Lebanon Biodiversity: Animal and Plant Species and What Is Under Threat
Lebanon is a country with immense natural beauty and is home to a remarkable array of flora and fauna. Despite its small size, Lebanon boasts a rich diversity of plant and animal species, making it a biodiversity hotspot. In fact, Lebanon occupies only 0.007% of the world’s land surface area but is home to 1.11% of the world’s plant species and 2.63% of reptile, bird, and mammal species.
Lebanon’s flora is exceptionally diverse, with about 2,600 terrestrial plant species, including some that are endemic to the region. The country also hosts tree species with critical biogeographical locations, such as the iconic Lebanese cedar (Cedrus libani). The Lebanese flora is known for its high density and unique contributions to the Mediterranean basin.
The fauna of Lebanon is equally impressive, with a diverse range of species. The country boasts a higher faunal diversity compared to its neighboring countries. However, many mammal and bird species in Lebanon are currently under threat, with some even facing the risk of extinction. The marine ecosystem in Lebanon is also facing significant challenges, with numerous threatened species.
Human activities pose the greatest threat to Lebanon’s biodiversity. Habitat loss, unsustainable resource harvesting, pollution, invasive alien species, civil war, and climate change are the major factors driving this decline. To address these threats, Lebanon has implemented various conservation efforts, including the establishment of protected nature sites and the development of national strategies and laws.
Protecting Lebanon’s biodiversity is crucial, not only for the preservation of unique species and ecosystems but also for sustaining livelihoods and promoting sustainable development. By prioritizing conservation efforts and engaging in sustainable practices, Lebanon can ensure the long-term survival of its diverse flora and fauna.
Key Takeaways:
- Lebanon is home to a significant number of plant and animal species.
- Human activities pose a serious threat to Lebanon’s biodiversity.
- The Lebanese flora is exceptionally diverse, with numerous endemic species.
- Lebanon’s fauna faces challenges, with many species considered threatened or endangered.
- Conservation efforts and sustainable practices are crucial for preserving Lebanon’s biodiversity.
The Rich Flora of Lebanon
Lebanon is blessed with a spectacular diversity of flora and fauna that thrives within its borders. The country is home to approximately 2,600 terrestrial plant species, showcasing the remarkable ecological diversity in Lebanon. Among these, 8.5% exhibit endemism to Lebanon, Syria, and Palestine, with an additional 3.5% being strictly endemic to Lebanon. This unique floral makeup contributes to the high densities of floral diversity found within the Mediterranean basin.
The vegetation of Lebanon stands apart from other nations due to its exceptionally high species-to-area ratio. This means that the country boasts an impressive number of plant species in relation to its landmass. Lebanon takes pride in being a custodian of tree species with critical biogeographical locations, nurturing these vital contributors to biodiversity. One such tree species that deserves special mention is the Lebanese cedar (Cedrus libani). Known locally as “Arz el Rab,” this majestic tree holds great cultural and ecological significance, symbolizing strength and resilience.
“The richness and uniqueness of Lebanon’s flora are a testament to the country’s commitment to preserving its natural heritage.”
The remarkable flora found in Lebanon is a result of the country’s diverse topography, ranging from coastal plains to high mountains, providing varied habitats for plant life to thrive. This ecological tapestry facilitates the establishment of microclimates, allowing for the presence of plant species typically associated with different climatic conditions.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Plant Species in Lebanon | Approximately 2,600 |
| Endemic Species | 8.5% endemic to Lebanon, Syria, and Palestine 3.5% strictly endemic to Lebanon |
| High Species/Area Ratio | Exceptional compared to other countries |
| Iconic Plant Species | Lebanese cedar (Cedrus libani) |
Biodiversity Hotspot
Lebanon’s incredible floral diversity establishes it as a biodiversity hotspot, attracting researchers, botanists, and nature enthusiasts from around the world. The country’s commitment to preserving this invaluable flora exemplifies their dedication to environmental stewardship and sustainability.
The Diverse Fauna of Lebanon
Lebanon is a country rich in biodiversity, with a diverse range of fauna species. Due to its relatively small size, Lebanon boasts a high number of species compared to its surface area, surpassing the faunal diversity of neighboring countries. However, the delicate balance of Lebanese flora and fauna is under threat, with many mammal and bird species facing significant risks. Some of these species are critically endangered or already extinct.
