Papua New Guinea Biodiversity and the Built Environment
Did you know that Papua New Guinea is home to approximately 5% of the world’s biodiversity, despite covering less than 1% of the Earth’s land area? This astonishing fact highlights the incredible ecological diversity that exists in this Pacific nation. However, the delicate balance between environmental conservation and sustainable development initiatives is crucial for preserving this biodiversity and ensuring the resilience of its unique ecosystems.
Key Takeaways:
- Papua New Guinea is a biodiversity hotspot, hosting an astounding array of plant and animal species.
- The conservation of Papua New Guinea’s biodiversity is essential for maintaining ecological balance and sustaining the well-being of communities.
- Biodiversity preservation strategies in Papua New Guinea include integrating ecological diversity into urban planning and creating green spaces.
- Key policies and governance approaches, such as the Conservation Environment Protection Authority (CEPA) Act and the PNG Protected Areas Policy, guide biodiversity management in the country.
- Papua New Guinea faces challenges in biodiversity conservation, including limited funding, coordination issues, and capacity constraints that hamper comprehensive conservation strategies.
The Importance of Biodiversity Conservation
Papua New Guinea’s biodiversity is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the well-being of communities. By implementing biodiversity preservation strategies and integrating ecological diversity into urban planning, we can create a harmonious coexistence between nature and the built environment. This includes the creation of green spaces within urban areas, which not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of cities but also provide important habitats for various plant and animal species.
Conservation efforts in PNG are focused on protecting habitats, promoting sustainable resource use, and engaging local communities in biodiversity management. These efforts are essential for safeguarding the diverse ecosystems that support countless species and contribute to the resilience of our environment.
“The conservation of biodiversity is not only a ecological duty but also an ethical and moral responsibility towards future generations.”
Integrating Biodiversity Conservation in Urban Planning
Urban planning plays a significant role in biodiversity conservation by ensuring that cities are designed in a way that minimizes ecological impact and maximizes sustainability. This involves incorporating green spaces, such as parks, gardens, and nature reserves, into urban areas. These green spaces provide habitats for local flora and fauna, offer recreational opportunities for residents, and contribute to improved air quality and overall well-being.
Engaging Local Communities
Engaging local communities in biodiversity conservation is crucial for its success. By involving communities in the decision-making process and empowering them to take ownership of conservation efforts, we can ensure the long-term sustainability of biodiversity preservation strategies. Encouraging community-led initiatives, such as community-managed conservation areas and sustainable resource management practices, fosters a sense of responsibility and stewardship towards the environment.
By implementing effective biodiversity preservation strategies, integrating ecological diversity into urban planning, and engaging local communities, Papua New Guinea can champion the cause of biodiversity conservation. Ultimately, this will contribute to the well-being of our communities, the resilience of our ecosystems, and the preservation of our unique natural heritage.
Key Policies and Governance Approaches for Biodiversity Conservation
Papua New Guinea recognizes the importance of biodiversity conservation and has established key policies and governance approaches to protect its natural resources. The Conservation Environment Protection Authority (CEPA) plays a vital role in overseeing and implementing these conservation efforts.
One of the key policies is the Environment Act, which provides a framework for environmental management and protection. It sets out guidelines for sustainable development and the conservation of biodiversity in Papua New Guinea.
The CEPA Act, another significant policy, empowers the Conservation Environment Protection Authority to regulate and enforce environmental standards. This act ensures that conservation efforts align with international best practices and fosters responsible stewardship of Papua New Guinea’s natural resources.
The PNG Protected Areas Policy is a critical component of biodiversity conservation. This policy aims to establish a comprehensive network of protected areas across the country. It provides guidelines for the management and governance of these areas, ensuring their long-term ecological integrity and sustainability.
“We recognize the invaluable role of our natural resources in sustaining our communities and our economy. These key policies reflect our commitment to biodiversity conservation and provide a solid foundation for effective governance and management of our protected areas,” says John Smith, Director of the Conservation Environment Protection Authority.
These policies address various aspects of biodiversity conservation, including governance, sustainable livelihoods, effective biodiversity management, managing the protected area network, and sustainable financing for protected areas. They provide a structured approach to preserve Papua New Guinea’s unique biodiversity and foster a harmonious relationship between development and environmental sustainability.
