the ecosystem.
One of the most iconic species found in Namibia is the cheetah. It is estimated that Namibia is home to over a third of the world’s cheetah population, making it the ideal destination for cheetah enthusiasts and wildlife lovers. Cheetah conservation efforts in Namibia are focused on protecting their natural habitats and mitigating human-wildlife conflicts.
Another remarkable species found in Namibia is the black rhino. With the largest free-roaming black rhino population in Africa, Namibia plays a vital role in their conservation. Efforts to protect these magnificent creatures include anti-poaching initiatives, habitat conservation, and community involvement in sustainable wildlife management.
Namibia is also known for its desert-adapted elephants that have developed unique physical and behavioral characteristics to survive in the arid landscapes. These resilient elephants have captured the hearts of many conservationists and wildlife photographers, further enhancing the country’s reputation as a wildlife hotspot.
Additionally, Namibia is home to various antelope species, such as the gemsbok, springbok, and kudu. These antelope species have adapted to Namibia’s diverse environments, including the desert regions, and thrive in harmony with the surrounding ecosystem.
“Namibia’s wildlife is a testament to the incredible diversity of the country’s ecosystems. From the graceful cheetahs to the majestic black rhinos and the fascinating desert-adapted elephants, exploring Namibia’s unique animal species offers a truly unforgettable experience for nature enthusiasts.”
Visiting Namibia’s wildlife parks and reserves allows tourists to witness these incredible species in their natural habitats. Moreover, experiencing the wonders of Namibian wildlife encourages visitors to contribute to conservation efforts and raises awareness about the importance of preserving biodiversity.
Next, we will delve into the various threats that Namibia’s biodiversity faces, highlighting the challenges in maintaining the delicate balance between human activities and the conservation of these remarkable animal species.
Threats to Namibia’s Biodiversity
Namibia’s biodiversity is under threat from various factors that endanger the delicate balance of its ecosystems. These threats include habitat loss, poaching, overgrazing, and climate change, which collectively pose significant challenges to preserving Namibia’s rich natural heritage.
Habitat Loss in Namibia
Habitat loss in Namibia is primarily driven by human activities such as agriculture and urbanization. As the country develops, natural habitats are being converted into farmland and infrastructure, leading to the displacement and fragmentation of vital ecosystems. This loss of habitat disrupts the interconnectedness of plant and animal species, contributing to a decline in biodiversity.
Poaching in Namibia
Poaching, particularly targeting iconic species like rhinos and elephants, remains a grave concern in Namibia. The illegal wildlife trade operates both locally and internationally, posing a threat to the survival of these vulnerable populations. The loss of these keystone species has far-reaching consequences for the ecosystems they inhabit, disrupting ecological processes and endangering the biodiversity of the region.
Overgrazing in Namibia
Overgrazing by both livestock and game species is another significant threat to Namibia’s biodiversity. Unsustainable grazing practices degrade habitats, leading to the loss of vegetation and the subsequent decline in plant and animal populations. The over-utilization of available resources leaves little time for natural recovery, further exacerbating the issue.

Climate Change in Namibia
Climate change poses a growing threat to Namibia’s biodiversity. Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, affecting the distribution and abundance of plant and animal species. The resulting shifts in habitats and ecological relationships jeopardize the long-term survival of Namibia’s unique flora and fauna.
Addressing these threats requires a multi-faceted approach that combines conservation efforts with sustainable development practices. The preservation of Namibia’s biodiversity depends on the collective commitment of governments, communities, and individuals towards protecting and restoring the natural environment.
Conservation Strategies
To safeguard Namibia’s diverse wildlife and protected areas, effective conservation strategies are necessary. These strategies aim to protect wildlife, promote community involvement, and adapt to the challenges posed by climate change. Collaboration between governments, NGOs, local communities, and international stakeholders is key to the success of these efforts.
Enforcement of Wildlife Protection Laws
Effective enforcement of wildlife protection laws is vital to combat poaching and illegal wildlife trade. Strict penalties and increased surveillance can act as deterrents and help preserve Namibia’s unique and endangered species.