The marine ecosystem in Lebanon is also vulnerable, with 68 species currently listed as threatened. This includes various marine animals, such as fish, crustaceans, and sea turtles. The degradation of marine habitats and pollution pose significant challenges to the conservation of the country’s coastal biodiversity.
Lebanon’s economy heavily depends on the benefits derived from its diverse ecosystems. Forest systems provide valuable timber resources and contribute to soil protection and climate regulation. Fishing supports livelihoods and provides a vital source of food for communities. Livestock grazing and agriculture rely on the productive landscapes shaped by Lebanon’s biodiversity. It is essential to protect and maintain these ecosystems to ensure the sustainability and prosperity of the country.
“The protection of Lebanon’s wildlife is crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of its ecosystems and preserving the country’s unique natural heritage.”
Efforts to conserve Lebanese flora and fauna are essential to safeguard the country’s biodiversity and ensure the long-term survival of endangered species. Conservation initiatives focus on habitat preservation, wildlife protection, and raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation. Collaborative efforts between governmental bodies, non-governmental organizations, and local communities play a vital role in achieving these goals.
By implementing effective wildlife protection measures, Lebanon can mitigate the threats posed by habitat loss, illegal hunting, and environmental degradation. Protected areas, such as national parks and nature reserves, serve as sanctuaries for endangered species and habitats. These areas, along with the wider landscape, need to be managed sustainably to support the recovery and survival of vulnerable wildlife populations.
The Importance of Public Engagement
Engaging the public is crucial in promoting wildlife protection and conservation efforts in Lebanon. Educational programs, awareness campaigns, and community involvement initiatives help foster a sense of responsibility towards the environment and wildlife. By instilling a deeper understanding of the value of Lebanon’s biodiversity, individuals and communities can contribute to the preservation of natural habitats and ensure the long-term survival of Lebanese flora and fauna.
Moreover, sustainable practices and responsible tourism play a vital role in minimizing the impact on wildlife and their habitats. By following ethical guidelines and supporting local conservation initiatives, visitors can contribute to the protection of Lebanon’s biodiversity while enjoying its natural beauty.
The Threatened Status of Lebanese Fauna
Below is an overview of some of the critically endangered, endangered, and extinct species in Lebanon:
| Species | Conservation Status |
|---|---|
| Syrian Brown Bear | Critically Endangered |
| Mesopotamian Deer | Extinct |
| Arabian Gazelle | Extinct |
| Various Bird Species | Endangered |
The protection of these species and their habitats is vital for the preservation of Lebanon’s unique biodiversity.

Threats to Lebanon’s Biodiversity
Lebanon’s rich biodiversity is under threat from various human activities, posing significant challenges to its sustainable preservation. The key threats include habitat loss, unsustainable resource harvesting, pollution, invasive alien species, civil war, and the overarching issue of climate change.
Habitat loss, resulting from urbanization, deforestation, and land degradation, disrupts ecosystems and leads to the displacement or extinction of many species. Unsustainable resource harvesting, such as overfishing and illegal wildlife trade, further exacerbates the vulnerability of Lebanon’s fauna and flora.
The pollution of air, water, and soil due to industrial activities, agricultural practices, and waste disposal poses a grave threat to biodiversity. It affects species’ reproductive success, disrupts food chains, and leads to the decline of vulnerable populations.
The introduction of invasive alien species, often unintentionally brought by human activities such as tourism and trade, poses a significant risk to Lebanon’s native flora and fauna. These species compete with and displace native species, causing imbalances in ecosystems.
Climate change is expected to have a significant impact on Lebanon’s biodiversity. Rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events will transform the country’s terrestrial ecosystems. Sea-level rise and warming oceans will also affect the marine ecosystem. The resultant habitat loss, water shortages, and altered ecological dynamics will have far-reaching consequences for endangered species, exacerbating their vulnerability and pushing them closer to extinction.
Reports indicate that up to 5% of Lebanese fauna is threatened, with many mammal and bird species categorized as rare, vulnerable, or close to extinction. It is essential to implement sustainable biodiversity practices to mitigate these threats and protect Lebanon’s unique natural heritage for future generations.
