Somalia Biodiversity: Animal and Plant Species and What Is Under Threat
Did you know that Somalia is considered one of the biodiversity hotspots in the Horn of Africa? With its diverse ecosystems and abundant wildlife, this East African country is a treasure trove of unique species and natural wonders. From endemic plant species to rare mammals and birds, Somalia’s biodiversity is both remarkable and under threat.
Key Takeaways:
- Somalia is a biodiversity hotspot in the Horn of Africa, with a high level of endemic plant and animal species.
- The country faces challenges such as weak institutional capacity and limited funding for conservation efforts.
- Various policies and legislation have been implemented to protect Somalia’s biodiversity, but their implementation is hindered by limited resources.
- Habitat loss, climate change, overexploitation, and pollution are among the threats to Somalia’s biodiversity.
- Conservation efforts, including community-managed plans and wildlife initiatives, have been undertaken, but more actions are needed for effective protection.
Key Policies and Governance Approach
Somalia has implemented several policies and legislation to conserve its rich biodiversity and protect the environment. These policies aim to address various challenges such as habitat loss, overexploitation, pollution, and the threat of invasive alien species.
“Conservation is not just an act; it’s a way of life.”
One of the key policies in place is the National Environment Policy, which provides a comprehensive framework for environmental protection and sustainable development in Somalia. This policy emphasizes the importance of preserving natural resources and promoting sustainable practices across sectors.
The Fisheries Law is another crucial legislation that regulates fishing activities in Somali waters. It helps to prevent overfishing, protect endangered species, and promote sustainable fishing practices. By implementing this law, Somalia aims to ensure the long-term viability of its marine resources.
The Wildlife Policy and Wildlife Strategic Plan work together to safeguard the diverse wildlife in Somalia. These policies focus on habitat preservation, wildlife conservation, and the prevention of illegal wildlife trade. They aim to protect endangered species and promote their recovery.
The Forestry and Wildlife Act is another key legislation that plays a vital role in protecting Somalia’s forests and wildlife. This act aims to prevent deforestation, promote sustainable forestry practices, and conserve the unique flora and fauna found in the country.
Moreover, Somalia has taken significant steps to combat deforestation by implementing a National Charcoal Policy. This policy aims to reduce the overexploitation of trees for charcoal production, promote sustainable alternatives, and combat the environmental degradation caused by deforestation.
However, despite the presence of these policies, the implementation process faces challenges due to weak institutional capacity and limited resources. This hinders the effective enforcement and monitoring of environmental protection measures in Somalia.
Table: Key Policies and Legislation for Biodiversity Conservation in Somalia
| Policy | Purpose |
|---|---|
| National Environment Policy | Comprehensive framework for environmental protection and sustainable development |
| Fisheries Law | Regulation of fishing activities and promotion of sustainable fishing practices |
| Wildlife Policy | Protection of wildlife, prevention of illegal wildlife trade, and habitat preservation |
| Wildlife Strategic Plan | Safeguarding diverse wildlife and promoting their conservation and recovery |
| Forestry and Wildlife Act | Prevention of deforestation, sustainable forestry practices, and conservation of flora and fauna |
| National Charcoal Policy | Combatting deforestation by promoting sustainable alternatives to charcoal production |
Somalia must prioritize strengthening institutional capacity, securing adequate resources, and enhancing collaboration among various stakeholders to effectively implement and enforce these policies. Only through concerted efforts can Somalia achieve its goals of biodiversity conservation and environmental protection.
Biodiversity Facts
Somalia is considered one of the biodiversity hotspots in the Horn of Africa, with a high level of endemic species. It is home to around 2,750 endemic plant species out of approximately 5,000 vascular plant species.
The country also has diverse bird and mammal species, with 24 endemic bird species and several endemic antelope species.
