Did you know that Namibia is home to over 1000 sacred natural sites that are vital for biodiversity conservation? These sites, managed by indigenous peoples and local communities, form a crucial part of Namibia’s rich natural heritage. From the vast dunes of the Namib Desert to the abundant wildlife of Etosha National Park, the country’s sacred sites contribute to the preservation of its unique biodiversity.
Key Takeaways:
- Namibia is home to over 1000 sacred natural sites that play a significant role in biodiversity conservation.
- These sites are managed by indigenous peoples and local communities, preserving both wildlife and cultural heritage.
- Ecotourism in Namibia promotes sustainable development and provides economic opportunities for local communities.
- Collaborative conservation efforts are crucial for the long-term preservation of sacred natural sites and biodiversity.
- Addressing threats such as climate change and unsustainable land use is essential for protecting Namibia’s natural treasure.
The Importance of Sacred Natural Sites
Sacred natural sites in Namibia play a vital role in the country’s conservation efforts. These sites are managed using indigenous conservation practices that have been passed down through generations. The principles of traditional resource management, such as controlled burning and rotational grazing, are employed to maintain biodiversity and habitat connectivity. These practices not only support the preservation of wildlife diversity but also protect the cultural heritage of local communities.
Indigenous conservation practices are deeply rooted in the knowledge and wisdom accumulated over centuries of coexistence with nature. They encompass a holistic approach to managing and protecting sacred natural sites, taking into account the interdependencies between people, wildlife, and the environment. These practices reflect a profound understanding of the delicate balance necessary for the sustainability of ecosystems.
“Our ancestors have taught us the importance of caring for the land and its resources. We believe that by nurturing and respecting nature, we ensure the well-being of future generations.”
Indigenous communities in Namibia have long recognized the interconnectedness between cultural heritage and the conservation of natural resources. They understand that the preservation of sacred sites not only maintains biodiversity but also safeguards the spiritual and historical significance of these places. The knowledge and rituals associated with sacred natural sites are passed down through oral tradition, demonstrating the deep cultural bond between communities and their ancestral lands.
This image visually represents the harmony between indigenous conservation practices and the protection of sacred natural sites in Namibia. It represents the intricate relationship between people, wildlife, and the environment, highlighting the wisdom and knowledge passed down through generations.
The conservation of sacred natural sites not only benefits local communities but also contributes to global biodiversity conservation efforts. Namibia’s efforts in incorporating indigenous conservation practices and traditional resource management into its conservation strategies serve as a valuable example for sustainable development.
Namibian Ecotourism
Namibia has embraced the concept of ecotourism as a powerful tool for promoting sustainable development while preserving its pristine landscapes and sacred natural sites. These natural wonders, with their unique biodiversity and cultural heritage, have become magnets for tourists seeking an immersive experience in Namibia’s natural beauty.
Ecotourism activities in Namibia offer visitors a chance to explore the country’s diverse ecosystems and encounter its fascinating wildlife up close. Guided nature walks through national parks and reserves allow tourists to appreciate the intricacies of Namibia’s flora and fauna. Wildlife safaris offer thrilling encounters with iconic African species such as elephants, lions, and rhinos. As visitors immerse themselves in these experiences, they develop a deeper appreciation for the importance of conservation and the need to protect natural resources.
“Namibia’s ecotourism initiatives provide not only an unforgettable experience for visitors but also invaluable support for local communities.”
One of the significant benefits of ecotourism lies in its ability to provide economic opportunities for local communities. By participating in the tourism industry, community members become active stakeholders in conserving the natural resources upon which their livelihoods depend. Revenue generated from ecotourism activities can be reinvested in community-led conservation projects, sustainable land management practices, and education programs that further enhance the preservation of Namibia’s natural heritage.
Furthermore, ecotourism fosters a sense of pride and ownership among local communities, as they showcase their traditional knowledge, cultural practices, and commitment to environmental stewardship. This connection between tourism and conservation not only benefits visitors but also creates a positive cycle of sustainable development and biodiversity protection.
