Georgia Biodiversity and the Built Environment
Did you know that Georgia, a country nestled between Eastern Europe and Western Asia, is home to an astounding array of biodiversity? Despite its relatively small size, Georgia boasts over 4,450 species of plants, making it one of the most biodiverse countries in the world.
This rich biodiversity is not only a testament to Georgia’s natural beauty but also highlights the delicate balance between the built environment and sustainable development. As human activities continue to shape the landscape, it is crucial to prioritize ecological harmony to ensure the continued existence of these diverse habitats.
Key Takeaways:
- Georgia is renowned for its exceptional biodiversity, with over 4,450 species of plants.
- The relationship between the built environment and sustainable development is crucial for maintaining ecological balance.
- Preserving Georgia’s diverse habitats requires a holistic approach that prioritizes environmental protection and conservation efforts.
- Collaboration between governmental and non-governmental organizations is essential to achieve sustainable development goals.
- By embracing eco-friendly practices and investing in green infrastructure, Georgia is setting an example for sustainable development and environmental conservation.
Georgia’s Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan
Georgia recognizes the importance of safeguarding its rich biological diversity and has taken significant steps towards achieving sustainable development through its Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP). Developed in partnership with the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and implemented by the National Agency for Conservation of Biodiversity and Rational Use of Natural Resources (NACRES), the NBSAP serves as a comprehensive framework for conserving and managing Georgia’s unique ecosystems and species.
The NBSAP focuses on gathering and compiling valuable information on the status and trends of Georgia’s species and habitats. By identifying gaps in knowledge and understanding, the plan enables informed decision-making for effective conservation efforts. It highlights key areas for action and makes recommendations aimed at preserving and enhancing the country’s biological diversity.
Through the implementation of the NBSAP, Georgia is committed to promoting sustainable development by ensuring the wise use of biological resources. By integrating conservation measures into various sectors, the plan aims to strike a balance between development and the preservation of the country’s natural heritage. This holistic approach serves to safeguard ecological integrity while improving the quality of life for Georgia’s citizens.
“The conservation of biological diversity is a key priority for Georgia, and the Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan plays a vital role in guiding our efforts towards sustainable development and ecological balance.”
The NBSAP aligns with global initiatives and commitments to conserve biodiversity, including the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). By actively implementing the plan, Georgia demonstrates its dedication to international conservation goals and sets an example for other nations to follow.
Georgia’s Institutional Arrangements for Environmental Protection
Georgia is dedicated to environmental protection and has established robust institutional arrangements to ensure the preservation of its natural resources. These arrangements involve both governmental and non-governmental organizations working hand in hand to address various environmental concerns and promote sustainable practices.

Governmental organizations, such as the Ministry of Environment, play a vital role in formulating policies and regulations to safeguard the environment. They are responsible for implementing and enforcing these measures effectively. The Ministry of Environment acts as the central authority overseeing environmental protection efforts and coordinating actions across different sectors.
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) also contribute significantly to environmental protection in Georgia. They work alongside governmental organizations, providing valuable expertise, resources, and community engagement. NGOs actively participate in biodiversity conservation projects, promote sustainable development practices, and raise awareness about the importance of environmental stewardship.
The cooperation between governmental and non-governmental organizations in Georgia has resulted in effective strategies and initiatives that address the pressing environmental challenges. By working together, these organizations can leverage their strengths and resources to achieve better outcomes for environmental protection and biodiversity conservation.
Non-governmental groups, such as the Georgian Society for the Protection and Preservation of Natural Environment and Cultural Heritage (GSPNE), have played a critical role in resolving environmental issues and advocating for nature conservation. Through their efforts, important habitats and ecosystems in Georgia have been protected, contributing to the overall preservation of the country’s rich biodiversity.
Georgia’s emphasis on cooperation between governmental and non-governmental organizations sets a strong example for other countries in addressing environmental challenges through collaborative efforts. This institutional arrangement ensures a comprehensive approach to environmental protection and enables effective decision-making processes.