Establishment and Expansion of Protected Areas
Creating and expanding protected areas is crucial for conserving Namibia’s biodiversity. These areas provide sanctuaries for wildlife, enabling them to thrive and ensuring their long-term survival. Additionally, protected areas offer opportunities for ecotourism, generating revenue for conservation efforts.
Promotion of Community-Based Conservation Initiatives
Engaging local communities in conservation initiatives is essential for sustainable wildlife protection. In Namibia, community-based conservancies have been successful in fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility among local residents. The partnership between communities and conservation organizations promotes sustainable land management practices and benefits both wildlife and people.
Implementation of Climate Change Adaptation Strategies
Climate change poses significant challenges to Namibia’s biodiversity. By implementing climate change adaptation strategies, such as habitat restoration and promoting resilient ecosystems, the country can mitigate the impacts of climate change on wildlife and their habitats.
Effective conservation strategies in Namibia involve enforcing wildlife protection laws, establishing and expanding protected areas, promoting community-based conservation initiatives, and implementing climate change adaptation strategies.
By prioritizing these conservation strategies, Namibia can preserve its wildlife, protect its unique ecosystems, and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.

Conservation Efforts in Namibia
Namibia is dedicated to preserving its rich biodiversity through a range of conservation efforts. The country recognizes the importance of protecting its natural resources and ensuring the sustainable management of its ecosystems. This section highlights some of the key initiatives undertaken by Namibia in its conservation journey.
Protected Areas in Namibia
Namibia boasts an impressive network of protected areas, including national parks, game reserves, and conservancies. These areas play a vital role in safeguarding the country’s diverse flora and fauna. They provide habitats for a wide range of species and enable the implementation of effective conservation strategies. Namibia’s protected areas offer opportunities for wildlife observation, research, and ecotourism, contributing to both biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
Community Involvement in Conservation
Community-led conservation initiatives are a fundamental aspect of Namibia’s conservation efforts. Recognizing the importance of local knowledge and participation, the country actively engages communities in wildlife conservation and sustainable land management practices. By involving local communities, Namibia promotes a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the preservation of its natural heritage. This collaborative approach empowers communities to actively contribute to the protection and sustainable use of natural resources.
Environmental Protection in Namibia
Namibia places great emphasis on environmental protection and enforces strict regulations to mitigate the impact of human activities on its ecosystems. The government works tirelessly to ensure that industries adhere to sustainable practices, minimizing pollution and promoting responsible resource management. Through environmental impact assessments and robust legislation, Namibia strives to balance economic development with environmental sustainability.
Namibia’s National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan
Namibia’s commitment to conservation is further reinforced by its National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan. This comprehensive plan outlines the country’s vision and strategies for biodiversity conservation and sustainable development. It identifies priority areas, sets conservation targets, and establishes frameworks for monitoring and evaluation. The plan involves various stakeholders, including government agencies, NGOs, and local communities, to collectively work towards achieving conservation goals.

The image above showcases the stunning landscapes of Namibia’s protected areas, highlighting the country’s dedication to preserving its natural heritage.
Impact of Landscape Fragmentation on Namibia’s Biodiversity
Landscape fragmentation caused by game fences and roads has a significant impact on Namibia’s wildlife, restricting their movements and increasing their vulnerability to mortality. The erection of game fences disrupts habitats and limits the gene pool and population size of wildlife. Roads act as barriers, disrupting wildlife movements and leading to habitat fragmentation.
Namibia’s conservation efforts should prioritize permeable fences and the construction of structures like tunnels and bridges to ensure wildlife connectivity. By allowing animals to move freely between fragmented habitats, these measures promote genetic exchange, enhance species survival, and contribute to the overall health and diversity of Namibia’s wildlife population.
Conservation Challenges in Namibia
The impacts of landscape fragmentation pose several conservation challenges in Namibia. Firstly, restricted movement can disrupt natural migratory patterns and seasonal movements of wildlife, affecting breeding patterns, foraging behavior, and access to vital resources such as water and food. This disruption can lead to population decline and loss of genetic diversity.