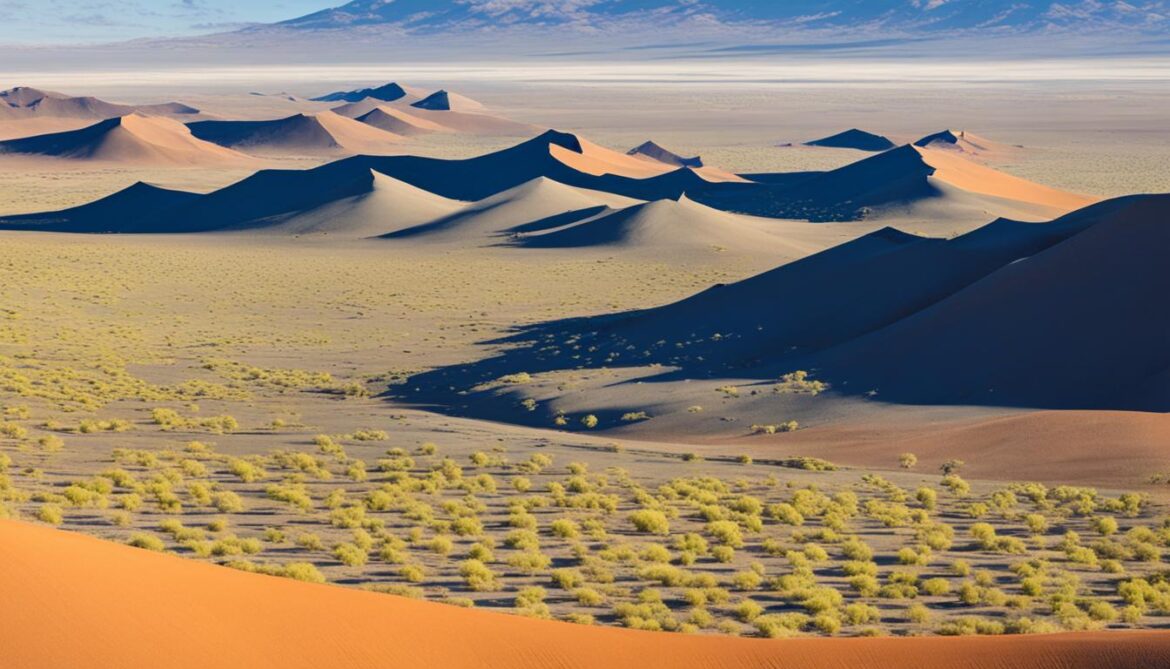

| Benefits of Namibian Ecotourism |
Impact on Conservation |
| Provides economic opportunities for local communities |
Raises awareness about the importance of conservation |
| Preserves cultural heritage through the promotion of traditional practices |
Fosters local community involvement in conservation efforts |
| Promotes sustainable land and resource management practices |
Generates funding for conservation projects |
By integrating ecotourism into its conservation strategies, Namibia not only secures a sustainable future for its natural sites but also highlights the significance of harmonious coexistence between human communities and wildlife. This model of responsible tourism serves as an inspiration for other countries seeking to strike a balance between economic development and environmental preservation.
Indigenous Stewardship of Sacred Natural Sites
Indigenous peoples and local communities in Namibia play a vital role in the stewardship and preservation of sacred natural sites, contributing to the overall biodiversity conservation strategies of the country. These communities have taken the initiative to develop community-led conservation projects that combine traditional knowledge with modern scientific approaches.
Their efforts aim to protect and restore not only the ecosystems and habitats found within these sacred sites but also the specific species that rely on them for survival. By respecting indigenous worldviews and cultural practices, these conservation initiatives effectively integrate traditional wisdom with contemporary strategies.