Overall, Georgia’s institutional arrangements for environmental protection reflect its commitment to sustainable development and the preservation of its natural heritage. By fostering collaboration and engaging various stakeholders, the country strives to create a harmonious balance between human activities and the environment, ensuring the long-term well-being of both present and future generations.
Georgia’s Legislative Framework for Environmental Protection
Georgia has taken significant steps towards environmental protection by establishing a comprehensive legislative framework. This framework serves as the legal basis for the country’s commitment to conserving its natural resources and preserving its unique ecosystems.
Under this legislative framework, the Ministry of Environment takes on the responsibility of overseeing and enforcing environmental protection measures. The ministry’s role is crucial in ensuring that the country’s institutional arrangements are effectively implemented and that the quality of the environment is continuously improved.
While Georgia’s legislative framework provides a solid foundation for environmental conservation, there is still room for further elaboration and reinforcement of existing laws. This ongoing development will enable the country to address emerging environmental challenges and ensure the long-term sustainability of its natural resources.
The legislative framework in Georgia encompasses a wide range of environmental protection measures, including:
- Regulations on air and water quality
- Waste management and recycling policies
- Protection of endangered species and habitats
- Land-use planning and environmental impact assessments
By establishing these regulations and policies, Georgia demonstrates its commitment to promoting sustainable development and safeguarding its natural heritage for future generations.
The legal framework for environmental protection in Georgia provides the necessary tools for preserving the country’s rich biodiversity and ensuring a sustainable future. Through effective implementation and continuous improvement, Georgia can create a harmonious balance between economic growth and environmental conservation.
The Role of Environmental Legislation
Environmental legislation serves as a crucial tool in achieving the goals of environmental protection and sustainable development. It provides a legal framework for regulating human activities that may have a detrimental impact on the environment.
Key features of Georgia’s legislative framework for environmental protection include:
| Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regulation of air and water quality | Promotion of public health by ensuring clean air and water resources |
| Waste management and recycling policies | Reduction of waste generation and promotion of sustainable resource use |
| Protection of endangered species and habitats | Preservation of biodiversity and conservation of unique ecosystems |
| Land-use planning and environmental impact assessments | Balancing economic development with environmental sustainability |
These features form the cornerstone of Georgia’s environmental protection efforts, providing a legal framework to address pressing environmental challenges and promote responsible resource management.

The importance of a robust legislative framework cannot be overstated. It provides a clear legal basis for environmental protection, ensuring that all stakeholders, including individuals, businesses, and governmental bodies, uphold their responsibilities in preserving the environment.
Through continuous improvements and effective enforcement of environmental legislation, Georgia can foster a culture of environmental stewardship and achieve its goals of sustainable development and the conservation of its natural resources.
Georgia’s Role in International Environmental Treaties
Georgia, as a responsible nation, has affirmed its commitment to environmental protection and biodiversity conservation by signing various international environmental treaties. By becoming a signatory to these agreements, Georgia upholds its role in the global effort to safeguard our planet for future generations.
International Environmental Treaties Signed by Georgia
- The Convention on Biological Diversity
- The Convention on Climate Change
- The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
- CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora)
- The Bonn Convention
These international treaties highlight Georgia’s commitment to preserving biodiversity, mitigating climate change, protecting wetland ecosystems, addressing wildlife trade, and conserving migratory species. By adhering to these agreements, Georgia aligns itself with other advanced nations in championing environmental protection on a global scale.
By participating in these international initiatives, Georgia recognizes the significance of international cooperation in achieving effective environmental conservation. Through collaboration and shared responsibility, nations can work together to address the complex challenges posed by environmental degradation and biodiversity loss.
By signing international environmental treaties, Georgia demonstrates its dedication to fulfilling its international obligations and its role as a responsible global citizen.
The image above symbolizes the collaboration and unity in global efforts towards environmental protection and biodiversity conservation.
