Did you know that Mauritania, a West African country in the Sahel-Saharan region, is home to sacred natural sites that are of immense cultural and spiritual significance? These sites, along with the country’s rich biodiversity, play a vital role in preserving Mauritania’s unique natural heritage, promoting environmental protection, and fostering the involvement of local communities in conservation efforts.
Key Takeaways:
- Mauritania is known for its sacred natural sites and rich biodiversity.
- These sites are of great cultural and spiritual significance to local communities.
- Efforts are being made to protect and preserve these sites and promote environmental protection.
- Mauritania’s biodiversity supports a wide variety of plant and animal species.
- Threats to biodiversity in Mauritania include overfishing, habitat fragmentation, and climate change.
Biodiversity in Mauritania
Mauritania is blessed with a diverse range of ecosystems that contribute to its remarkable biodiversity. From the picturesque Atlantic coast to wetlands, forests, and desert landscapes, the country offers a unique and rich habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal species.
The Mauritanian biodiversity is a true treasure, providing essential ecosystem services that support the well-being of both nature and people. These services include the purification of air and water, soil fertility, climate regulation, and the provision of food and raw materials.
One of the significant economic sectors in Mauritania is the fish industry, which heavily depends on the country’s coastal and marine resources. The fish industry contributes to the country’s GDP and provides employment opportunities for many locals, contributing to the socio-economic development of the nation.
Despite the immense value of biodiversity and the economic benefits it provides, there are several threats that pose a risk to Mauritania’s delicate ecosystems. Overfishing, habitat fragmentation, and climate change are some of the challenges that need urgent attention and conservation efforts.
Efforts are underway to monitor and conserve biodiversity in Mauritania. The government, in collaboration with local communities and international organizations, is implementing sustainable practices and regulations to protect the country’s natural resources. By promoting responsible fishing practices, supporting habitat restoration, and raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation, Mauritania aims to safeguard its unique and valuable ecosystems for future generations.
Biodiversity Conservation Initiatives in Mauritania
Mauritania has undertaken various initiatives to protect and conserve its biodiversity. These include:
- Establishment of protected areas to preserve critical habitats and species diversity.
- Implementation of sustainable land and water management practices to prevent habitat degradation.
- Collaboration with international organizations and research institutions to share knowledge and best practices in biodiversity conservation.
- Educational programs and public awareness campaigns to promote the importance of biodiversity and sustainable practices among local communities.
These efforts are essential in ensuring the long-term survival of Mauritania’s unique ecosystems and the sustainable use of its natural resources. By valuing and protecting biodiversity, Mauritania can secure a resilient future for its environment, economy, and people.
| Ecosystem Services |
Importance |
| Air and water purification |
Ensures clean and healthy environments for both people and wildlife |
| Soil fertility |
Sustains agricultural productivity and contributes to food security |
| Climate regulation |
Helps mitigate the impacts of climate change by regulating temperature and rainfall patterns |
| Food and raw materials |
Provides essential resources for human livelihoods and economic activities |
Protected Areas in Mauritania
Mauritania boasts several protected areas that play a critical role in the conservation of its rich biodiversity. These protected areas are managed with a focus on sustaining natural resources and preserving the country’s unique ecosystems.
One notable protected area is the Banc d’Arguin National Park, recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site. This coastal wetland is of international significance and serves as a breeding ground for a diverse range of marine species and water birds. The park’s pristine habitats support the sustenance and reproduction of various species, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the region.
Additionally, the Diawling National Park is an essential site for migratory birds and marine species. Its rich coastal and marine ecosystems provide vital resources and habitats for numerous species. The park serves as a sanctuary and a safe passage for these migratory species, playing a significant role in their conservation.
These protected areas are also classified as Ramsar sites, which are wetland areas of international importance. These designations emphasize the ecological value of these habitats and the need for their sustainable management and conservation.
As part of international conservation efforts, these protected areas are meticulously managed to ensure the preservation of biodiversity and the sustainable utilization of natural resources. They serve as models for effective conservation practices and inspire similar initiatives around the world.