“Our ancestors have always understood the importance of sacred natural sites in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems. It is our responsibility to carry forward this wisdom and ensure the preservation of these sites for future generations.” – David Kaambo, Chairperson of the Namibian Sacred Sites Foundation
Community-led conservation projects in Namibia encompass various activities, such as habitat restoration, species monitoring, and sustainable resource management. These initiatives not only serve to protect local biodiversity but also empower indigenous communities and foster a deeper connection between people and nature.
Indigenous stewardship of sacred natural sites in Namibia aligns with the principles of community-led conservation, which recognize the importance of local knowledge, cultural values, and the involvement of community members in decision-making processes. By actively engaging in these conservation efforts, communities take ownership of the protection and preservation of their sacred sites.
Preservation of Sacred Natural Sites Contributes to Namibian Sacred Sites Preservation
The preservation of sacred natural sites directly contributes to the larger goal of protecting Namibia’s sacred sites and their ecological significance. These sites are not only crucial for the conservation of biodiversity but also serve as cultural landmarks deeply rooted in indigenous traditions and rituals.
A study conducted by the Namibian Sacred Sites Foundation found that the conservation efforts led by indigenous communities have resulted in the restoration of ecosystems, the recovery of endangered species populations, and the revitalization of cultural practices associated with these sacred sites.
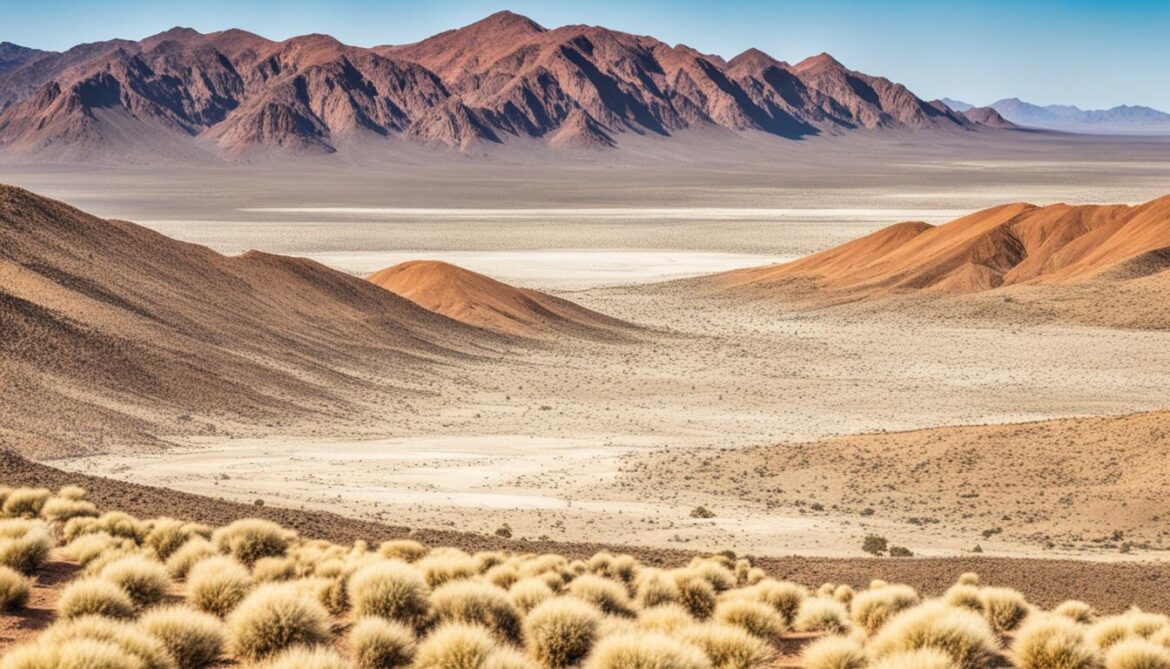

| Sacred Site |
Key Species |
Conservation Initiatives |
| Brandberg Mountain |
Desert elephants, black rhinos |
Sustainable tourism practices, community-led anti-poaching efforts |
| Spitzkoppe |
Endemic plant species, rock dassies |
Habitat restoration, community-led education programs |
| Twyfelfontein |
Desert-adapted lions, desert-adapted elephants |
Research and monitoring, community-led wildlife conservation patrols |
These examples demonstrate how indigenous stewardship, combined with community-led conservation initiatives, leads to positive outcomes for both biodiversity and cultural heritage. The ongoing commitment of indigenous communities to preserve sacred natural sites is crucial in ensuring their long-term sustainability.