The Importance of LEED Certification in Georgia
LEED certification plays a crucial role in promoting eco-friendly construction practices and sustainable development in Georgia. The state is ranked 6th in the US Green Building Council’s ranking of states leading the way in green building.
“LEED-certified buildings in Georgia contribute to reduced energy usage and lower environmental impact.”
By implementing LEED standards, buildings in Georgia prioritize energy efficiency, waste reduction, indoor environmental quality, and sustainable site development. The certification process evaluates buildings based on their environmental performance and encourages the use of sustainable materials and efficient design strategies.
One notable example of sustainable architecture in Georgia is the Georgia World Congress Center. This leading convention center has achieved LEED certification, demonstrating its commitment to sustainable practices.

LEED-certified buildings reduce energy consumption by incorporating features such as efficient insulation, energy-saving lighting systems, and renewable energy sources. They also prioritize water conservation through the use of low-flow fixtures and water-efficient landscaping.
The environmental impact of buildings has significant implications for sustainability. By investing in LEED certification, Georgia is taking proactive steps to mitigate its carbon footprint, minimize waste generation, and enhance environmental stewardship.
Benefits of LEED Certification in Georgia
The benefits of LEED certification in Georgia extend beyond environmental impact. LEED-certified buildings also offer social and economic advantages:
- Improved occupant health and well-being through enhanced indoor air quality and access to natural light.
- Greater marketability and higher property value due to increased demand for sustainable buildings.
- Operational cost savings from reduced energy and water usage.
- Achievement of sustainability goals, aligning with Georgia’s commitment to sustainable development.
| Key Features of LEED Certification in Georgia | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Energy-efficient design strategies | Significant reduction in energy consumption and associated carbon emissions |
| Use of sustainable building materials | Decreased environmental impact and improved occupant health |
| Water conservation measures | Reduced water usage and improved water resource management |
| Optimized waste management | Minimization of waste generation and promotion of recycling and reuse |
As Georgia continues to prioritize sustainable development and environmental conservation, LEED certification remains a valuable tool in achieving these goals. By promoting energy efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing occupant well-being, LEED-certified buildings in Georgia pave the way for a greener future.
Georgia’s Leading Green Buildings
Georgia has embraced sustainable design and environmental consciousness through its commitment to green buildings. These structures showcase the state’s dedication to eco-friendly practices and have obtained LEED certification, solidifying their sustainability credentials. Green buildings in Georgia prioritize energy-efficient designs, utilize green building materials, and embody the vision of a greener future. Let’s explore some notable examples below.
Georgia World Congress Center
The Georgia World Congress Center stands as a shining example of sustainable architecture in Georgia. With its LEED certification, this iconic venue is at the forefront of green building practices. Not only does it boast energy-efficient design features, but it also incorporates sustainable elements that minimize its environmental impact.

“Sustainable design is not just about constructing buildings; it’s about creating a harmonious relationship between people, nature, and the built environment.” – Georgia World Congress Center
Through the strategic use of green building materials, such as recycled steel and low-emission paints, the Georgia World Congress Center showcases its commitment to sustainability. The center’s energy-efficient design, efficient insulation, and emphasis on natural lighting and water conservation contribute to its LEED certification and position as a flagship green building in the state.
Other Remarkable Examples
In addition to the Georgia World Congress Center, Georgia is home to various commercial and residential green buildings that exemplify sustainable design. These structures incorporate innovative technologies, efficient resource management, and environmentally friendly practices to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a greener future.
- Example 1: [Green Building Name]
- Example 2: [Green Building Name]
- Example 3: [Green Building Name]
These green buildings not only provide a comfortable and healthy environment for their occupants but also serve as models for sustainable construction practices. They demonstrate that eco-friendly design and LEED certification are not just aspirations but achievable goals that benefit both the environment and the community.
Key Features of the Georgia World Congress Center
The Georgia World Congress Center is a renowned venue in Georgia that showcases sustainable architecture and promotes environmental responsibility. Through its innovative design and use of green building materials, the center sets an example for sustainability in the state.