Threats to Biodiversity in Mauritania
Like many other countries, Mauritania faces various threats to its biodiversity. Overgrazing by livestock, desertification, climate change, and pollution pose significant challenges to the vegetation and wildlife populations in the country.
Overgrazing, primarily driven by livestock rearing, leads to the depletion of vegetation, soil erosion, and the destruction of habitats. It negatively impacts biodiversity by reducing the availability of food and shelter for plant and animal species. Efforts are being made to promote sustainable land management practices and implement grazing management plans to mitigate the impacts of overgrazing.
Desertification is another major threat to biodiversity in Mauritania. The expansion of desert areas due to factors such as deforestation, drought, and unsustainable agricultural practices leads to the loss of plant and animal species and the degradation of ecosystems. Conservation initiatives focus on restoring degraded lands, implementing reforestation programs, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
“Climate change poses significant risks to biodiversity in Mauritania,” says Dr. Ahmed, an environmental scientist. “Rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events affect the distribution and abundance of species. It can lead to shifts in habitat ranges, alter natural ecosystems, and disrupt the delicate balance of biodiversity.”
Pollution from industrial activities and improper fishing practices threatens marine ecosystems in Mauritania. Industrial pollution, including the discharge of chemicals and waste into water bodies, leads to water contamination and the destruction of marine habitats. Improper fishing practices, such as overfishing and destructive fishing methods, deplete fish stocks and harm marine biodiversity. Stringent regulations on industrial activities, improved waste management practices, and the enforcement of sustainable fishing practices are essential for safeguarding marine ecosystems.
Awareness and measures are being implemented to address these threats to biodiversity in Mauritania. Sustainable land management practices, such as conservation agriculture and agroforestry, aim to restore degraded lands and improve soil fertility. Climate change adaptation strategies, including the promotion of renewable energy sources and the development of climate-resilient infrastructure, help mitigate the impacts of climate change on biodiversity.
The government of Mauritania has also established regulations on fishing practices to ensure sustainable resource management. Environmental impact assessments are conducted for industrial projects to minimize their negative effects on biodiversity. These initiatives, coupled with education and awareness programs, contribute to the conservation and protection of Mauritania’s unique biodiversity.
By addressing threats such as overgrazing, desertification, climate change, and pollution, Mauritania can preserve its rich biodiversity for future generations and create a sustainable environment for both wildlife and local communities.
National Biodiversity Strategy in Mauritania
Mauritania has developed a National Biodiversity Strategy (NBSAP) to guide conservation efforts and promote the sustainable use of biodiversity. The NBSAP is a comprehensive framework that encompasses various aspects of biodiversity conservation, including awareness, preservation, investment, equitable use, policy coherence, and knowledge sharing.
The NBSAP sets specific targets, actions, indicators, and costs for implementation, ensuring a systematic approach to conservation. By aligning with the Aichi Biodiversity Targets and relevant Millennium Development Goals, Mauritania is making significant progress in safeguarding its rich ecological heritage.
“The National Biodiversity Strategy outlines our commitment to preserving biodiversity and ensuring its sustainable utilization. Through coordinated efforts, we aim to protect our natural resources, enhance environmental resilience, and foster harmony between humans and nature.” – Minister of Environment and Sustainable Development
Conservation Targets
The National Biodiversity Strategy sets ambitious conservation targets to address the challenges facing Mauritania’s biodiversity. These targets include preserving and restoring critical habitats, conserving endangered species, promoting sustainable resource management, and integrating biodiversity considerations into development plans and policies.
Policy Coherence
An essential aspect of the National Biodiversity Strategy is policy coherence, ensuring that biodiversity conservation is integrated into various sectors and decision-making processes. This approach facilitates the harmonization of environmental protection with economic development, agriculture, fisheries, energy, and other relevant sectors.
Knowledge Sharing
The NBSAP emphasizes the importance of knowledge sharing among stakeholders, including government agencies, non-governmental organizations, local communities, and research institutions. By fostering collaboration, sharing best practices, and promoting scientific research, Mauritania aims to enhance its understanding of biodiversity and strengthen conservation efforts.