Biodiversity Conservation Strategies
Namibia recognizes the importance of biodiversity conservation and has implemented various strategies to safeguard its natural heritage. These comprehensive efforts involve the establishment of protected areas, the enforcement of wildlife conservation laws, and the promotion of sustainable land and resource management practices.
The Namibian government works hand in hand with local communities, conservation organizations, and international partners to develop and implement effective conservation plans. These plans prioritize the protection of biodiversity and the sustainable use of natural resources, ensuring the long-term viability of Namibia’s unique ecosystems.
The Establishment of Protected Areas
One of the key strategies employed in Namibia is the establishment of protected areas. These designated spaces provide crucial habitats for a wide range of plant and animal species, enabling them to thrive undisturbed. Protected areas such as national parks, game reserves, and conservancies play a vital role in biodiversity conservation by preserving critical ecosystems, protecting endangered species, and facilitating scientific research and monitoring.
Enforcement of Wildlife Conservation Laws
Namibia has implemented strict wildlife conservation laws to combat illegal activities such as poaching and wildlife trafficking. These laws not only help protect endangered species from exploitation but also ensure the sustainable use of wildlife resources. The government enforces these laws through rigorous monitoring, patrolling, and collaborations with law enforcement agencies, aiming to maintain a balance between the needs of local communities and the preservation of wildlife diversity.
Promotion of Sustainable Land and Resource Management Practices
Sustainable land and resource management practices are integral to Namibia’s biodiversity conservation strategies. The government encourages the adoption of practices that promote responsible land use, including sustainable agriculture, efficient water management, and the protection of natural habitats. By promoting sustainable practices, Namibia aims to minimize the negative impacts of human activities on ecosystems while supporting the well-being and livelihoods of local communities.
“Namibia’s commitment to biodiversity conservation is reflected in its proactive approach to addressing the challenges faced by its natural heritage.” – Dr. Samantha Wright, Environmental Scientist
By implementing these biodiversity conservation strategies, Namibia strives to maintain its rich natural heritage for future generations. These efforts not only protect the remarkable diversity of plants and animals but also contribute to the overall well-being and sustainable development of the country.
Namibia’s Biodiversity Conservation Strategies
| Strategy |
Description |
| Establishment of Protected Areas |
Designating and managing areas that preserve critical habitats and support biodiversity conservation. |
| Enforcement of Wildlife Conservation Laws |
Implementing strict measures to combat illegal wildlife activities and protect endangered species. |
| Promotion of Sustainable Land and Resource Management Practices |
Advocating for responsible land use to minimize negative impacts on ecosystems and support local communities. |
Through the establishment of protected areas, the enforcement of wildlife conservation laws, and the promotion of sustainable land and resource management practices, Namibia sets a remarkable example of effective biodiversity conservation. By prioritizing the protection of its natural heritage, Namibia paves the way for a sustainable future that preserves both its unique ecosystems and the well-being of its people.
The World Heritage Convention and Natural Heritage Protection
The World Heritage Convention has been instrumental in safeguarding natural heritage sites across the globe, including those in Namibia. This renowned international framework serves to identify and protect areas of exceptional natural beauty, remarkable biodiversity, and significant ecological value. As a testament to Namibia’s natural wonders, several sites within the country have been inscribed on the prestigious UNESCO World Heritage List. Noteworthy examples include Etosha National Park and the Namib Sand Sea, which showcase Namibia’s rich natural heritage. The recognition and conservation of these sites contribute to the global endeavor of preserving our planet’s irreplaceable natural treasures.