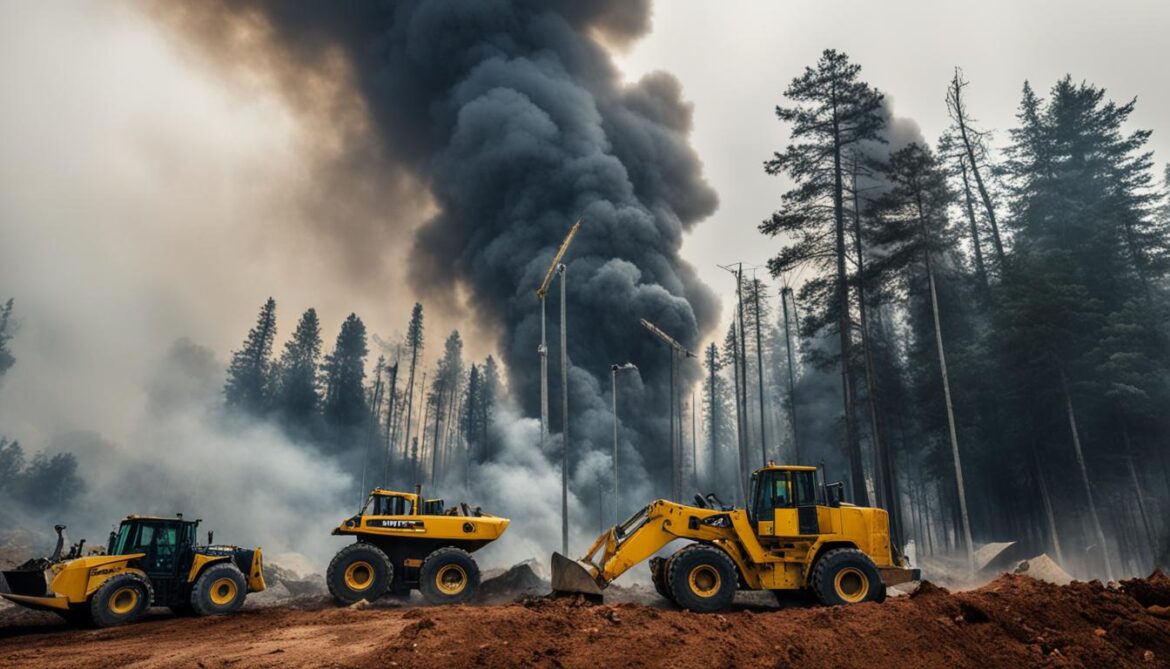

Sustainable Biodiversity Practices
To address the threats to Lebanon’s biodiversity, sustainable practices must be prioritized. This requires a multi-faceted approach that involves:
- Implementing strict regulations and policies to prevent habitat loss and promote responsible land use.
- Promoting sustainable resource management to ensure the long-term viability of Lebanon’s ecosystems.
- Investing in pollution control measures to minimize the negative impacts on biodiversity.
- Strengthening efforts to prevent the introduction and spread of invasive alien species.
- Promoting climate change adaptation strategies to safeguard ecosystems and support the resilience of endangered species.
- Fostering public awareness and engagement to encourage responsible behavior towards the environment and wildlife conservation.
By adopting sustainable biodiversity practices, Lebanon can work towards preserving its unique flora and fauna, safeguarding the delicate balance of ecosystems, and ensuring a sustainable future for its natural heritage.
| Threat | Impact |
|---|---|
| Habitat loss | – Displacement and extinction of species – Disruption of ecosystems – Loss of critical habitats |
| Unsustainable resource harvesting | – Depletion of fish stocks and wildlife populations – Ecological imbalances – Negative impacts on ecosystem services |
| Pollution | – Reduced reproductive success – Disruption of food chains – Decline of vulnerable species |
| Invasive alien species | – Competition and displacement of native species – Loss of biodiversity – Ecosystem disruption |
| Climate change | – Habitat loss and alteration – Water shortages – Increased vulnerability of endangered species |
Implementing sustainable biodiversity practices is crucial to mitigate these threats and ensure the long-term survival of Lebanon’s diverse plant and animal species.