Through the National Biodiversity Strategy, Mauritania is committed to safeguarding its unique ecological heritage and promoting sustainable development for the benefit of present and future generations.
Conservation Measures and Actions in Mauritania
Mauritania is committed to implementing a range of conservation measures and actions to enhance the protection of its unique biodiversity. These initiatives focus on preserving natural resources, promoting renewable energy sources, studying carbon stocks, and integrating environmental impact assessments into development projects.
One significant aspect of conservation in Mauritania is the emphasis on preserving natural resources. The country recognizes the importance of maintaining the balance between human activities and ecosystem health. By implementing sustainable practices, such as responsible fishing, land management, and water resource management, Mauritania aims to ensure the long-term viability of its natural resources.
Renewable energy plays a crucial role in Mauritania’s conservation efforts. The country has significant potential for harnessing solar and wind energy, and efforts are underway to increase the use of renewable energy sources. This not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also helps mitigate climate change, reducing the environmental impact of energy generation.
Studying carbon stocks is another important aspect of conservation in Mauritania. Understanding the amount of carbon stored in forests, wetlands, and other ecosystems is crucial for formulating effective climate change mitigation strategies. By conducting research and monitoring carbon stocks, the country can make informed decisions regarding land use and the protection of carbon-rich areas.
“Conservation in Mauritania is not limited to protecting biodiversity; it is also about considering the environmental impact of development projects. Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) play a crucial role in evaluating the potential social, economic, and environmental consequences of proposed projects. By incorporating EIAs into the decision-making process, Mauritania can ensure that development is carried out in a sustainable and environmentally responsible manner.”
Mauritania recognizes the importance of collaboration with international organizations and research institutions in implementing effective conservation measures. By sharing knowledge, expertise, and best practices, Mauritania can enhance its conservation efforts and benefit from global experiences and insights.

Conservation Measures in Mauritania – Overview
| Conservation Measures |
Description |
| Promotion of renewable energy sources |
Increasing the use of solar and wind energy to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change. |
| Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) |
Evaluating the potential social, economic, and environmental consequences of development projects to ensure sustainable and responsible development. |
| Preserving natural resources |
Implementing sustainable practices in fishing, land management, and water resource management to maintain the balance between human activities and ecosystem health. |
| Studying carbon stocks |
Researching and monitoring the amount of carbon stored in ecosystems to inform land use decisions and climate change mitigation strategies. |
Capacity-building and Support Mechanisms in Mauritania
Mauritania recognizes the importance of capacity-building and support mechanisms in driving effective implementation of biodiversity conservation. To achieve this, the country has implemented various measures including sectoral reform, inter-sectoral coordination, and institutional development. These efforts aim to enhance the country’s ability to manage and protect its natural resources sustainably.
One of the key frameworks guiding environmental policy in Mauritania is the National Action Plan for the Environment (PANE). The PANE provides a comprehensive roadmap for addressing environmental challenges and promoting sustainable development. It outlines specific goals, objectives, and actions to be undertaken across various sectors to ensure effective environmental management and conservation.
Furthermore, Mauritania has developed the National Strategy for Sustainable Development (SNDD) as a blueprint for long-term environmental planning and sustainable development. The SNDD sets forth strategic objectives and action plans to integrate social, economic, and environmental considerations into decision-making processes.
In addition to these overarching policy frameworks, Mauritania has also implemented specific strategies for protected areas management. These strategies prioritize the conservation and sustainable use of protected areas, aiming to preserve their ecological values and promote local livelihoods.
“Capacity-building is crucial for effective biodiversity conservation. It equips individuals and institutions with the knowledge, skills, and resources needed to protect and manage our natural resources sustainably. Through capacity-building initiatives, Mauritania is ensuring that its environmental policies and strategies are implemented effectively, leading to positive outcomes for both the environment and local communities.” – Environmental Expert
Mauritania’s commitment to capacity-building and support mechanisms underscores its dedication to environmental stewardship and sustainable development. By strengthening institutional capacities, fostering inter-sectoral collaboration, and implementing targeted strategies, the country is taking significant steps towards achieving its environmental conservation goals.