However, there is evidence of declining trends in biodiversity and ecosystems, particularly in forestry, agriculture, rangelands, marine and coastal areas, wetlands, and wildlife habitats.
| Type of Habitat | Key Biodiversity |
|---|---|
| Forestry | – Declining forest cover – Loss of tree species diversity – Threatened plant communities |
| Agriculture | – Decreased crop diversity – Loss of traditional farming practices – Soil degradation |
| Rangelands | – Overgrazing – Loss of pastoral species – Desertification |
| Marine and Coastal Areas | – Coral reef degradation – Declining fish populations – Destruction of coastal habitats |
| Wetlands | – Wetland habitat loss – Decline in waterbird populations – Pollution and eutrophication |
| Wildlife Habitats | – Habitat fragmentation – Decrease in wildlife populations – Illegal wildlife trade |
Threats to Biodiversity
Several factors pose threats to biodiversity in Somalia, including habitat loss and degradation, climate change, overexploitation, pollution, invasive alien species, civil war, and tsunamis. These threats have led to declining populations and the approaching extinction of many species. For example, the Somali wild ass, black rhino, lion, and Swayne’s hartebeest have been wiped out from most of the country, while the wild ass population has drastically declined. Additionally, unsustainable fishing practices, illegal fishing, and the absence of a surveillance mechanism have caused significant decline in marine resources, including coral reefs.

These threats to biodiversity in Somalia have far-reaching consequences for the delicate ecosystems and the species that depend on them. Habitat loss and degradation due to human activities, such as deforestation and land conversion for agriculture, are major drivers of biodiversity decline. Climate change exacerbates these threats by altering habitats, disrupting seasonal patterns, and increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events.
Overexploitation of natural resources, including hunting and fishing, has resulted in the depletion of important animal and plant species. The demand for bushmeat, illegal wildlife trade, and unsustainable fishing practices contribute to this problem. Pollution, both land-based and marine, from industrial activities, agricultural runoff, and improper waste disposal, further degrades ecosystems and harms biodiversity.
“The loss of biodiversity is not just an environmental issue; it has significant social and economic impacts as well.” – Dr. Ahmed, Biodiversity expert
Invasive alien species also pose a significant threat to native species in Somalia. These non-native species can outcompete native species for resources, disrupt food webs, and alter ecosystems. The lack of effective measures to control and manage invasive species exacerbates the problem.
The civil war in Somalia has had devastating effects on biodiversity conservation efforts. It has disrupted environmental governance, hindered enforcement of conservation laws, and allowed for increased illegal activities, including poaching, logging, and illegal fishing. The absence of a functioning surveillance mechanism makes it difficult to monitor and protect wildlife and their habitats.
The Extinction Crisis
The decline in biodiversity in Somalia has pushed many species to the edge of extinction. The Somali wild ass, once widespread in the country, is now critically endangered with a small population remaining in few protected areas. The black rhino, lion, and Swayne’s hartebeest have been completely eradicated from most parts of Somalia. This loss of iconic species not only affects the balance of ecosystems but also erodes cultural and ecological heritage.
In the marine realm, unsustainable fishing practices, including bottom trawling and dynamite fishing, have decimated fish populations and damaged vital coral reef ecosystems. With the absence of effective management and monitoring, these practices continue to threaten the marine biodiversity of Somalia.
| Threats to Biodiversity | Impact |
|---|---|
| Habitat loss and degradation | Declining populations, loss of habitat, disruption of food chains |
| Climate change | Altered habitats, disrupted seasonal patterns, increased extreme weather events |
| Overexploitation | Depletion of animal and plant species, disruption of ecosystems |
| Pollution | Environmental degradation, harm to biodiversity |
| Invasive alien species | Competition with native species, disruption of food webs |
| Civil war | Disrupted conservation efforts, increased illegal activities |
| Unsustainable fishing practices | Depletion of fish populations, damage to coral reefs |
Endemic Species
Somalia is renowned for its rich biodiversity, boasting a high number of endemic species that are found nowhere else in the world. These unique organisms contribute to the country’s ecological diversity and play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of its ecosystems.
Among the endemic plant species in Somalia, Boswellia sacra and B. frereana stand out. These trees are the primary source of frankincense, a valuable resin used in incense production. Commiphora myrrha and C. guidottii are also endemic to Somalia and are known for their production of myrrh, a highly prized aromatic resin.
Somalia is also home to several endemic bird species, adding to its avian diversity. Notable examples include the Warsangli linnet and Djibouti francolin. These birds have adapted to the unique environments of Somalia and have evolved distinct characteristics found nowhere else.