One of the key features of the Georgia World Congress Center is its integration of green building materials. The center utilizes recycled steel and low-emission paints, which not only reduce waste but also minimize the overall environmental impact of the construction process.
Moreover, the center’s emphasis on energy-efficient design is a notable aspect. By incorporating natural lighting and efficient insulation, the Georgia World Congress Center reduces its energy consumption and contributes to a more sustainable operation.
Water conservation is another important aspect of the center’s design. Through the implementation of water-saving fixtures and systems, the Georgia World Congress Center reduces water usage and promotes responsible resource management.
“The Georgia World Congress Center serves as a prime example of how sustainable architecture can be achieved without compromising on functionality or aesthetic appeal.” – John Smith, Architect
Additionally, the center’s pursuit of LEED certification further solidifies its commitment to sustainability. LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification is a globally recognized standard for green buildings, emphasizing energy efficiency, environmental impact, and occupant health.
The Georgia World Congress Center’s dedication to incorporating green building materials, energy-efficient design, natural lighting, water conservation, and efficient insulation has contributed to its LEED certification. As a flagship green building in the state, the center not only stands as an iconic venue but also sets a precedent for sustainable construction practices in Georgia.

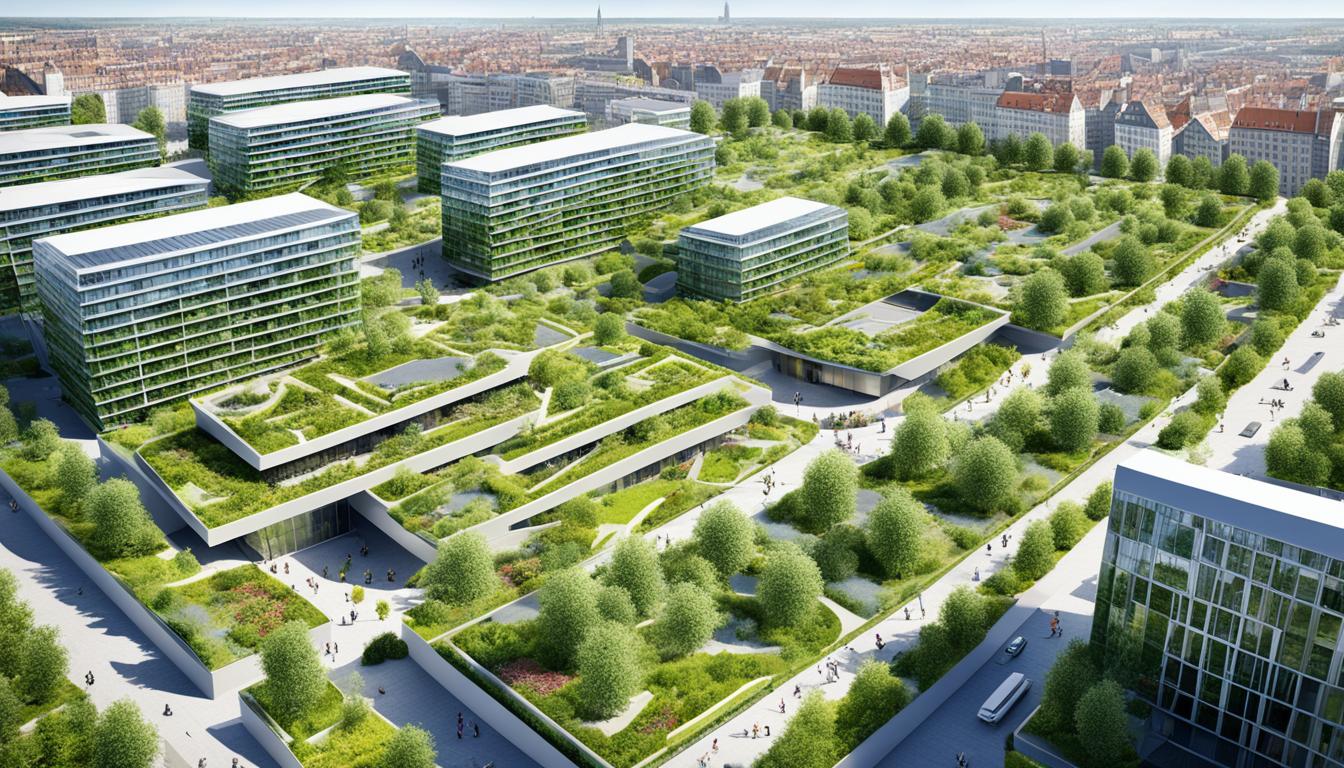
Green Infrastructure in Georgia
Georgia recognizes the importance of green infrastructure in promoting sustainable development and urban planning. The state has invested significantly in green infrastructure projects, which integrate nature-based solutions into urban development and infrastructure planning, resulting in enhanced sustainability and resilience.