Capacity-building Initiatives
Mauritania has undertaken a range of initiatives to build capacity at various levels, including:
- Providing training programs and workshops on biodiversity conservation, environmental management, and sustainable development for government officials, local communities, and relevant stakeholders.
- Collaborating with international organizations and research institutions to access expertise and resources that support capacity-building efforts.
- Establishing partnerships with civil society organizations and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) to facilitate knowledge sharing and community engagement in environmental conservation initiatives.
- Incorporating environmental education into school curricula to promote awareness and understanding of biodiversity, conservation, and sustainable development among young generations.
Support Mechanisms
In addition to capacity-building initiatives, Mauritania has implemented support mechanisms to facilitate effective environmental management and conservation. These include:
- Establishing monitoring and evaluation systems to assess the effectiveness of environmental policies and strategies, and to track progress towards conservation targets.
- Encouraging public participation in decision-making processes, ensuring that local communities have a voice in environmental management and conservation initiatives.
- Promoting research and innovation in environmental sciences, enabling the development of evidence-based strategies and solutions to address biodiversity conservation challenges.
- Developing financial mechanisms, such as grants, loans, and subsidies, to support sustainable environmental projects and initiatives.
Summary of Capacity-building and Support Mechanisms in Mauritania
| Initiative |
Description |
| Training and workshops |
Providing capacity-building programs on biodiversity conservation, environmental management, and sustainable development. |
| Collaboration with international organizations |
Partnering with international organizations and research institutions to access expertise and resources. |
| Partnerships with civil society organizations |
Facilitating knowledge sharing and community engagement in environmental conservation initiatives. |
| Integration of environmental education |
Incorporating biodiversity, conservation, and sustainable development into school curricula. |
| Monitoring and evaluation systems |
Assessing the effectiveness of environmental policies and strategies and tracking progress towards conservation targets. |
| Public participation |
Ensuring the inclusion of local communities in decision-making processes related to environmental management and conservation. |
| Research and innovation |
Promoting scientific research and innovation to address conservation challenges. |
| Financial mechanisms |
Developing funding options to support sustainable environmental projects and initiatives. |

World Heritage Sites in Mauritania
Mauritania is proud to host two UNESCO World Heritage Sites that celebrate both its cultural and natural heritage. These sites are the Ancient Ksour of Ouadane, Chinguetti, Tichitt, and Oualata, and the Banc d’Arguin National Park.
The Ancient Ksour of Ouadane, Chinguetti, Tichitt, and Oualata are cultural gems that transport visitors back to the 11th and 12th centuries. These ancient ksour, or fortified towns, played a vital role in trade and Islamic culture. Today, visitors can explore the well-preserved architectural marvels and experience the rich history and heritage of these sites.
“The Ancient Ksour of Ouadane, Chinguetti, Tichitt, and Oualata are a testament to the architectural and cultural brilliance of Mauritania’s past. These sites offer a window into the significant role that Mauritania played in the region’s historical trade routes and Islamic intellectual tradition.”
The Banc d’Arguin National Park, on the other hand, is a natural wonder that encompasses a diverse range of ecosystems. Located along the Atlantic coast, this national park is home to breathtaking sand dunes, picturesque islands, and vibrant coastal waters. Its unique blend of terrestrial and marine habitats supports a rich array of wildlife, including migratory birds, dolphins, and sea turtles.