Furthermore, the country is teeming with endemic mammal species that are exclusive to the region. The beira, dibatag, and Speke’s gazelle are iconic examples of endemic mammal species in Somalia. Their presence in the region highlights the importance of preserving their habitats and protecting their populations.
Reptiles and amphibians also showcase high levels of endemism in Somalia. These unique creatures have adapted to the specific ecological niches within the country and contribute to its overall biodiversity.
“The endemic species found in Somalia are valuable treasures that reflect the country’s extraordinary natural heritage. It is vital that we prioritize their conservation to secure their future and ensure the preservation of Somalia’s unique biodiversity.”
To summarize, Somalia’s endemic species contribute to its vibrant ecosystem and highlight the country’s natural diversity. From endemic plants used in traditional practices to endemic birds, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians, these unique creatures are an integral part of Somalia’s natural heritage.
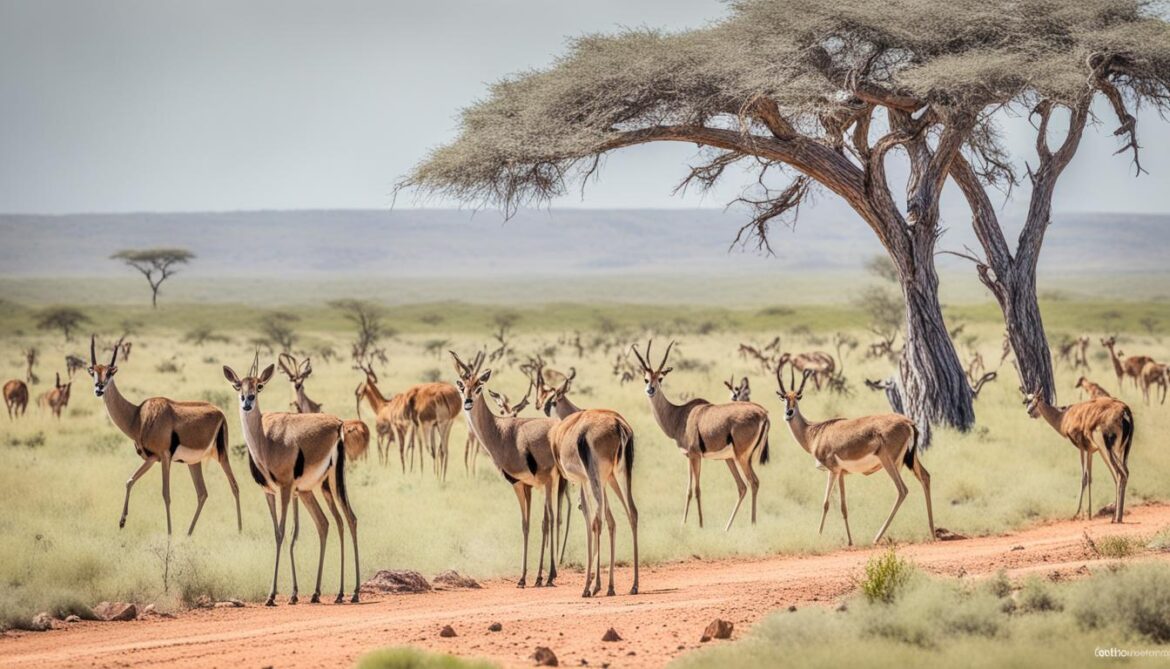

Conservation Efforts
Despite the challenges, Somalia has implemented various conservation efforts to protect its biodiversity. These initiatives are aimed at safeguarding the diverse ecosystems and species that make up Somalia’s natural heritage. By employing a combination of emergency interventions, community-based programs, and wildlife conservation initiatives, Somalia strives to overcome the threats facing its precious biodiversity.
One of the key conservation efforts in Somalia is emergency interventions for pastoral communities. These interventions provide essential support to communities affected by environmental disasters, such as droughts and floods. By offering assistance with food security, livestock health, and resource management, these interventions help ensure the well-being of both humans and animals.