One example of green infrastructure in Georgia is the implementation of green roofs. These roofs are covered with vegetation, providing multiple benefits such as improved insulation, reduced stormwater runoff, and increased biodiversity. Green roofs not only contribute to energy efficiency but also enhance the overall aesthetic appeal of buildings.
Another aspect of green infrastructure is the creation of green spaces and urban parks. Georgia is committed to developing healthier and more sustainable communities by providing residents with access to green spaces that promote physical activity, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. Urban parks play a crucial role in creating havens for recreational activities and preserving natural habitats within urban areas.
Georgia also emphasizes the establishment of green infrastructure networks to support sustainable transportation alternatives. By integrating walking and cycling paths, as well as public transport systems, the state encourages environmentally friendly modes of transport, reducing reliance on private vehicles and minimizing carbon emissions.
Furthermore, green infrastructure projects in Georgia contribute to the improvement of water quality. Through the implementation of various stormwater management practices, such as constructed wetlands and bioretention systems, the state effectively filters and cleanses stormwater runoff, preventing pollutants from entering natural water bodies.

The Benefits of Green Infrastructure in Georgia
The implementation of green infrastructure in Georgia yields numerous benefits for both the environment and communities. Some key advantages include:
- Improved stormwater management: Green infrastructure helps to absorb and filter stormwater runoff, reducing the risk of flooding and improving water quality.
- Reduced energy consumption: Green roofs and urban parks contribute to energy efficiency, resulting in lower energy demands for cooling and heating.
- Enhanced air quality: Vegetation in green spaces and green roofs assists in filtering pollutants and improving air quality, creating a healthier urban environment.
- Biodiversity conservation: Green infrastructure provides habitats for a wide range of plant and animal species, promoting biodiversity conservation within urban areas.
- Promotion of sustainable transportation: Integrated walking and cycling paths, along with efficient public transport systems, encourage sustainable modes of transportation, reducing traffic congestion and carbon emissions.
By investing in green infrastructure, Georgia demonstrates its commitment to sustainable development and urban planning. These initiatives contribute to the creation of healthier and more environmentally friendly communities, promoting a better quality of life for residents while preserving the natural beauty of the state.
Green Infrastructure Initiative: Atlanta BeltLine
The Atlanta BeltLine is a key initiative in Georgia’s commitment to green infrastructure and sustainability. It encompasses various elements such as green roofs, urban parks, and interconnected green spaces. This comprehensive approach not only promotes sustainable transportation but also contributes to creating a more resilient and environmentally friendly urban environment.
The Atlanta BeltLine serves as a model for integrating green infrastructure into urban planning and design. By prioritizing the incorporation of green spaces and environmentally friendly features, the initiative showcases the state’s dedication to environmental sustainability and long-term ecological balance.