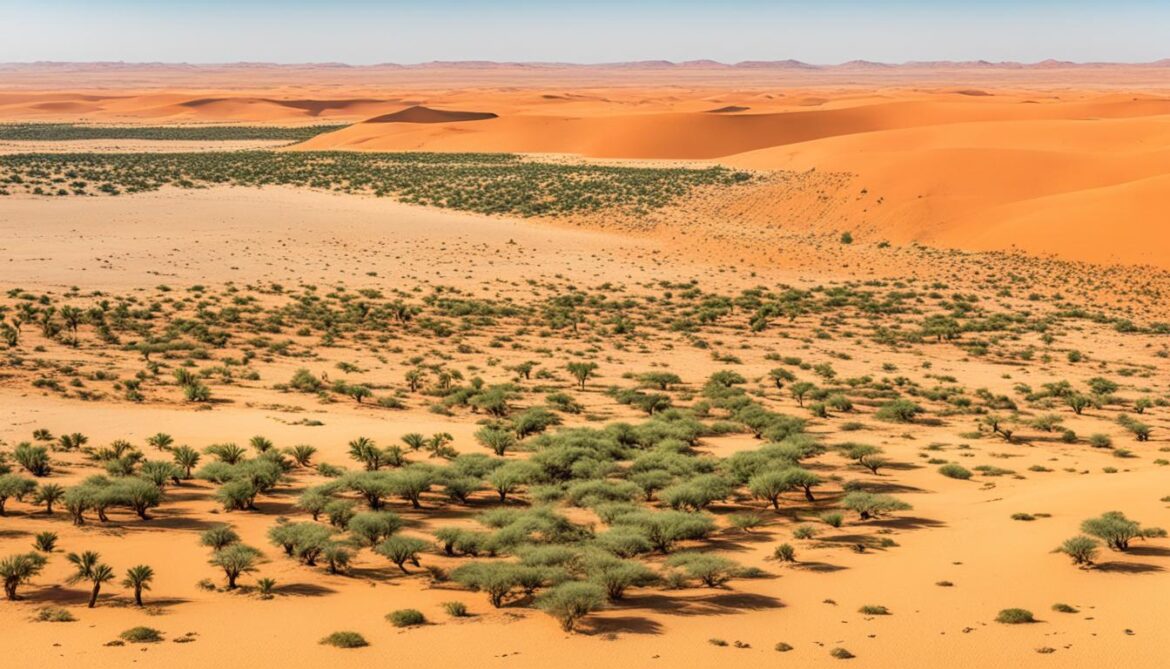

These World Heritage Sites are testaments to the rich history and natural beauty of Mauritania. Whether exploring the ancient towns or immersing oneself in the stunning landscapes of the national park, visitors are sure to be captivated by the cultural and natural heritage that Mauritania has to offer.
Vegetation Zones and Wildlife in Mauritania
Mauritania boasts diverse vegetation zones that are influenced by varying degrees of aridity. In the southern region, the country is adorned with the lush Sudanic savanna. This verdant landscape is home to majestic baobab and palmyra palm trees, creating a vibrant and enchanting environment.
Transitioning towards the southern edge of the Sahara, we enter the Sahel region. Here, the vegetation becomes sparser, characterized by the presence of acacias, euphorbia bushes, and resilient grasses. It’s a delicate belt that demonstrates nature’s resilience within a challenging environment.
As we venture further north, the landscape transforms into a picturesque desert terrain. The vegetation diminishes significantly, making way for stunning desert landscapes that stretch as far as the eye can see. This ethereal realm captures the imagination and ignites a sense of awe.
The diverse vegetation zones of Mauritania are not just a sight to behold; they are also home to a remarkable array of wildlife populations. The Sudanic savanna and steppe regions provide a sanctuary for gazelles, ostriches, warthogs, and even the elusive panthers. These majestic creatures call these habitats their home, relying on the delicate balance of nature to thrive.
Conservation efforts are essential in preserving these vegetation zones and protecting the wildlife populations they support. Through sustainable management practices and heightened awareness, we can ensure the longevity of these habitats and the well-being of the resident species.