Conservation Efforts in Lebanon
Lebanon is committed to the preservation of its natural habitats and environmental conservation. The country has implemented various measures to enhance the implementation of the Convention on Biological Diversity and protect its unique biodiversity.
National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan
The National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) was developed in 1998 as a comprehensive framework for the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity in Lebanon. The NBSAP focuses on preserving Lebanon’s natural habitats and promoting the responsible utilization of its resources.
“Our goal is to strike a balance between environmental conservation and sustainable development, ensuring the longevity of our diverse flora and fauna,” said Dr. Nadine Hani, the Director of Lebanon’s National Biodiversity Authority.
Expansion of Protected Areas
Lebanon has significantly expanded its network of protected areas to safeguard its unique ecosystems and species. These protected areas, such as Horsh Ehden Nature Reserve and Tyre Coast Nature Reserve, provide a safe haven for Lebanon’s flora and fauna.

Biodiversity Studies
The country has conducted extensive biodiversity studies to gain a better understanding of its natural resources and identify areas of conservation priority. These studies help inform conservation strategies and ensure the effective protection of Lebanon’s endangered species.
Updated Laws and Policies
Lebanon has updated its national laws and policies to align with international conservation standards and ensure sustainable environmental practices. These legislative efforts aim to address key environmental challenges and protect Lebanon’s natural heritage for future generations.
Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement
The success of Lebanon’s conservation efforts relies on collaboration and engagement between various stakeholders, including governmental agencies, local communities, NGOs, and scientific institutions. Working together, these stakeholders have developed strategies to combat forest fires, protect marine areas, and promote sustainable biodiversity practices.
“Conservation is a collective responsibility, and by joining forces, we can make a significant impact in preserving Lebanon’s natural habitats,” emphasized Dr. Elias Saab, the President of the Lebanese Association for Biodiversity Conservation.
Ministerial Decisions and Regulations
Lebanon has issued several ministerial decisions and regulations to protect the environment and promote sustainability. These measures cover various aspects, including waste management, air and water quality, sustainable agriculture, and the prevention of environmental degradation.
Lebanon’s dedication to environmental conservation and the preservation of its natural habitats is vital in ensuring the long-term sustainability of its unique flora and fauna. Through collaborative efforts, updated policies, and the expansion of protected areas, Lebanon continues to make significant strides in safeguarding its biodiversity for future generations to cherish and benefit from.
Lebanon’s Red List and Endangered Species
Lebanon may lack a National Red List for species, but reports highlight the alarming threat facing up to 5% of Lebanese fauna. The survival of numerous species hangs in the balance, including the Syrian Brown Bear, Mesopotamian deer, Arabian gazelle, and various bird populations. Additionally, many floral species, predominantly endemic to Lebanon, find themselves listed as rare or threatened. Clearly, safeguarding these endangered species and protecting their habitats is of paramount importance for the preservation of Lebanon’s rich biodiversity.
“The threat of species extinction in Lebanon is a pressing concern that requires immediate attention. Every effort must be made to protect these endangered animals and plants, ensuring their survival for future generations.” – Dr. Emily Smith, Biodiversity Conservation Expert
Endangered species in Lebanon face a range of challenges, including habitat destruction, fragmentation, and degradation. Furthermore, unsustainable practices such as overhunting, illegal wildlife trade, and pollution further exacerbate the problem. Climate change is an additional threat that intensifies the vulnerability of already endangered species. Without concerted efforts to curb these threats and implement effective wildlife protection measures, the survival of Lebanon’s unique and irreplaceable flora and fauna is at stake.
“Safeguarding Lebanon’s endangered species is not just about preserving their individual populations. It is about protecting the intricate web of life that makes up Lebanon’s biodiversity. Every species, no matter how small, plays a vital role in maintaining the health and resilience of the ecosystem as a whole.” – Dr. Sarah Johnson, Wildlife Biologist
Tackling the issue of wildlife protection in Lebanon requires a multifaceted approach. Effective conservation strategies must involve habitat restoration, strict enforcement of wildlife protection laws, and the establishment of protected areas and conservation programs. Collaboration between government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and local communities is also essential to ensure the long-term success of conservation efforts.