The distribution of seeds for flood recession planting is another vital conservation measure in Somalia. This program aims to restore and rehabilitate degraded areas by promoting the growth of native plant species. Flood recession planting not only increases vegetation cover but also helps mitigate soil erosion, enhancing overall ecosystem health and resilience.
Livelihood restoration programs play a crucial role in Somalia’s biodiversity conservation efforts. By providing alternative income-generating activities to local communities, these programs help reduce their dependence on unsustainable practices that contribute to habitat degradation. This approach ensures that communities have viable alternatives that support their livelihoods while preserving the precious biodiversity of the region.
“Conservation is a collective effort, and community participation is paramount in protecting our natural resources.” – Abdullahi Jilibe, Director of Biodiversity Conservation, Somalia
Community-managed conservation plans have been instrumental in fostering local ownership and stewardship of biodiversity in Somalia. These plans empower communities to actively participate in the management and conservation of their natural resources. Through collaborative and inclusive decision-making processes, communities become key actors in preserving their wildlife, habitats, and ecosystems.
The implementation of wildlife conservation initiatives is crucial for safeguarding the rich biodiversity of Somalia. These initiatives focus on protecting and preserving wildlife habitats, combating wildlife trafficking, and supporting anti-poaching efforts. By raising awareness and enforcing regulations, Somalia aims to conserve its iconic species, such as elephants, lions, and antelopes.
| Conservation Efforts | Objectives |
|---|---|
| Emergency Interventions for Pastoral Communities | Provide support to communities affected by environmental disasters and prevent further degradation of habitats. |
| Seed Distribution for Flood Recession Planting | Restore and rehabilitate degraded areas, enhancing ecosystem health and resilience. |
| Livelihood Restoration Programs | Offer alternative income-generating activities to reduce dependence on unsustainable practices and protect biodiversity. |
| Community-Managed Conservation Plans | Promote local ownership and stewardship of biodiversity through collaborative decision-making processes. |
| Wildlife Conservation Initiatives | Protect and preserve wildlife habitats, combat wildlife trafficking, and support anti-poaching efforts. |
Freshwater and Marine Biodiversity
Somalia boasts a rich variety of freshwater and marine biodiversity. The country is home to approximately 10 endemic species of freshwater fish, including unique cave-dwelling fish found exclusively in Somalia. These endemic species contribute to the ecological diversity and uniqueness of Somalia’s aquatic ecosystems.
However, the sustainability of offshore and inshore fish resources is currently under threat, leading to a significant decline in marine biodiversity. Illegal fishing practices and the absence of a proper surveillance mechanism exacerbate the issue, posing further risks to Somalia’s marine resources.
The detrimental consequences of unsustainable fishing practices extend beyond the decline of fish populations. Coral reefs, crucial in nurturing marine biodiversity, also face destruction in Somalia. This places marine species, especially those dependent on coral reef ecosystems, at risk.

It is essential to address these threats and protect the ecological integrity of Somalia’s marine habitats. Implementing sustainable fishing practices, establishing effective surveillance mechanisms, and raising awareness about the importance of marine biodiversity are vital steps towards conserving and preserving Somalia’s valuable marine ecosystems.
Economic Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in Somalia’s economy. The country heavily relies on pastoralism, crop production, fisheries, and forestry for livelihoods and exports. Frankincense and myrrh production, in particular, are major economic activities. Additionally, agriculture, livestock, and natural resources contribute to the country’s economic growth.
However, the decline in biodiversity and ecosystems poses risks to these sectors, affecting the overall economy of Somalia.

“Conserving Somalia’s biodiversity is not only crucial for the preservation of unique ecosystems but also for the sustained economic growth of the country. It is imperative that we prioritize and invest in biodiversity protection, as it directly impacts our livelihoods and future prosperity.” – Dr. Hussein Ali, Environmental Economist
By preserving diverse ecosystems and safeguarding species, Somalia can enhance its long-term economic resilience. The economic value of biodiversity extends beyond direct economic benefits, such as revenue from exports and resource extraction. It includes ecosystem services, such as pollination, soil fertility, water purification, and climate regulation, which support agricultural productivity and human well-being.