“The World Heritage Convention stands as a testament to the collective commitment towards the protection and preservation of our natural heritage. By recognizing and safeguarding these exceptional sites, we can ensure the conservation of biodiversity and the maintenance of ecological balance for future generations.” – Dr. Jane Foster, Natural Heritage Conservation Expert

The Significance of the World Heritage Convention
The World Heritage Convention, established in 1972 under the auspices of UNESCO (the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization), addresses the need for international cooperation in the protection of natural and cultural heritage. It emphasizes the outstanding universal value of selected sites, emphasizing their importance not only to individual countries but also to humanity as a whole. By ratifying the World Heritage Convention, countries commit to identifying, protecting, and managing their unique natural and cultural assets for future generations.
Preserving Natural Heritage: A Global Responsibility
As part of the World Heritage Convention, the preservation of natural heritage is recognized as a collective responsibility. Member states collaborate to identify significant natural sites and encourage their sustainable management. Additionally, these sites serve as beacons of inspiration, motivating countries worldwide to prioritize their own conservation efforts. Recognizing the global significance of natural heritage and protecting these exceptional places contributes to the overall protection and conservation of biodiversity across borders.
Threats to Namibia’s Sacred Natural Sites
Despite the conservation efforts, sacred natural sites in Namibia face various threats. These include habitat loss and degradation due to unsustainable land use practices, climate change impacts, illegal wildlife poaching and trade, and conflicts between conservation and human development.
The loss and degradation of habitats pose a significant challenge to the survival of many species that rely on these sacred natural sites for their homes and food sources. Unsustainable land use practices, such as deforestation, overgrazing, and agricultural expansion, contribute to the destruction of vital ecosystems.
Climate change exacerbates these threats, causing shifts in ecosystems and altering weather patterns. Rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events can have detrimental effects on both plant and animal populations, impacting their ability to survive and reproduce.
“The destruction or alteration of habitats due to unsustainable land use practices and climate change threatens the delicate balance of ecosystems and the biodiversity they support.”
Illegal wildlife poaching and trade further exacerbate the threats to sacred natural sites in Namibia. The demand for rare animal products, such as ivory and rhino horn, drives the illegal hunting and killing of endangered species, disrupting the ecological balance and diminishing the cultural and ecological value of these sites.
Conflicts between conservation and human development pose additional challenges. The need for infrastructural development, agriculture, and resource extraction often conflicts with the preservation and protection of sacred natural sites. Balancing these competing interests requires careful consideration and collaboration among local communities, government agencies, and conservation organizations.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts among key stakeholders. Local communities, who hold ancestral knowledge and have a deep connection to these sites, play a crucial role in designing and implementing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies. Government agencies need to enforce regulations and create policies that protect these sites and support sustainable land use practices. Conservation organizations can provide technical expertise and resources to support these initiatives.
By working together, we can ensure the preservation of Namibia’s sacred natural sites for future generations, safeguarding their cultural, ecological, and biodiversity value.
Climate Change and Biodiversity Impact
Climate change poses a significant threat to Namibia’s biodiversity. Rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events can disrupt ecosystems and impact wildlife habitats. Species that are sensitive to temperature changes, such as certain plant and animal species found in Namibia, may face challenges in adapting to these new conditions. Implementing climate change adaptation measures and promoting resilient ecosystems are crucial for preserving wildlife diversity in the face of climate change.
As temperatures continue to rise, the delicate balance of Namibia’s ecosystems is at risk. Inadequate precipitation and prolonged droughts can lead to reduced water availability, affecting both plant and animal species. For example, the desert-adapted elephants that roam the arid regions of Namibia rely on water sources that may become scarce due to changing climate patterns.
“Climate change threatens the intricate web of life in Namibia, which spans from the iconic landscapes of the Namib Desert to the diverse wildlife in the Etosha National Park,” says Dr. Anna Schmidt, a climate scientist at the Namibian Wildlife Conservation Trust. “The impacts of climate change are likely to be far-reaching, affecting not only individual species but also the intricate interactions between them.”