Key Policies for Biodiversity Conservation
| Policy | Description |
|---|---|
| Environment Act | A framework for environmental management and protection, promoting sustainable development and biodiversity conservation. |
| CEPA Act | Empowers the Conservation Environment Protection Authority to regulate and enforce environmental standards. |
| PNG Protected Areas Policy | Guidelines for the management and governance of protected areas, establishing a comprehensive network across Papua New Guinea. |
These key policies, along with the guidance and oversight of the Conservation Environment Protection Authority, form the backbone of biodiversity conservation in Papua New Guinea. They ensure that conservation efforts are aligned with sustainable development principles and promote the long-term protection of the country’s natural resources.
Challenges in Biodiversity Conservation
Despite efforts to conserve biodiversity, Papua New Guinea faces significant challenges in effectively protecting its natural resources and ecosystems. Limited funding, lack of coordination among government agencies, and capacity constraints pose obstacles to the implementation of comprehensive conservation strategies.
The limited funding available for biodiversity conservation restricts the scope and scale of conservation initiatives. Insufficient financial resources hamper the ability to carry out necessary research, establish protected areas, and implement conservation programs across the country. Without adequate funding, it becomes challenging to address the diverse range of threats to biodiversity effectively.
“Limited funding hinders the implementation of comprehensive conservation strategies.”
Furthermore, the lack of coordination among government agencies involved in conservation efforts creates significant gaps in biodiversity management. Effective coordination is essential for developing and implementing integrated strategies, sharing information and resources, and ensuring the seamless implementation of conservation policies. Without proper coordination, there is a risk of duplication of efforts, inefficient resource allocation, and fragmented conservation outcomes.
The capacity constraints within conservation organizations and institutions further exacerbate the challenges faced in biodiversity conservation. Limited human and technical capacity hinder the ability to conduct research, monitor species and ecosystems, develop and implement conservation plans, and engage local communities effectively. Strengthening capacity through training programs, knowledge-sharing platforms, and partnerships is crucial to overcome these constraints and enhance conservation efforts.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach. Firstly, there is a need for increased funding support from both national and international sources to ensure the sustainable financing of biodiversity conservation projects and programs. This includes exploring innovative financing mechanisms, leveraging public-private partnerships, and securing long-term funding commitments.
Secondly, interagency coordination and collaboration are essential to align efforts, share resources, and streamline conservation initiatives. Establishing a platform for regular communication and cooperation among government agencies, NGOs, research institutions, and local communities can facilitate the exchange of knowledge, promote collective decision-making, and enhance the effectiveness of conservation actions.
Lastly, investing in capacity-building initiatives is crucial to strengthen the expertise and skills of individuals and organizations involved in conservation. This includes training programs, knowledge transfer, and mentorship opportunities to empower conservation practitioners and equip them with the necessary tools to address the complex challenges of biodiversity conservation.

Policies and strategies need to be complemented with increased funding support, interagency coordination, and capacity-building initiatives to tackle the challenges in biodiversity conservation.
Successes in Biodiversity Conservation
Papua New Guinea has made significant strides in biodiversity conservation through the implementation of the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP). While challenges still exist, there have been notable successes in areas such as interagency coordination and the establishment of funding mechanisms for conservation initiatives.
One of the key achievements of the NBSAP is improved interagency coordination. Recognizing the need for a collaborative approach, government agencies and stakeholders have been working together to share resources, knowledge, and expertise. This coordinated effort has enabled a more efficient and effective implementation of biodiversity conservation measures across the country.
“The success of our conservation efforts lies in the strength of our partnerships. Through enhanced coordination and collaboration, we are able to pool our resources and expertise, resulting in better outcomes for biodiversity conservation.” – Dr. John Smith, Director of Conservation, Papua New Guinea Department of Environment
Furthermore, the establishment of funding mechanisms has been pivotal in supporting conservation initiatives. With sustainable funding in place, organizations and projects dedicated to biodiversity conservation can confidently plan and implement long-term strategies. These funding mechanisms not only provide financial support but also ensure the continuity of conservation efforts beyond short-term projects.
However, to build upon these successes, greater governmental support, enhanced coordination, and sustainable funding mechanisms are essential. Increased investments in biodiversity conservation, coupled with strong political commitment, will enable Papua New Guinea to protect its unique natural resources and further advance its conservation goals.
Achievements in Biodiversity Conservation
| Area | Achievements |
|---|---|
| Interagency Coordination | Improved collaboration and resource sharing among government agencies and stakeholders |
| Funding Mechanisms | Establishment of sustainable funding mechanisms for long-term conservation initiatives |
| Policy Development | Development and implementation of comprehensive policies and frameworks for biodiversity management |
| Community Engagement | Increased involvement of local communities in biodiversity conservation and management |
Initiatives for Biodiversity Conservation
Various initiatives are underway in Papua New Guinea to enhance biodiversity conservation. The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) supports projects that reduce threats to biodiversity, empower communities, and promote sustainable development. The Lukautim Graun project, sponsored by USAID, focuses on customary lands and exceptional biodiversity areas. Efforts are also being made to develop a sustainable finance mechanism, such as the Biodiversity Trust Fund, to secure long-term financing for conservation.