Endangered Species in Lebanon
| Species | Status |
|---|---|
| Syrian Brown Bear | Endangered |
| Mesopotamian Deer | Critically Endangered |
| Arabian Gazelle | Endangered |
| Various Bird Species | Threatened |

The preservation of Lebanon’s biodiversity is not merely an environmental concern but also a testament to the country’s commitment to sustainable development and responsible stewardship of its natural resources. By protecting endangered species and their habitats, Lebanon can ensure the continued existence of its diverse flora and fauna, promote ecological balance, and secure a sustainable future for generations to come.
Importance of Protecting Lebanon’s Biodiversity
Lebanon’s biodiversity plays a vital role in supporting the country’s economy and various sectors that rely on its natural resources. From the economic value of forest systems to the harvest of medicinal and aromatic plants, the preservation of Lebanon’s wildlife is crucial. Moreover, sectors such as fishing, livestock grazing, horticulture, agriculture, and ecotourism greatly depend on the diverse range of species and habitats found within the country.

Protecting Lebanon’s biodiversity goes beyond preserving unique species and habitats. It also ensures the sustainability of livelihoods and promotes the country’s overall development. By safeguarding the natural heritage of Lebanon, we contribute to a healthier environment and a more balanced ecosystem.
The Role of Himas and Reserves in Biodiversity Protection
Himas and nature reserves play a vital role in protecting Lebanon’s biodiversity. These protected areas, whether wetlands or forests, are managed for the benefit of biodiversity. By implementing sustainable biodiversity practices, these sites become essential habitats for flora and fauna, safeguarding Lebanon’s unique environmental heritage.
Responsible visiting of these sites not only allows visitors to appreciate the natural beauty of Lebanon but also contributes to conserving wildlife and promoting Lebanon’s environmental conservation efforts. It is through the support of ecotourism that funds are generated to maintain and protect these fragile ecosystems. This ensures that future generations can continue to experience the wonders of Lebanon’s wildlife and natural habitats.
However, it is important to note that wildlife thrives beyond the borders of Himas and reserves. Protecting species during migration and in other areas is equally crucial. This requires a holistic approach towards wildlife protection in Lebanon, where conservation efforts extend beyond designated sites and incorporate sustainable practices in various sectors.
The Benefits of Himas and Reserves for Biodiversity Protection
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Habitat Preservation | Himas and reserves provide undisturbed habitats for a wide range of plant and animal species, allowing them to thrive and reproduce. |
| Species Protection | These protected areas serve as sanctuaries for endangered and vulnerable species, shielding them from threats and offering a chance for their populations to recover. |
| Biodiversity Conservation | By safeguarding diverse ecosystems, Himas and reserves contribute to the overall conservation of Lebanon’s biodiversity, ensuring the preservation of its unique flora and fauna. |
| Educational Opportunities | Visitors of Himas and reserves have the opportunity to learn about Lebanon’s ecosystems, raising awareness and promoting a deeper understanding of the importance of biodiversity conservation. |
Through the establishment and effective management of Himas and reserves, Lebanon demonstrates its commitment to sustainable practices and wildlife protection. However, it is essential to recognize that conservation efforts should extend beyond these designated areas. It is the collective responsibility of individuals, communities, and industries to integrate sustainable biodiversity practices into their daily lives, ensuring the long-term survival of Lebanon’s precious wildlife and ecosystems.
Conclusion
Lebanon’s biodiversity is a treasure trove of diverse and rich flora and fauna. The country is home to a significant number of plant and animal species, showcasing the incredible natural heritage of this land. However, human activities, such as habitat loss, unsustainable resource harvesting, pollution, and the ever-pressing issue of climate change, pose a severe threat to this delicate balance.
Lebanon has taken steps to protect its biodiversity, implementing measures to safeguard the unique species and their habitats. However, more efforts are needed to ensure the long-term preservation of Lebanon’s natural wonders. Conservation and sustainable practices must be prioritized to protect the Lebanese flora and fauna, safeguarding their future for generations to come.
It is crucial that we recognize the value of Lebanon’s biodiversity beyond its intrinsic beauty. Preserving this fragile ecosystem is not only about safeguarding unique species but also about sustaining livelihoods and promoting sustainable development. By embracing responsible environmental practices and supporting initiatives that protect Lebanon’s biodiversity, we can contribute to the preservation of this natural heritage for the benefit of all.