Key Economic Sectors
Let’s explore how different economic sectors in Somalia rely on biodiversity:
- Pastoralism: Somalia’s pastoral communities heavily depend on biodiversity-rich rangelands for livestock grazing. Livestock products, including meat, milk, hides, and skins, contribute significantly to the country’s food security and export earnings.
- Crop Production: Agriculture in Somalia benefits from diverse ecosystems, which provide essential services, including soil fertility, pest control, and genetic diversity for crop breeding. Staple crops like maize, sorghum, and beans are crucial for food security and income generation.
- Fisheries: Somalia’s coastal waters are abundant with diverse marine species, providing a source of protein, employment, and income for coastal communities. Sustainable fishing practices and biodiversity protection are essential for maintaining fish populations and ensuring the long-term resilience of the fisheries sector.
- Forestry: The forests of Somalia contain valuable timber resources and contribute to carbon sequestration. Sustainable forestry practices promote biodiversity conservation, while timber exports generate revenue and support local livelihoods.
Table: Economic Sectors Dependent on Biodiversity
| Sector | Dependence on Biodiversity |
|---|---|
| Pastoralism | High |
| Crop Production | Medium |
| Fisheries | High |
| Forestry | Medium |
The economic value of Somalia’s biodiversity extends beyond immediate monetary benefits. The preservation of wildlife, forests, and diverse ecosystems contributes to sustainable development, resilience to climate change, and the preservation of cultural heritage.
Conclusion
Somalia faces numerous challenges in conserving its biodiversity, including weak institutional capacity, limited resources, and a lack of baseline assessments. To address these conservation challenges, it is crucial for the country to strengthen its policies and improve coordination among biodiversity managing actors. Additionally, enhancing capacity-building efforts will help build a more sustainable and effective conservation framework.
Raising public awareness about the importance of biodiversity and the need for its protection is essential in securing support and active participation from local communities. By promoting community-based conservation initiatives, Somalia can empower its citizens to take an active role in preserving their natural heritage.
Furthermore, comprehensive assessments of biodiversity resources are vital for developing targeted conservation strategies. By understanding the current state of wildlife habitats, ecosystems, and plant species, Somalia can prioritize its conservation efforts and allocate resources more effectively.
FAQ
What is the status of biodiversity conservation in Somalia?
Somalia is a party to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and has developed a National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) to guide its efforts in biodiversity conservation.
What are some of the challenges faced by Somalia in biodiversity conservation?
Somalia faces challenges such as weak institutional capacity, lack of baseline assessments, and limited funding for conservation efforts.
What policies and legislation has Somalia implemented to protect its biodiversity?
Somalia has implemented various policies and legislation, including the National Environment Policy, Fisheries Law, Wildlife Policy, Wildlife Strategic Plan, and Forestry and Wildlife Act, to address issues such as habitat loss and overexploitation.
What are some of the threats to biodiversity in Somalia?
Habitat loss and degradation, climate change, overexploitation, pollution, invasive alien species, civil war, and tsunamis are among the threats to biodiversity in Somalia.
What are some endemic species found in Somalia?
Somalia is home to endemic plant species such as Boswellia sacra and B. frereana (used for frankincense production) and Commiphora myrrha and C. guidottii (sources of myrrh). It also has endemic bird species like the Warsangli linnet and Djibouti francolin, and endemic mammal species including the beira, dibatag, Speke’s gazelle, and silver dikdik.
What conservation efforts have been undertaken in Somalia?
Somalia has implemented various conservation efforts, including emergency interventions for pastoral communities, livelihood restoration programs, and community-managed conservation plans.
What is the status of freshwater and marine biodiversity in Somalia?
Somalia has diverse freshwater and marine biodiversity. It is home to around 10 endemic freshwater fish species and faces issues with unsustainable fishing practices and the decline of marine resources.
How important is biodiversity to Somalia’s economy?
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in Somalia’s economy, particularly in sectors such as pastoralism, crop production, fisheries, and forestry.
What are the conservation challenges faced by Somalia?
Somalia faces challenges such as weak institutional capacity, limited resources, and a lack of baseline assessments in conserving its biodiversity.