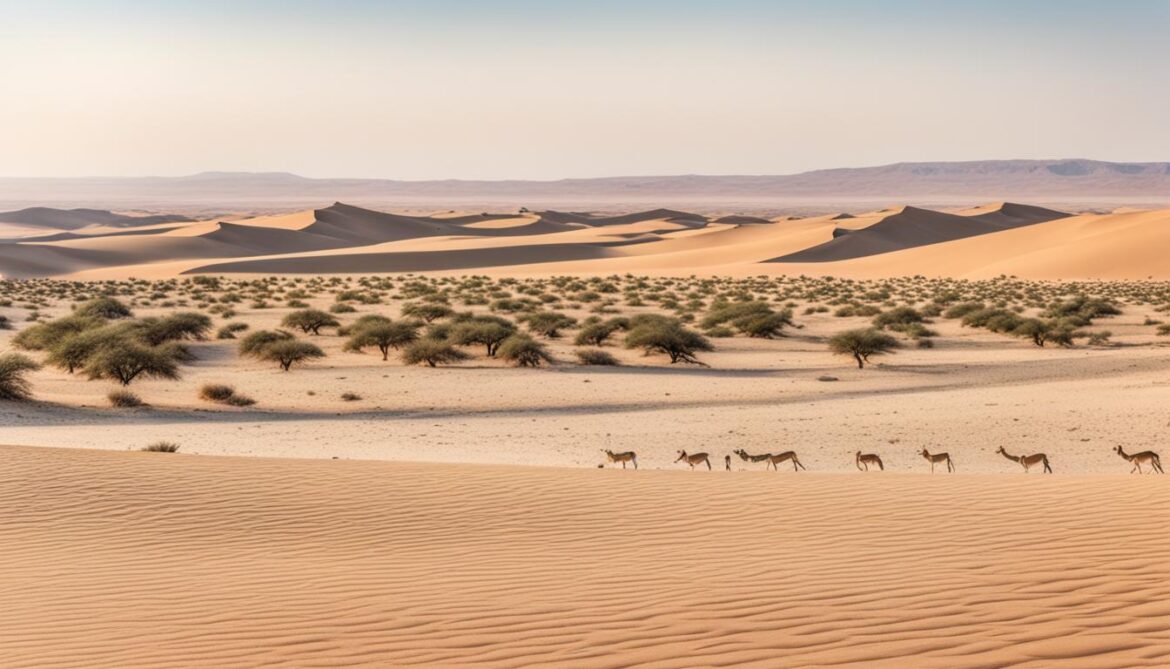

Exploring the rich vegetation zones and encountering the diverse wildlife of Mauritania is an awe-inspiring journey. The interconnectedness between the vegetation and the wildlife creates a delicate tapestry that we must strive to protect. By valuing and preserving these unique ecosystems, we can ensure a harmonious coexistence between humans and the natural world.
Ethnic Diversity in Mauritania
Mauritania is a country known for its diverse range of ethnic groups, each contributing to the cultural fabric of the nation. Understanding the country’s ethnic diversity is key to appreciating its rich heritage and social dynamics.
Moors: Ḥarāṭīn and Bīḍān
The majority population in Mauritania consists of Moors, a group of people with a shared Arab-Berber heritage. Within the Moorish community, there are two distinct subgroups: Ḥarāṭīn and Bīḍān. The Ḥarāṭīn are traditionally descendants of enslaved individuals, while the Bīḍān are considered to be noble or “white Moors.” This social division has had a historical influence on the country’s social structure and dynamics.
- Ethnic groups: Moors, Ḥarāṭīn, Bīḍān
Other Ethnic Groups
Aside from the Moors, there are several other ethnic groups in Mauritania, each with their own distinct cultural practices and languages. These include:
- Tukulor: The Tukulor people are primarily found in the southern regions of the country. They have a rich agricultural heritage and are known for their cultural traditions.
- Fulani: The Fulani people are semi-nomadic pastoralists who have historically played a significant role in cattle herding activities in Mauritania.
- Soninke: The Soninke people have a long history in the region and are known for their agricultural practices, craftsmanship, and trading skills.
- Wolof: The Wolof people, who predominantly reside in the northern regions of Mauritania, have a rich cultural heritage, including music, dance, and storytelling traditions.
- Ethnic groups: Tukulor, Fulani, Soninke, Wolof
Historical Social Structure
Traditionally, Mauritania’s social structure has been hierarchical, with a clear distinction between different classes within society. In the past, the nobles and vassals occupied the top tier, followed by artisans, and then the servant classes. This structure has influenced societal dynamics and relationships among different ethnic groups.
“The historical social structure in Mauritania has influenced social relationships and dynamics among different ethnic groups.”
- Social structure: Hierarchical
Efforts towards Inclusivity
In recent years, efforts have been made to address social inequalities and promote inclusivity among different ethnic groups in Mauritania. The government and various organizations are working towards fostering a more equitable society, where all citizens can actively participate and contribute to the nation’s growth and development.