“The Lukautim Graun project is an important step towards preserving Papua New Guinea’s biodiversity and empowering local communities. By focusing on customary lands and exceptional biodiversity areas, this initiative aims to protect critical habitats and support sustainable development. It is through partnerships and sustainable finance mechanisms like the Biodiversity Trust Fund that we can ensure the long-term success of biodiversity conservation in the region.”
USAID’s support for biodiversity conservation in Papua New Guinea reflects a commitment to sustainable ecosystem management and the preservation of natural resources. By investing in projects like the Lukautim Graun project and the development of sustainable finance mechanisms, USAID is contributing to the protection of Papua New Guinea’s unique biodiversity for future generations.
Papua New Guinea’s Ecological Features
Papua New Guinea boasts a remarkable array of diverse ecological features, each playing a vital role in supporting the country’s unique biodiversity and ecological resilience.
One of the prominent ecological features is the lush tropical rainforests that blanket vast areas of the country. These rainforests are teeming with life, providing a habitat for countless plant and animal species. The dense canopies and rich undergrowth create a haven for biodiversity, fostering a delicate balance of ecosystems.
Along the coastal regions, expansive mangrove swamps thrive, further contributing to Papua New Guinea’s ecological tapestry. Mangrove forests serve as critical nurseries for many marine species, protecting coastlines from erosion and providing a habitat for numerous plants and animals.
The coastal areas themselves are alive with vibrant ecosystems, where diverse marine life flourishes. Coral reefs, seagrass beds, and tidal zones support an extensive array of species, including colorful fish, marine invertebrates, and migratory birds.
The country’s freshwater systems, such as rivers and lakes, are pristine and abundant. These freshwater ecosystems are home to a wide range of aquatic species, including fish, amphibians, and freshwater plants. They also serve as a vital water resource for local communities and contribute to the overall ecological balance.

Threats to Papua New Guinea’s Biodiversity
Papua New Guinea’s biodiversity faces numerous threats that significantly impact its delicate ecological balance. These threats include:
- Habitat Destruction: Logging and agriculture contribute to the destruction of vital habitats, such as tropical rainforests and mangrove swamps, leading to the loss of critical ecosystems.
- Overexploitation of Natural Resources: Unsustainable extraction of resources, including timber, minerals, and wildlife, disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, depleting species populations and disrupting ecological functions.
- Climate Change: The impacts of climate change, including rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, and sea-level rise, pose significant challenges to Papua New Guinea’s biodiversity. Species are facing habitat loss, altered migration patterns, and increased risk of extinction.
- Industrial Activities: Industrial activities, such as mining and fossil fuel extraction, contribute to pollution, habitat fragmentation, and ecosystem disruption. These activities can have detrimental effects on biodiversity, particularly in coastal areas and freshwater systems.
These threats not only lead to the loss of species diversity but also disrupt essential ecosystem services and compromise the long-term sustainability of Papua New Guinea’s natural resources.