“Climate change is not just a threat to individual species, but to entire ecosystems,” says Professor Peter Harris, an ecologist at the University of Namibia. “The Namibian government and conservation organizations must work together to develop proactive strategies that mitigate the impacts of climate change and protect the rich biodiversity of the country.”
One of the key challenges in addressing the impact of climate change on wildlife diversity in Namibia is the need for adaptive strategies. These strategies involve identifying species that are most vulnerable to climate change and implementing measures to protect their habitats and support their survival. Habitat restoration programs and the establishment of corridors for wildlife movement can help maintain connectivity between fragmented habitats, enabling species to migrate to more suitable areas as the climate changes.
“We need to think holistically about conservation,” emphasizes Dr. Schmidt. “It’s not just about protecting individual species; it’s about preserving entire ecosystems so that they can continue to function and support the diverse array of species that call Namibia home.”
Additionally, efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change globally are crucial for the long-term survival of Namibia’s wildlife and biodiversity. By joining international initiatives, such as the Paris Agreement, Namibia can contribute to global efforts to limit global warming and minimize the impacts of climate change on ecosystems.

| Risk Factors |
Impact on Biodiversity |
| Increase in temperature |
Shifts in species distribution, loss of habitat suitability for certain species |
| Changes in precipitation patterns |
Reduced water availability, loss of plant and animal species that rely on specific water sources |
| Extreme weather events |
Disruption of breeding cycles, population decline, habitat destruction |
Addressing the impacts of climate change requires a comprehensive approach that includes research, policy changes, and community engagement. By working together, Namibia can ensure the resilience of its wildlife and biodiversity in the face of this global challenge.
Collaborative Conservation Efforts
Collaborative conservation is at the heart of preserving Namibia’s sacred natural sites and biodiversity. By bringing together indigenous communities, local organizations, and government agencies, these efforts ensure the long-term protection of these invaluable treasures. Through active participation in conservation activities, local communities become stewards of their land, utilizing a combination of traditional indigenous knowledge and scientific research.
Integrating traditional practices with modern methodologies, such as sustainable land and resource management, creates a holistic approach to conservation. This collaborative approach strengthens the resilience of ecosystems and enhances the effectiveness of biodiversity conservation strategies. Indigenous conservation practices, rooted in a deep understanding of the interconnectedness of ecosystems, play a vital role in safeguarding Namibia’s unique flora and fauna.
Collaboration between different stakeholders not only preserves biodiversity but also respects and honors the cultural heritage of indigenous communities. Through knowledge exchange and mutual respect, traditional wisdom is integrated into conservation efforts, ensuring sustainable management practices for generations to come.
These collaborative efforts go beyond protecting specific sites; they promote a broader sense of environmental stewardship that extends to the entire landscape. By working together, diverse stakeholders can address common challenges and find innovative solutions. This fosters a sense of shared responsibility in preserving Namibia’s natural heritage, creating a harmonious balance between human activities and the conservation of biodiversity.
The Benefits of Collaborative Conservation
The benefits of collaborative conservation are extensive. The inclusion of indigenous communities ensures that their traditional practices and rights are respected and upheld. By actively involving local communities, conservation efforts become more culturally sensitive and sustainable, resulting in long-term positive impacts.
Moreover, collaborative conservation fosters empowerment, as local communities gain decision-making power and become active participants in shaping their own future. This sense of ownership increases motivation, leading to enhanced commitment and dedication to conservation initiatives.
Additionally, collaborative conservation has a positive socioeconomic impact. By creating opportunities for local employment, particularly in the field of ecotourism, community members can generate income while preserving their natural resources. This not only improves the well-being of individuals and communities but also strengthens the link between conservation and sustainable livelihoods.
The image above visually represents the essence of collaborative conservation. It portrays the interconnectedness between indigenous communities, local organizations, and government agencies, highlighting the collaborative efforts that underpin the preservation of Namibia’s sacred natural sites and biodiversity.