Image: Ethnic Diversity in Mauritania
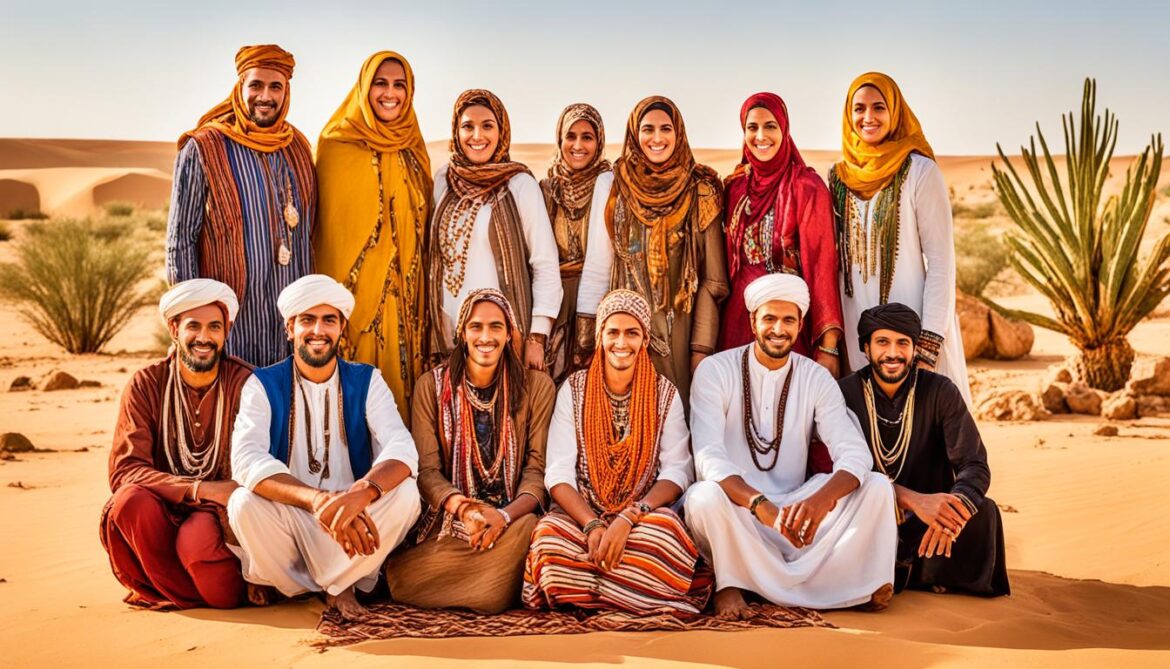

The image above visually represents the diverse ethnic groups in Mauritania, showcasing the unique cultural traditions and identities that contribute to the nation’s multicultural tapestry.
Languages in Mauritania
In Mauritania, the official language is Arabic, with the majority of the population speaking Ḥassāniyyah Arabic. This form of Arabic has been influenced by the local dialects and is widely understood and spoken across the country. Additionally, there are other national languages spoken in Mauritania, including Fula, Soninke, and Wolof. These languages are part of the Niger-Congo language family and are primarily spoken by specific ethnic groups in the country.
Due to the prominence of Arabic in Mauritania, it has become the primary language of instruction in schools. However, efforts are being made to preserve and promote the use of other languages in educational settings to maintain cultural diversity and ensure inclusivity. Recognizing the importance of multilingualism, initiatives are underway to incorporate Fula, Soninke, and Wolof into the curriculum, allowing students to learn and appreciate the richness of these languages.
Promoting Language Diversity
Preserving and promoting the use of Fula, Soninke, and Wolof in educational settings is vital for maintaining cultural heritage and fostering inclusivity. It allows individuals from different ethnic backgrounds to express themselves freely and engage fully in the learning process. Moreover, embracing language diversity contributes to a deeper understanding and appreciation of the various cultures within Mauritania.
Language is not only a means of communication but also a vessel for cultural expression and identity. By promoting the use of multiple languages in education, Mauritania can preserve its linguistic diversity and ensure that future generations have a strong connection to their cultural roots.