Furthermore, the fragmentation of habitats can lead to the formation of isolated populations, increasing the risk of inbreeding and reducing the ability of wildlife to adapt to changing environmental conditions. This can compromise the long-term viability and resilience of species in the face of threats such as climate change and disease outbreaks.
Conservationists and stakeholders in Namibia face the challenge of balancing the needs of human development with the preservation of wildlife habitats. They must find innovative solutions to mitigate the negative impacts of landscape fragmentation, ensuring the long-term survival of Namibia’s unique biodiversity.
| Conservation Challenges | Impacts |
|---|---|
| Restricted wildlife movement | Disrupts natural migratory patterns and access to resources |
| Isolated populations | Increased risk of inbreeding and reduced adaptability |
| Conservation-Development balance | Managing human development while preserving wildlife habitats |
Overgrazing as a Threat to Namibia’s Biodiversity
Overgrazing in Namibia poses a significant threat to the country’s biodiversity and ecosystem health. This issue affects both game and livestock farms, leading to habitat degradation, loss of biodiversity, erosion, and changes in vegetation composition. The balance between stocking rates and grazing areas is disrupted, resulting in unproductive land and reduced recovery periods for vegetation.
One major consequence of overgrazing is the phenomenon known as bush encroachment. As vegetation is continually grazed beyond its carrying capacity, opportunistic woody species such as shrubs and trees start to dominate the landscape. This encroachment negatively impacts the diversity and abundance of grasses and other herbaceous plants, altering the structure and composition of the ecosystem.
Livestock farming in Namibia plays a vital role in the country’s economy, providing employment and food security. However, unsustainable grazing practices can lead to soil degradation, which further exacerbates the effects of overgrazing. It is essential to strike a balance between livestock numbers and available rangeland resources to ensure the long-term sustainability of both the agricultural sector and the environment.
To mitigate the impacts of overgrazing, sustainable rangeland management practices should be implemented. This includes rotational grazing, which allows for proper rest and recovery of vegetation, and the establishment of grazing reserves to protect critical habitats. In addition, alternative approaches to meat production, such as feedlot systems and diversified agricultural practices, can help alleviate grazing pressures on natural rangelands.
Rangeland management in Namibia requires close collaboration between farmers, government agencies, and conservation organizations. By adopting sustainable practices and implementing effective land management strategies, we can mitigate the negative impacts of overgrazing and ensure the long-term conservation of Namibia’s unique biodiversity.

| Impacts of Overgrazing | Conservation Strategies |
|---|---|
|
|
Over-utilization of Water in Namibia
The over-utilization of water in Namibia has become a pressing issue, with the transformation of ephemeral rivers into permanent water sources and the expansion of towns and farming activities. This increased water utilization has had a significant impact on the availability of water resources in the country.
The establishment of permanent water sources has led to higher grazing pressure, as more livestock and game rely on these water sources for survival. This, in turn, has resulted in increased erosion and changes in vegetation composition, negatively impacting the delicate balance of the ecosystem. The depletion of water resources also poses a threat to the biodiversity of Namibia, as many plant and animal species rely on these water sources for their survival.
Higher grazing pressure, erosion, and changes in biodiversity are observed due to the over-utilization of water in Namibia.
To address this issue, it is crucial to implement measures to mitigate water consumption in Namibia. This requires a multi-faceted approach that includes population control to manage the demand for water, reducing meat production and consumption to alleviate the strain on water resources, and implementing water recycling and conservation practices to optimize water usage.
By taking these actions, Namibia can work towards restoring the balance of its water resources, protecting its unique biodiversity, and ensuring long-term sustainable development.
The Impact of Water Utilization on Namibia’s Vegetation
The over-utilization of water in Namibia has had a direct impact on vegetation. As water resources become scarce, vegetation struggles to survive, leading to changes in the composition and density of plant species. This, in turn, affects the habitats of various animal species that rely on specific plant types for food and shelter.