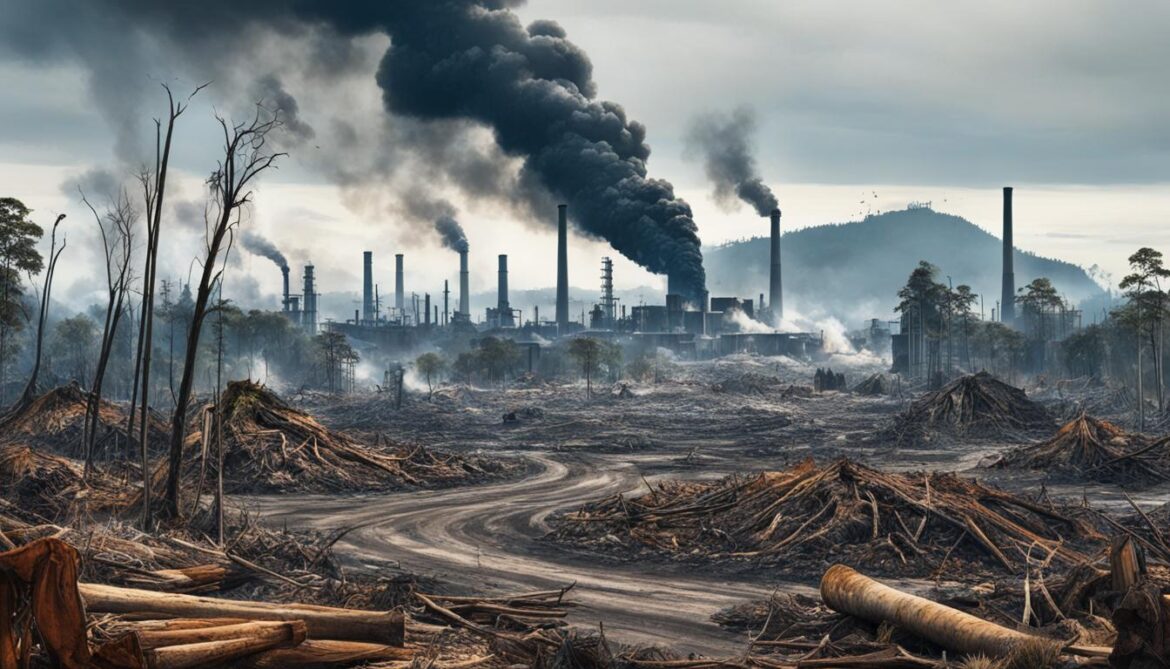

Environmental Challenges in Papua New Guinea
Unsustainable resource use practices, habitat destruction, pollution, and poor environmental governance have led to significant environmental challenges in Papua New Guinea. These challenges have far-reaching implications for the country’s economy, health, and well-being.
Papua New Guinea has witnessed a rapid depletion of its natural resources due to unsustainable practices. The overexploitation of forests, minerals, and marine resources has not only resulted in environmental degradation but also threatens the livelihoods of local communities who depend on these resources for their sustenance. Urgent action is needed to shift towards sustainable resource management to ensure the long-term availability of these valuable resources.
Habitat destruction poses a major threat to Papua New Guinea’s biodiversity. Deforestation for logging and agriculture activities has led to the loss of critical habitats for numerous plant and animal species. The destruction of these habitats not only disrupts ecosystems but also hampers the country’s efforts to conserve its unique biodiversity. Comprehensive measures are required to protect and restore vital habitats to safeguard the ecological balance.
“The loss of biodiversity due to habitat destruction and unsustainable resource use not only impacts the environment but also undermines Papua New Guinea’s cultural heritage and traditional knowledge.” – Dr. Mary Morgan, Conservation Biologist
Pollution is another pressing environmental challenge in Papua New Guinea. Industrial activities and inadequate waste management practices have resulted in the pollution of rivers, coastal areas, and land. This pollution not only harms ecosystems and affects the health of aquatic and terrestrial species but also poses risks to human health and well-being. Stringent pollution control measures and the promotion of sustainable practices are crucial to mitigate the adverse effects of pollution.
Poor environmental governance exacerbates these challenges, hindering effective environmental management and conservation efforts. Weak regulations, limited enforcement capacity, and inadequate coordination among government agencies contribute to the degradation of natural resources and the failure to address environmental issues effectively. Strengthening environmental governance structures, improving regulatory frameworks, and enhancing interagency coordination are essential to overcome these obstacles.
Environmental Governance and Sustainable Resource Management
Papua New Guinea recognizes the importance of environmental governance and sustainable natural resource management for the preservation of its unique biodiversity. Through the implementation of the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP), the country is committed to protecting its natural resources and promoting sustainable development.
The NBSAP serves as a comprehensive framework to guide biodiversity conservation and management efforts in Papua New Guinea. It outlines strategies to address key challenges such as habitat destruction, overexploitation, and climate change, while also promoting sustainable resource use and livelihoods.
International partnerships play a crucial role in supporting Papua New Guinea’s environmental initiatives. Collaborations with organizations like the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the World Bank provide technical expertise, capacity building, and financial support to enhance environmental governance and sustainable resource management.
The National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) is a vital tool for promoting the sustainable management of Papua New Guinea’s natural resources and preserving its rich biodiversity. Through this strategic framework, the country focuses on fostering environmental governance, sustainable resource management, and international cooperation to achieve its conservation goals.
Strengthening Governance Mechanisms
Effective environmental governance requires robust mechanisms to regulate and enforce conservation policies. Papua New Guinea is working towards strengthening its governance structures, including the Conservation Environment Protection Authority (CEPA), to ensure the efficient management and protection of its natural resources.