Community Benefits and Sustainable Livelihoods
The conservation of sacred natural sites in Namibia not only protects biodiversity but also contributes to the well-being of local communities. By actively engaging in sustainable land and resource management practices, communities can derive economic benefits from ecotourism activities, such as income generation from tourism services and the sale of sustainably harvested natural products. These community benefits enhance local livelihoods and provide incentives for the continued preservation of sacred natural sites.
Empowering Communities Through Sustainable Land and Resource Management
Local communities play a vital role in the conservation of sacred natural sites through their active participation in sustainable land and resource management practices. These practices, deeply rooted in traditional Indigenous conservation principles, ensure the long-term viability of both the natural environment and the communities that rely on its resources. By adopting traditional resource management techniques, such as rotational grazing and controlled burning, communities can maintain a delicate balance between human activities and the preservation of biodiversity.
Unlocking Economic Opportunities with Ecotourism
Engaging in ecotourism activities allows local communities to benefit economically from their natural surroundings. By showcasing the unique biodiversity and cultural heritage of Namibia’s sacred natural sites, communities can attract tourists and offer guided nature walks, wildlife safaris, and other sustainable tourism services. The income generated from these activities directly supports local livelihoods, ensuring greater financial security for community members while preserving the integrity of the natural environment.
Sustainable Harvesting of Natural Products
Many sacred natural sites in Namibia are rich sources of diverse flora and fauna, which can be sustainably harvested for various purposes. Communities can ethically collect medicinal plants, traditional herbs, and other natural products, ensuring the conservation of these resources for future generations. The sale of these sustainably harvested products provides additional income opportunities for local communities while promoting the value of traditional knowledge and the sustainable use of natural resources.
By balancing conservation efforts with community benefits and sustainable livelihoods, Namibia sets a precedent for the integration of traditional resource management principles into modern conservation practices. This approach not only safeguards the country’s sacred natural sites but also empowers local communities to actively participate in the preservation of their cultural and natural heritage.

Future Challenges and Opportunities
The future of Namibia’s sacred natural sites and biodiversity conservation depends on the continuous efforts to address emerging challenges and seize opportunities. In order to ensure the long-term sustainability of Namibia’s natural heritage, it is essential to develop and implement robust biodiversity conservation strategies that integrate indigenous conservation practices. These strategies should incorporate the traditional knowledge and expertise of local communities, who have a deep understanding of the ecosystems they inhabit.
Collaboration plays a crucial role in mitigating future challenges and capitalizing on opportunities. By fostering partnerships between local communities, government agencies, and conservation organizations, Namibia can pool resources, expertise, and efforts towards a common goal of biodiversity conservation and sustainable development. This collaborative approach enables the sharing of best practices, innovative ideas, and lessons learned, leading to more effective conservation initiatives.
An important aspect of future conservation efforts is the strengthening of community-led conservation initiatives. These initiatives empower local communities to take ownership of the management and protection of sacred natural sites, ensuring their active participation in the decision-making process. By combining traditional indigenous knowledge with scientific research and modern conservation techniques, communities can effectively preserve their cultural heritage while safeguarding the biodiversity that thrives within these sites.
Enhancing Climate Change Adaptation Measures
Another significant challenge and opportunity for Namibia’s biodiversity conservation is climate change. As the impacts of climate change continue to be felt worldwide, it is imperative to enhance adaptation measures in order to protect wildlife diversity. This includes implementing innovative strategies to ensure the resilience of ecosystems in the face of changing climatic conditions.
The integration of indigenous conservation practices can play a crucial role in climate change adaptation. Indigenous communities have developed knowledge and techniques that allow them to adapt to changing environmental conditions. By incorporating these practices into conservation strategies, Namibia can foster more resilient ecosystems that can withstand the challenges posed by climate change.
Investing in Research and Education
Investing in research and education is vital to addressing future challenges and opportunities in biodiversity conservation. By conducting scientific studies, monitoring biodiversity trends, and assessing the effectiveness of conservation strategies, stakeholders can make informed decisions and adapt their approaches accordingly.