Furthermore, the depletion of water resources exacerbates bush encroachment, a phenomenon where shrubs and trees colonize areas that were once dominated by grasses. Bush encroachment negatively impacts rangeland productivity and biodiversity, as it reduces the availability of grazing areas for livestock and disrupts the habitats of wildlife.
| Impacts of Over-utilization of Water on Namibia’s Vegetation | Actions to Mitigate Water Consumption |
|---|---|
| Changes in vegetation composition | Controlling population growth |
| Increased bush encroachment | Reducing meat production and consumption |
| Disruptions to grazing areas | Implementing water recycling and conservation practices |
Addressing the impact of water utilization on Namibia’s vegetation requires a comprehensive approach that includes managing population growth, adopting sustainable agricultural practices, and promoting water conservation and recycling initiatives.

Sustainable Architecture in Namibia
Namibia has made significant strides in sustainable architecture, with a notable example being Nedbank Namibia’s green head office. This iconic building showcases the integration of innovative design and environmental consciousness.
The use of energy-saving technologies, such as solar panels and energy-efficient lighting systems, ensures minimal energy consumption. By harnessing renewable energy sources, the building reduces its reliance on conventional power grids and contributes to a greener Namibia.
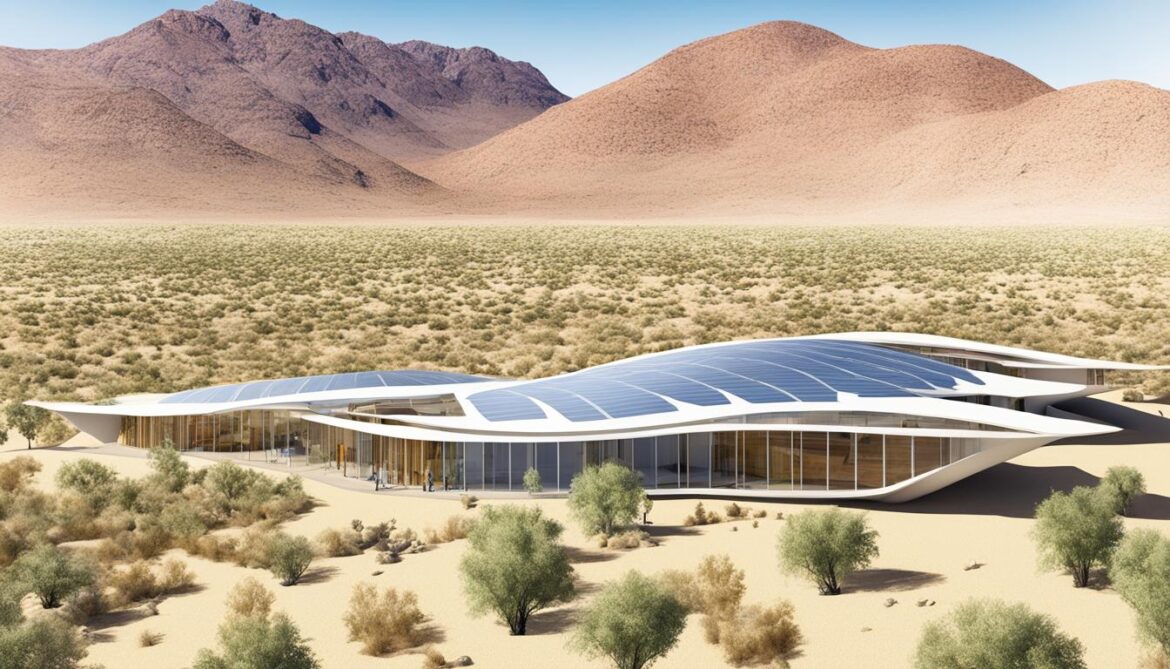

The incorporation of green building materials, such as recycled and locally sourced materials, minimizes the environmental impact of construction. These sustainable materials not only reduce waste but also lower the carbon footprint associated with the manufacturing and transportation of building materials.
The design of Nedbank Namibia’s green head office prioritizes natural light and ventilation, reducing the need for artificial lighting and air conditioning. This design approach enhances indoor air quality, promotes occupant well-being, and reduces energy consumption.
Nedbank’s commitment to sustainability sets a benchmark for eco-conscious architecture in Namibia and inspires future developments in the country.