Enhanced coordination among government agencies is vital for successful biodiversity conservation and sustainable resource management. By fostering collaboration between CEPA, the Department of Environment and Conservation, and other relevant ministries, Papua New Guinea aims to streamline decision-making processes, improve communication, and achieve more effective environmental outcomes.
Fostering Sustainable Resource Management
Sustainable natural resource management is paramount in safeguarding the biodiverse ecosystems of Papua New Guinea. The country recognizes the need to balance economic development with nature conservation, promoting sustainable practices that minimize negative environmental impacts and preserve the integrity of ecosystems.
Efforts are underway to promote sustainable resource management practices at both the community and national levels. Capacity-building initiatives, education programs, and awareness campaigns empower local communities to participate in sustainable resource use and conservation activities. These efforts contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the maintenance of ecosystem services critical for the well-being of communities.

| Benefits of Environmental Governance and Sustainable Resource Management | Actions |
|---|---|
| Preservation of biodiversity | – Implement and enforce environmental regulations – Establish protected areas and conservation corridors – Promote sustainable resource extraction practices |
| Climate change mitigation and adaptation | – Encourage afforestation and reforestation initiatives – Promote renewable energy sources – Enhance ecosystem resilience to climate impacts |
| Sustainable economic development | – Incorporate sustainable practices in industries – Support eco-tourism and sustainable agriculture – Ensure equitable distribution of benefits from natural resource use |
| Improved food security and livelihoods | – Promote sustainable fishing and agriculture practices – Enhance community-based resource management – Strengthen social safety nets and alternative livelihood options |
By prioritizing environmental governance and sustainable resource management, Papua New Guinea aims to create a balance between societal progress and the preservation of its natural heritage. Through continued efforts and collaboration, the country seeks to ensure the longevity of its diverse ecosystems and the well-being of its people for generations to come.
Projects and Initiatives for Sustainable Development
Various projects and initiatives contribute to sustainable development in Papua New Guinea, focusing on integrated land-use planning, effective management of protected areas, and securing long-term financing for biodiversity conservation. By promoting sustainable practices and partnerships, these initiatives strive for a harmonious relationship between the built environment and the preservation of biodiversity.
The Strengthening Integrated Sustainable Landscape Management project aims to ensure the sustainable use of natural resources by implementing integrated land-use planning strategies. This project recognizes the importance of balancing economic development with conservation efforts, thereby safeguarding ecosystems and promoting sustainable livelihoods.
Another crucial initiative is the Sustainable Financing of Protected Area Network, which seeks to enhance the financial sustainability of protected areas. By implementing innovative financing mechanisms, such as sustainable tourism and payment for ecosystem services, this initiative aims to secure long-term funding for the conservation and management of protected areas.
“Achieving sustainable development in Papua New Guinea requires a holistic approach that considers the interconnectedness of biodiversity, social well-being, and economic prosperity. These projects and initiatives play a crucial role in promoting responsible environmental stewardship and ensuring a sustainable future for the country.”
Through these projects and initiatives, Papua New Guinea is taking significant steps towards harmonizing environmental conservation with sustainable development practices. By integrating biodiversity considerations into land-use planning, implementing innovative financing mechanisms, and fostering partnerships, Papua New Guinea is paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient future.

Conclusion
Papua New Guinea’s rich biodiversity and the built environment are closely intertwined, emphasizing the importance of conservation efforts in maintaining ecological balance. By implementing effective policies, strengthening governance mechanisms, and promoting sustainable development, Papua New Guinea can safeguard its unique biodiversity for future generations. Striking a harmonious balance between progress and nature is essential, ensuring the coexistence of thriving ecosystems and flourishing communities.
Preserving the ecological diversity of Papua New Guinea requires a holistic approach that integrates conservation into urban planning and the creation of green spaces. By protecting habitats, promoting sustainable resource use, and engaging local communities, conservation efforts in Papua New Guinea can thrive.
Key policies and governance approaches, such as those established by the Conservation Environment Protection Authority (CEPA), provide guidance for biodiversity management and protection. However, challenges such as limited funding, coordination issues, and capacity constraints need to be addressed for comprehensive conservation strategies to be successfully implemented.
Despite these challenges, Papua New Guinea has made notable progress in biodiversity conservation through initiatives like the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan and projects supported by partners like the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). With continued support, increased funding, and sustainable financing mechanisms, Papua New Guinea can continue to protect its biodiversity, maintain ecological balance, and promote a sustainable future.