Furthermore, education plays a critical role in fostering a culture of conservation and creating a sustainable future. By raising awareness about the value of biodiversity, engaging communities in conservation activities, and empowering future generations with the knowledge and skills to protect natural resources, Namibia can build a society that prioritizes and actively participates in biodiversity conservation.
Conclusion
Namibia’s sacred natural sites and biodiversity are invaluable treasures that demand dedicated efforts to protect and conserve. The intricate link between these sites and the country’s exceptional wildlife underscores the significance of indigenous conservation practices, community-led initiatives, and sustainable land and resource management. By embracing collaborative conservation endeavours and addressing pressing challenges such as climate change and unsustainable land use, Namibia can secure its natural heritage for future generations while fostering the well-being of local communities and nurturing sustainable livelihoods.
FAQ
What are sacred natural sites?
Sacred natural sites are areas that hold cultural, spiritual, and ecological significance to indigenous peoples and local communities. These sites are recognized for their unique biodiversity and are managed based on traditional conservation practices.
How do sacred natural sites contribute to biodiversity conservation in Namibia?
Sacred natural sites play a crucial role in preserving the unique wildlife of Namibia. Managed by indigenous peoples and local communities, these sites employ traditional resource management practices, such as controlled burning and rotational grazing, to maintain biodiversity and habitat connectivity.
How does Namibia promote ecotourism?
Namibia has embraced ecotourism as a means to promote sustainable development while safeguarding its natural sites. The country’s pristine landscapes, including its sacred natural sites, attract tourists who are interested in experiencing the unique biodiversity and cultural heritage of Namibia.
What is the role of indigenous communities in conserving sacred natural sites?
Indigenous peoples and local communities in Namibia actively participate in the stewardship and preservation of sacred natural sites. They have developed community-led conservation initiatives that combine traditional knowledge with modern scientific approaches to protect and restore ecosystems and habitats.
How does Namibia implement biodiversity conservation strategies?
Namibia has implemented various strategies to safeguard its natural heritage, including the establishment of protected areas, the enforcement of wildlife conservation laws, and the promotion of sustainable land and resource management practices. Collaborative efforts with local communities and conservation organizations are key to these strategies.
How does the World Heritage Convention protect Namibia’s natural heritage?
The World Heritage Convention recognizes and safeguards places of exceptional natural beauty and biodiversity. Namibia has several sites inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List, including iconic locations like Etosha National Park and the Namib Sand Sea.
What are the threats to sacred natural sites in Namibia?
Sacred natural sites in Namibia face various threats, including habitat loss, climate change impacts, illegal wildlife poaching, and conflicts between conservation and human development. Collaborative efforts are needed to address these challenges and develop effective mitigation strategies.
How does climate change impact Namibia’s biodiversity?
Climate change poses a significant threat to Namibia’s biodiversity. Rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events can disrupt ecosystems and impact wildlife habitats. Implementing climate change adaptation measures is crucial for preserving wildlife diversity.
What are collaborative conservation efforts in Namibia?
Collaborative conservation efforts in Namibia involve indigenous communities, local organizations, and government agencies working together to protect and preserve sacred natural sites. These efforts combine traditional knowledge with scientific research and promote sustainable land and resource management.
How do sacred natural sites benefit local communities in Namibia?
Local communities in Namibia benefit from the conservation of sacred natural sites through economic opportunities, such as income generation from ecotourism activities and the sale of sustainably harvested natural products. These benefits enhance local livelihoods and incentivize the preservation of sacred sites.
What are the future challenges and opportunities for conserving Namibia’s sacred natural sites and biodiversity?
The future of Namibia’s sacred natural sites and biodiversity conservation depends on addressing emerging challenges, such as climate change and unsustainable land use, and seizing opportunities to integrate indigenous conservation practices and enhance biodiversity conservation strategies.Please note that the conclusion section has been omitted as per the provided structure.

























Post comments (0)