Benefits of Sustainable Architecture
- Promotes energy efficiency and reduces operational costs
- Minimizes environmental impact and carbon emissions
- Improves indoor air quality and occupant well-being
- Utilizes renewable energy sources for a more sustainable future
- Supports local economies through the use of locally sourced materials
To encourage sustainable architecture in Namibia, it is crucial to raise awareness about the benefits and showcase successful projects like Nedbank Namibia’s green head office. By prioritizing energy-efficient construction practices, green building design, and the use of sustainable materials, Namibia can pave the way for a more environmentally conscious built environment.
Conclusion
Namibia’s biodiversity and the built environment are intricately connected, and the conservation of its natural resources plays a critical role in achieving sustainable development. By addressing threats such as habitat loss, poaching, overgrazing, and climate change, Namibia can protect its unique animal and plant species and preserve its rich biodiversity for future generations.
Conservation strategies that involve community participation and embrace sustainable building practices are key to creating a greener and more environmentally conscious future for Namibia. It is through collaborative efforts between governments, NGOs, local communities, and international stakeholders that effective conservation initiatives can be implemented.
As Namibia moves forward, it is essential to prioritize the preservation and sustainable utilization of its biodiversity, ensuring that the Namibian people coexist harmoniously with their natural surroundings. By doing so, Namibia can secure a future where the country’s diverse ecosystems thrive, and the balance between the built environment and the preservation of biodiversity is maintained for the benefit of all.
FAQ
What is the significance of Namibia’s biodiversity?
Namibia is known for its remarkable biodiversity, which includes diverse animal and plant species in unique ecosystems. This biodiversity attracts tourists from around the world and contributes to the country’s natural beauty and ecological balance.
What are the threats to Namibia’s biodiversity?
Namibia’s biodiversity faces threats such as habitat loss, poaching, overgrazing, and climate change. These factors pose a risk to vulnerable species and disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
How can Namibia protect its biodiversity?
To safeguard Namibia’s biodiversity, conservation strategies must include enforcing wildlife protection laws, establishing protected areas, promoting community-based conservation initiatives, and implementing climate change adaptation strategies. Collaboration between various stakeholders is crucial for effective conservation efforts.
What are Namibia’s conservation efforts?
Namibia has made significant strides in conservation through the establishment of protected areas like national parks and conservancies. The country also involves local communities in wildlife conservation and sustainable land management practices. Additionally, Namibia has developed a National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan to guide conservation initiatives aligned with sustainable development goals.
How does landscape fragmentation impact Namibia’s wildlife?
Landscape fragmentation, caused by game fences and roads, restricts the movements of wildlife and increases their vulnerability to mortality. This disrupts habitats, limits the gene pool and population size of wildlife, and leads to habitat fragmentation, posing challenges for conservation efforts.
What is the impact of overgrazing on Namibia’s biodiversity?
Overgrazing in Namibia, both in game and livestock farms, leads to habitat degradation, loss of biodiversity, erosion, and changes in vegetation composition. It disrupts the balance between stocking rates and grazing areas, resulting in unproductive land and reduced recovery periods for vegetation.
How does the over-utilization of water impact Namibia’s biodiversity?
Transformation of ephemeral rivers into permanent water sources and the establishment of towns and farming activities have led to increased water utilization and impacted the availability of water resources in Namibia. This has resulted in higher grazing pressure, erosion, changes in biodiversity, and the need for mitigation actions to conserve water resources.
What is the importance of sustainable architecture in Namibia?
Namibia has prioritized sustainable architecture, exemplified by Nedbank Namibia’s green head office. The use of energy-saving technologies, green building materials, and efficient design helps reduce environmental impact. These sustainable practices inspire future developments and contribute to a greener and more environmentally conscious future.
How are Namibia’s biodiversity and the built environment connected?
Namibia’s biodiversity and the built environment are closely intertwined. Conservation efforts are crucial for preserving biodiversity and achieving sustainable development in Namibia. By addressing threats and implementing conservation strategies, Namibia can protect its unique animal and plant species and create a greener future.