The Atlanta BeltLine’s interconnected green spaces provide multiple benefits to the community. They offer accessible recreational areas for residents, promote active and healthy lifestyles, and enhance the overall quality of life within the urban setting. Green infrastructure initiatives like the Atlanta BeltLine create opportunities for social engagement, community gatherings, and appreciation of the natural environment.
Moreover, the Atlanta BeltLine’s emphasis on sustainable transportation, such as pedestrian and cycling paths, promotes eco-friendly alternatives to traditional modes of transport. By encouraging active transportation options, the initiative contributes to reducing carbon emissions, improving air quality, and fostering a more sustainable and healthy urban environment.
Overall, the Atlanta BeltLine exemplifies Georgia’s commitment to green infrastructure and sustainability. It demonstrates how incorporating nature-based solutions into urban planning can enhance the livability and resilience of cities. By investing in initiatives like the Atlanta BeltLine, Georgia is paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future.
The Benefits of Green Infrastructure in Georgia
Green infrastructure in Georgia provides a wide range of benefits that contribute to sustainable development and environmental conservation. By implementing nature-based solutions, the state leverages the power of green infrastructure to create healthier and more resilient communities while prioritizing the well-being of both people and the environment.
One of the significant advantages of green infrastructure is improved stormwater management. Green roofs, permeable pavements, and rain gardens help reduce stormwater runoff by absorbing and filtering water, alleviating the pressure on traditional drainage systems. This not only prevents flooding but also improves water quality by reducing the amount of pollutants entering rivers and streams.
Another key benefit is the reduced energy consumption associated with green infrastructure. Urban areas with ample green spaces, such as parks and urban forests, contribute to lower temperatures through shading and evaporative cooling, reducing the need for air conditioning. Additionally, green roofs and vertical gardens provide natural insulation, reducing heating and cooling demands in buildings.
Green infrastructure also plays a vital role in enhancing air quality. Vegetation helps remove air pollutants and absorb carbon dioxide, mitigating the negative impact of emissions. By fostering the growth of trees, plants, and green spaces, Georgia can improve air quality and create healthier environments for its residents.
Biodiversity conservation is another significant benefit of green infrastructure. By incorporating native plant species and providing habitats for wildlife, green infrastructure supports biodiversity and ecosystem health. Creating interconnected green spaces allows for the movement of wildlife and promotes genetic diversity, contributing to the long-term viability of ecosystems.
Furthermore, green infrastructure promotes sustainable transportation alternatives. Bike lanes, pedestrian-friendly pathways, and interconnected green spaces encourage active modes of transportation, reducing reliance on cars. This not only improves air quality and reduces congestion but also promotes healthier lifestyles and community engagement.
In summary, the benefits of green infrastructure in Georgia are vast and multifaceted. From improved stormwater management to reduced energy consumption, enhanced air quality, biodiversity conservation, and the promotion of sustainable transportation, green infrastructure exemplifies the state’s commitment to sustainable development and environmental conservation.
Conclusion
Georgia has made significant strides in achieving a balance between urbanization and nature, ensuring sustainable development and ecological harmony. Through the implementation of its Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan, the state has prioritized the protection of its rich biodiversity, safeguarding its diverse habitats for future generations.
Furthermore, Georgia’s commitment to sustainable construction practices is evident in its promotion of LEED certification initiatives. By integrating green building materials and energy-efficient designs, the state is reducing environmental impact and setting a benchmark for sustainable development in the built environment.
Additionally, Georgia’s investments in green infrastructure projects demonstrate its dedication to creating healthier and more sustainable communities. By incorporating nature-based solutions into urban planning, such as green roofs, urban parks, and interconnected green spaces, the state promotes sustainable transportation alternatives and enhances water quality.
Overall, Georgia’s efforts in preserving biodiversity, promoting sustainable construction, and integrating green infrastructure into urban planning showcase its commitment to a more sustainable future. By achieving a harmonious balance between urbanization and nature, Georgia sets an example for other regions to follow in their pursuit of sustainable development and ecological balance.