Benefits of Multilingual Education
A multilingual education system offers several benefits, both academically and culturally. It enhances cognitive development, as studies show that individuals who are proficient in multiple languages exhibit improved problem-solving skills and enhanced creativity. Moreover, learning in one’s mother tongue fosters a stronger sense of identity and self-confidence. By integrating Fula, Soninke, and Wolof into the education system, Mauritania can provide students with a well-rounded and inclusive learning experience.
In conclusion, while Arabic remains the official language of Mauritania, efforts are being made to promote the use of other languages, such as Fula, Soninke, and Wolof, in educational settings. Embracing language diversity not only enriches the educational experience but also preserves the cultural heritage of different ethnic groups in Mauritania. By nurturing linguistic diversity, Mauritania can create a more inclusive and vibrant society.
Conclusion
Mauritania’s sacred natural sites and rich biodiversity are of immense value both culturally and ecologically. These sites, along with the diverse ecosystems found in the country, play a vital role in sustainable development and the well-being of local communities. Conservation and protection efforts are essential to ensure the preservation of Mauritania’s natural heritage for future generations.
Collaboration between government entities, international organizations, and local communities is crucial for the success of conservation and sustainable management initiatives. By working together, we can enhance the understanding and appreciation of the interplay between spirituality and nature in Mauritania’s sacred sites, promoting a deeper connection between culture and the environment.
Furthermore, the integration of traditional knowledge in conservation practices can lead to innovative solutions that balance the preservation of biodiversity with the needs and aspirations of local communities. Through continued conservation efforts, research, and education, Mauritania can create a sustainable future that harmoniously coexists with its natural landscapes and cultural heritage.
In conclusion, the protection and conservation of Mauritania’s sacred natural sites and biodiversity are paramount. By recognizing the significance of these sites, collaborating with stakeholders, and integrating traditional knowledge, we can ensure the preservation of Mauritania’s unique natural heritage for generations to come.
FAQ
What is the importance of sacred natural sites in Mauritania?
Sacred natural sites in Mauritania play a crucial role in conserving the country’s unique natural heritage and are of great cultural and spiritual significance to local communities.
What is the biodiversity like in Mauritania?
Mauritania is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, supporting a wide variety of plant and animal species. The country’s biodiversity is rich and unique.
What are some threats to biodiversity in Mauritania?
Overgrazing, desertification, climate change, pollution, and improper fishing practices are some of the threats to biodiversity in Mauritania.
What is the National Biodiversity Strategy in Mauritania?
The National Biodiversity Strategy (NBSAP) in Mauritania guides conservation efforts and promotes the sustainable use of biodiversity.
What conservation measures are being implemented in Mauritania?
Mauritania has implemented various conservation measures, including preserving natural resources, promoting renewable energy sources, and integrating environmental impact assessments into development projects.
How is capacity-building and support for biodiversity conservation being addressed in Mauritania?
Mauritania is focused on capacity-building, inter-sectoral coordination, and institutional development to effectively implement biodiversity conservation.
What are the World Heritage Sites in Mauritania?
Mauritania is home to two UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the Ancient Ksour and the Banc d’Arguin National Park.
What are the vegetation zones and wildlife in Mauritania?
Mauritania has various vegetation zones, including the Sudanic savanna, Sahel, and desert landscapes, which are inhabited by wildlife such as gazelles, ostriches, warthogs, and panthers.
What is the ethnic diversity like in Mauritania?
Mauritania is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups, including Moors, Ḥarāṭīn, Bīḍān, Tukulor, Fulani, Soninke, and Wolof.
What languages are spoken in Mauritania?
Arabic is the official language, with Ḥassāniyyah Arabic being the widely spoken dialect. Other national languages include Fula, Soninke, and Wolof.
How can we preserve the sacred natural sites and biodiversity in Mauritania?
Preserving the sacred natural sites and biodiversity in Mauritania requires collaboration between government entities, international organizations, and local communities, as well as the integration of traditional knowledge.

























Post comments (0)